Abstract
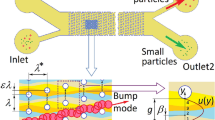
Direct-current insulator-based dielectrophoresis (DC-iDEP) is a well-known technique that benefits from the electric field gradients generated by an array of insulating posts to separate or trap biological particles. The aim of this study is to provide a first geometrical relationship of the post array that independent of the particles and/or medium, maximizes the trapping. A novel figure of merit is proposed to maximize the particle trapping in the post array while minimizing the required voltage, with a similar footprint and channel thickness. Different post array models with the variation of transversal distance (10 to 60 μm), longitudinal distance (10 to 80 μm), and post radius (10 to 150 μm) were analyzed using COMSOL Multiphysics finite element software. The obtained results indicated that a post radius of 40 μm larger than the transversal distance between posts could enhance the trapping condition between 56 % (for a transversal distance of 10 μm) and 341 % (for a transversal distance of 60 μm). For the validation of the numerical results, several microchannels with embedded post arrays were manufactured in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and the particle trapping patterns of 6-μm-diameter polystyrene particles were measured experimentally. The experiments confirm the same trends as pointed out by the numerical analysis. The results show that this new figure of merit and geometrical relationship can be used to reduce the required electric field to achieve effective particle trapping and, therefore, avoid the negative effects of Joule heating in cells or viable particles. The main advantage of these results is that they depend only on the geometry of the micropost array and are valid for trapping different particles suspended in different media.

Analysis to maximize the particle trapping in the post array while minimizing the required voltage. I. Microfluidic channel design and experimental setup II. Numerical and experimental results. III. Maximum trapping value





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DC:
-
Direct current
- DEP:
-
Dielectrophoresis
- eDEP:
-
Electrode-based DEP
- EK:
-
Electrokinetic
- iDEP:
-
Insulator-based DEP
- RBC:
-
Red blood cell
References
Whitesides G. The lab finally comes to the chip. Lab Chip. 2014;14:3125–6.
Lenshof A, Laurell T. Continuous separation of cells and particles in microfluidic systems. Chem Soc Rev. 2010;39(3):1203–17.
Sajeesh P, Sen AK. Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid Nanofluid. 2014;17(1):1–52.
Clague D, Wheeler E. Dielectrophoretic manipulation of macromolecules: the electric field. Phys Rev E. 2001;64(2):026605.
Gascoyne P, Vykoukal J. Particle separation by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2002;23:1973–83.
Cetin B, Kang Y, Wu Z, Li D. Continuous particle separation by size via AC-dielectrophoresis using a lab-on-a-chip device with 3-D electrodes. Electrophoresis. 2009;30(5):766–72.
Qian C, Huang H, Chen L, Li X, Ge Z, Chen T, et al. Dielectrophoresis for bioparticle manipulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(10):18281–309.
Jubery TZ, Srivastava SK, Dutta P. Dielectrophoretic separation of bioparticles in microdevices: a review. Electrophoresis. 2014;35(5):691–713.
Braff WA, Pignier A, Buie CR. High sensitivity three-dimensional insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip. 2012;12(7):1327–31.
Regtmeier J, Eichhorn R, Viefhues M, Bogunovic L, Anselmetti D. Electrodeless dielectrophoresis for bioanalysis: theory, devices and applications. Electrophoresis. 2011;32(17):2253–73.
Cummings EB, Singh AK. Dielectrophoresis in microchips containing arrays of insulating posts theoretical and experimental results. Anal Chem. 2003;75(18):4724–31.
Srivastava SK, Baylon-Cardiel JL, Lapizco-Encinas BH, Minerick AR. A continuous DC-insulator dielectrophoretic sorter of microparticles. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218(13):1780–9.
Lapizco-encinas BH, Simmons BA, Cummings EB, Fintschenko Y. Dielectrophoretic concentration and separation of live and dead bacteria in an array of insulators. Anal Chem. 2004;76(6):1571–9.
Cho YK, Kim S, Lee K, Park C, Lee JG, Ko C. Bacteria concentration using a membrane type insulator-based dielectrophoresis in a plastic chip. Electrophoresis. 2009;30(18):3153–9.
