Abstract
Rationale
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a disabling and life-threatening disease characterized by states of depression and mania. New and efficacious treatments have not been forthcoming partly due to a lack of well-validated models representing both facets of BD.
Objectives
We hypothesized that cholinergic- and dopaminergic-pharmacological manipulations would model depression and mania respectively, each attenuated by lithium treatment.
Methods
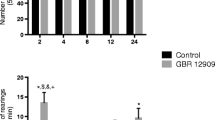
C57BL/6 J mice received the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor physostigmine or saline before testing for “behavioral despair” (immobility) in the tail suspension test (TST) and forced swim test (FST). Physostigmine effects on exploration and sensorimotor gating were assessed using the cross-species behavioral pattern monitor (BPM) and prepulse inhibition (PPI) paradigms. Other C57BL/6 J mice received chronic lithium drinking water (300, 600, or 1200 mg/l) before assessing their effects alone in the BPM or with physostigmine on FST performance. Another group was tested with acute GBR12909 (dopamine transporter inhibitor) and chronic lithium (1000 mg/l) in the BPM.
Results
Physostigmine (0.03 mg/kg) increased immobility in the TST and FST without affecting activity, exploration, or PPI. Lithium (600 mg/l) resulted in low therapeutic serum concentrations and normalized the physostigmine-increased immobility in the FST. GBR12909 induced mania-like behavior in the BPM of which hyper-exploration was attenuated, though not reversed, after chronic lithium (1000 mg/ml).
Conclusions
Increased cholinergic levels induced depression-like behavior and hyperdopaminergia induced mania-like behavior in mice, while chronic lithium treated some, but not all, facets of these effects. These data support a cholinergic-monoaminergic mechanism for modeling BD aspects and provide a way to assess novel therapeutics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adida M, Jollant F, Clark L, Besnier N, Guillaume S, Kaladjian A, Mazzola-Pomietto P, Jeanningros R, Goodwin GM, Azorin JM, Courtet P (2011) Trait-related decision-making impairment in the three phases of bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry 70:357–65
Anand A, Barkay G, Dzemidzic M, Albrecht D, Karne H, Zheng QH, Hutchins GD, Normandin MD, Yoder KK (2011) Striatal dopamine transporter availability in unmedicated bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord 13:406–13
Beaulieu JM, Marion S, Rodriguiz RM, Medvedev IO, Sotnikova TD, Ghisi V, Wetsel WC, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG (2008) A beta-arrestin 2 signaling complex mediates lithium action on behavior. Cell 132:125–36
Begley CE, Annegers JF, Swann AC, Lewis C, Coan S, Schnapp WB, Bryant-Comstock L (2001) The lifetime cost of bipolar disorder in the US: an estimate for new cases in 1998. Pharmacoeconomics 19:483–95
Belmaker RH, Bersudsky Y (2004) Bipolar disorder: mania and depression. Discov Med 4:239–45
Berggren U (1985) Effects of chronic lithium treatment on brain monoamine metabolism and amphetamine-induced locomotor stimulation in rats. J Neural Transm 64:239–50
Bersudsky Y, Shaldubina A, Belmaker RH (2007) Lithium’s effect in forced-swim test is blood level dependent but not dependent on weight loss. Behav Pharmacol 18:77–80
Brambilla P, Perlini C, Bellani M, Tomelleri L, Ferro A, Cerruti S, Marinelli V, Rambaldelli G, Christodoulou T, Jogia J, Dima D, Tansella M, Balestrieri M, Frangou S (2012) Increased salience of gains versus decreased associative learning differentiate bipolar disorder from schizophrenia during incentive decision making. Psychological Medicine: 1–10
Can A, Blackwell RA, Piantadosi SC, Dao DT, O'Donnell KC, Gould TD (2011) Antidepressant-like responses to lithium in genetically diverse mouse strains. Genes Brain Behav 10:434–43
Cipriani A, Barbui C, Salanti G, Rendell J, Brown R, Stockton S, Purgato M, Spineli LM, Goodwin GM, Geddes JR (2011) Comparative efficacy and acceptability of antimanic drugs in acute mania: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 378:1306–15
Clark MG, Sun W, Myers TM, Bansal R, Doctor BP, Saxena A (2005) Effects of physostigmine and human butyrylcholinesterase on acoustic startle reflex and prepulse inhibition in C57BL/6J mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:497–505
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A (2005) The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:571–625
Dehpour AR, Farsam H, Azizabadi-Farahani M (1995) Inhibition of the morphine withdrawal syndrome and the development of physical dependence by lithium in mice. Neuropharmacology 34:115–21
Dehpour AR, Sadr SS, Azizi MR, Namiranian K, Farahani M, Javidan AN (2002) Lithium inhibits the development of physical dependence to clonidine in mice. Pharmacol Toxicol 90:89–93
DSM-V (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental health disorders: DSM-5 (5th ed.). American Psychiatric Publishing, American Psychiatric Publishing
Dulcis D, Jamshidi P, Leutgeb S, Spitzer NC (2013) Neurotransmitter switching in the adult brain regulates behavior. Science 340:449–53
Dunstan R, Jackson DM (1977) The demonstration of a change in responsiveness of mice to physostigmine and atropine after withdrawal from long-term haloperidol pretreatment. J Neural Transm 40:181–9
El-Yousef MK, Janowsky DS, Davis JM, Rosenblatt JE (1973) Induction of severe depression by physostigmine in marihuana intoxicated individuals. Br J Addic Alcohol Other Drugs 68:321–5
Esumi S, Sagara H, Nakamoto A, Kawasaki Y, Gomita Y, Sendo T (2013) Effect of GBR12909 on affective behavior: distinguishing motivational behavior from antidepressant-like and addiction-like behavior using the runway model of intracranial self-stimulation. Behav Brain Res 243:313–21
Gard PR, Naylor C, Ali S, Partington C (2012) Blockade of pro-cognitive effects of angiotensin IV and physostigmine in mice by oxytocin antagonism. Eur J Pharmacol 683:155–60
Geddes JR, Burgess S, Hawton K, Jamison K, Goodwin GM (2004) Long-term lithium therapy for bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Psychiatr 161:217–22
Geyer MA, McIlwain KL, Paylor R (2002) Mouse genetic models for prepulse inhibition: an early review. Mol Psychiatry 7:1039–53
Geyer MA, Russo PV, Masten VL (1986) Multivariate assessment of locomotor behavior: pharmacological and behavioral analyses. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:277–88
Ghasemi M, Sadeghipour H, Poorheidari G, Dehpour AR (2009) A role for nitrergic system in the antidepressant-like effects of chronic lithium treatment in the mouse forced swimming test. Behav Brain Res 200:76–82
Gould TD, O'Donnell KC, Picchini AM, Manji HK (2007) Strain differences in lithium attenuation of d-amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion: a mouse model for the genetics of clinical response to lithium. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1321–33
Gould TJ, Keith RA, Bhat RV (2001) Differential sensitivity to lithium's reversal of amphetamine-induced open-field activity in two inbred strains of mice. Behav Brain Res 118:95–105
Green MF (2006) Cognitive impairment and functional outcome in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry 67(Suppl 9):3–8, discussion 36–42
Hannestad JO, Cosgrove KP, DellaGioia NF, Perkins E, Bois F, Bhagwagar Z, Seibyl JP, McClure-Begley TD, Picciotto MR, Esterlis I (2013) Changes in the cholinergic system between bipolar depression and euthymia as measured with [123I]5IA single photon emission computed tomography. Biol Psychiatry 74:768–76
Hasey G, Hanin I (1991) The cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of depression reexamined using clonidine, metoprolol, and physostigmine in an animal model. Biol Psychiatry 29:127–38
Henry BL, Minassian A, Patt VM, Hua J, Young JW, Geyer MA, Perry W (2013) Inhibitory deficits in euthymic bipolar disorder patients assessed in the human behavioral pattern monitor. J Affect Disord 150:948–54
Henry BL, Minassian A, Young JW, Paulus MP, Geyer MA, Perry W (2010) Cross-species assessments of motor and exploratory behavior related to bipolar disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:1296–306
Janowsky DS, el-Yousef MK, Davis JM (1974) Acetylcholine and depression. Psychosom Med 36:248–57
Janowsky DS, el-Yousef MK, Davis JM, Sekerke HJ (1972) A cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of mania and depression. Lancet 2:632–5
Jope R (1979) Effects of lithium treatment in vitro and in vivo on acetylcholine metabolism in rat brain. J Neurochem 33:487–95
Jope RS, Morrisett RA (1986) Neurochemical consequences of status epilepticus induced in rats by coadministration of lithium and pilocarpine. Exp Neurol 93:404–14
Kohl S, Heekeren K, Klosterkotter J, Kuhn J (2013) Prepulse inhibition in psychiatric disorders—apart from schizophrenia. J Psychiatr Res 47:445–52
Kwek P, van den Buuse M (2013) Modafinil disrupts prepulse inhibition in mice: strain differences and involvement of dopaminergic and serotonergic activation. Eur J Pharmacol 699:132–40
Lerer B (1985) Studies on the role of brain cholinergic systems in the therapeutic mechanisms and adverse effects of ECT and lithium. Biol Psychiatry 20:20–40
Loos M, Staal J, Schoffelmeer AN, Smit AB, Spijker S, Pattij T (2010) Inhibitory control and response latency differences between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice in a Go/No-Go and 5-choice serial reaction time task and strain-specific responsivity to amphetamine. Behav Brain Res 214:216–24
Machado-Vieira R, Kapczinski F, Soares JC (2004) Perspectives for the development of animal models of bipolar disorder. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:209–24
Malhi GS, Tanious M, Das P, Berk M (2012) The science and practice of lithium therapy. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 46:192–211