Kang Y, Li D, Kalams SA, Eid JE. DC-dielectrophoretic separation of biological cells by size. Biomed Microdevices. 2008;10(2):243–9.
Srivastava SK, Artemiou A, Minerick AR. Direct current insulator-based dielectrophoretic characterization of erythrocytes: ABO-Rh human blood typing. Electrophoresis. 2011;32(18):2530–40.
Jones PV, Staton SJR, Hayes MA. Blood cell capture in a sawtooth dielectrophoretic microchannel. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;401(7):2103–11.
Lapizco-Encinas BH, Davalos RV, Simmons BA, Cummings EB, Fintschenko Y. An insulator-based (electrodeless dielectrophoretic concentrator for microbes in water. J Microbiol Methods. 2005;62:317–26.
Srivastava SZ, Gencoglu A, Minerick AR. DC insulator dielectrophoretic applications in microdevice technology: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399(1):301–21.
Barbulovic-Nad I, Xuan X, Lee JSH, Li D. DC-dielectrophoretic separation of microparticles using an oil droplet obstacle. Lab Chip. 2006;6(2):274–9.
Kang KH, Kang Y, Xuan X, Li D. Continuous separation of microparticles by size with direct current-dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2006;27:694–702.
Nakano A, Chao TC, Camacho-Alanis F, Ros A. Immunoglobulin G and bovine serum albumin streaming dielectrophoresis in a microfluidic device. Electrophoresis. 2011;32(17):2314–22.
Kim D, Shim J, Chuang HS, Kim KC. Effect of array and shape of insulating posts on proteins focusing by direct current dielectrophoresis. J Mech Sci Technol. 2014;28(7):2629–36.
Kwon JS, Maeng JS, Chun MS, Song S. Improvement of microchannel geometry subject to electrokinesis and dielectrophoresis using numerical simulations. Microfluid Nanofluid. 2007;5(1):23–31.
Lalonde A, Gencoglu A, Romero-Creel MF, Koppula KS, Lapizco-Encinas BH. Effect of insulating posts geometry on particle manipulation in insulator based dielectrophoretic devices. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1344:99–108.
Mohammadi M, Madadi H, Casals-Terré J, Sellarès J. Hydrodynamic and direct-current insulator-based dielectrophoresis (H-DC-iDEP) microfluidic blood plasma separation. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(16):4733–44.
Baylon-Cardiel JL, Lapizco-Encinas BH, Reyes-Betanzo C, Chávez-Santoscoy AV, Martínez-Chapa SO. Prediction of trapping zones in an insulator-based dielectrophoretic device. Lab Chip. 2009;9(20):2896–901.
Saucedo-Espinosa MA, Lapizco-Encinas BH. Experimental and theoretical study of dielectrophoretic particle trapping in arrays of insulating structures: effect of particle size and shape. Electrophoresis. 2015;36:1086–97.
Mohammadi M, Madadi H, Casals-Terré J. Microfluidic point-of-care blood panel based on a novel technique: reversible electroosmotic flow. Biomicrofluidics. 2015;9(5):054106.
Dehghan Manshadi MK, Khojasteh D, Mohammadi M, Kamali R. Electroosmotic micropump for lab-on-a-chip biomedical applications. Int J Numer Modell. 2016. doi:10.1002/jnm.2149.
Mescher M, Brinkman AGM, Bosma D, Klootwijk JH, Sudhölter EJR, Smet LCPMD. Influence of conductivity and dielectric constant of water-dioxane mixtures on the electrical response of SiNW-based FETs. Sensors (Switzerland). 2014;14:2350–61.
Weiss NG, Jones PV, Mahanti P, Chen KP, Taylor TJ, Hayes MA. Dielectrophoretic mobility determination in DC insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 2011;32:2292–7.
Ermolina I, Morgan H. The electrokinetic properties of latex particles: comparison of electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2005;285:419–28.
Acknowledgments
The project has been funded by BIOPAPμFLUID CTQ2013-48995-C2-1-R of the Ministerio de Economia y Competitividad of Spain
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, M., Zare, M.J., Madadi, H. et al. A new approach to design an efficient micropost array for enhanced direct-current insulator-based dielectrophoretic trapping. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 5285–5294 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9629-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9629-2