Malkesman O, Austin DR, Chen G, Manji HK (2009) Reverse translational strategies for developing animal models of bipolar disorder. Dis Model Mech 2:238–45
Merikangas KR, Jin R, He JP, Kessler RC, Lee S, Sampson NA, Viana MC, Andrade LH, Hu C, Karam EG, Ladea M, Medina-Mora ME, Ono Y, Posada-Villa J, Sagar R, Wells JE, Zarkov Z (2011) Prevalence and correlates of bipolar spectrum disorder in the world mental health survey initiative. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:241–51
Minassian A, Henry BL, Young JW, Masten V, Geyer MA, Perry W (2011) Repeated assessment of exploration and novelty seeking in the human behavioral pattern monitor in bipolar disorder patients and healthy individuals. Public Library of Science One 6, e24185
Mineur YS, Obayemi A, Wigestrand MB, Fote GM, Calarco CA, Li AM, Picciotto MR (2013) Cholinergic signaling in the hippocampus regulates social stress resilience and anxiety- and depression-like behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:3573–8
Novick DM, Swartz HA, Frank E (2010) Suicide attempts in bipolar I and bipolar II disorder: a review and meta-analysis of the evidence. Bipolar Disord 12:1–9
Osby U, Brandt L, Correia N, Ekbom A, Sparen P (2001) Excess mortality in bipolar and unipolar disorder in Sweden. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:844–50
Overstreet DH (1993) The Flinders sensitive line rats: a genetic animal model of depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 17:51–68
Paulus MP, Geyer MA (1991) A temporal and spatial scaling hypothesis for the behavioral effects of psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 104:6–16
Perry W, Minassian A, Feifel D (2004) Prepulse inhibition in patients with non-psychotic major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 81:179–84
Perry W, Minassian A, Feifel D, Braff DL (2001) Sensorimotor gating deficits in bipolar disorder patients with acute psychotic mania. Biol Psychiatry 50:418–24
Perry W, Minassian A, Henry B, Kincaid M, Young JW, Geyer MA (2010) Quantifying over-activity in bipolar and schizophrenia patients in a human open field paradigm. Psychiatry Res 178:84–91
Perry W, Minassian A, Paulus MP, Young JW, Kincaid MJ, Ferguson EJ, Henry BL, Zhuang X, Masten VL, Sharp RF, Geyer MA (2009) A reverse-translational study of dysfunctional exploration in psychiatric disorders: from mice to men. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:1072–80
Petit-Demouliere B, Chenu F, Bourin M (2005) Forced swimming test in mice: a review of antidepressant activity. Psychopharmacology 177:245–55
Quednow BB, Westheide J, Kuhn KU, Werner P, Maier W, Hawellek B, Wagner M (2006) Normal prepulse inhibition and habituation of acoustic startle response in suicidal depressive patients without psychotic symptoms. J Affect Disord 92:299–303
Rao JS, Kellom M, Reese EA, Rapoport SI, Kim HW (2012) Dysregulated glutamate and dopamine transporters in postmortem frontal cortex from bipolar and schizophrenic patients. J Affect Disord 136:63–71
Risbrough VB, Masten VL, Caldwell S, Paulus MP, Low MJ, Geyer MA (2006) Differential contributions of dopamine D1, D2, and D3 receptors to MDMA-induced effects on locomotor behavior patterns in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2349–58
Risch SC, Cohen RM, Janowsky DS, Kalin NH, Sitaram N, Gillin JC, Murphy DL (1981) Physostigmine induction of depressive symptomatology in normal human subjects. Psychiatry Res 4:89–94
Roybal K, Theobold D, Graham A, DiNieri JA, Russo SJ, Krishnan V, Chakravarty S, Peevey J, Oehrlein N, Birnbaum S, Vitaterna MH, Orsulak P, Takahashi JS, Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr, McClung CA (2007) Mania-like behavior induced by disruption of CLOCK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:6406–11
Saricicek A, Esterlis I, Maloney KH, Mineur YS, Ruf BM, Muralidharan A, Chen JI, Cosgrove KP, Kerestes R, Ghose S, Tamminga CA, Pittman B, Bois F, Tamagnan G, Seibyl J, Picciotto MR, Staley JK, Bhagwagar Z (2012) Persistent beta2*-nicotinic acetylcholinergic receptor dysfunction in major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatr 169:851–9
Sarkisyan G, Roberts AJ, Hedlund PB (2010) The 5-HT(7) receptor as a mediator and modulator of antidepressant-like behavior. Behav Brain Res 209:99–108
Shaldubina A, Einat H, Szechtman H, Shimon H, Belmaker RH (2002) Preliminary evaluation of oral anticonvulsant treatment in the quinpirole model of bipolar disorder. J Neural Transm 109:433–40
Sherman JA (2012) Evolutionary origin of bipolar disorder-revised: EOBD-R. Med Hypotheses 78:113–22
Tanaka S, Young JW, Halberstadt AL, Masten VL, Geyer MA (2012) Four factors underlying mouse behavior in an open field. Behav Brain Res 233:55–61
van Enkhuizen J, Geyer MA, Kooistra K, Young JW (2013a) Chronic valproate attenuates some, but not all, facets of mania-like behaviour in mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:1021–31
van Enkhuizen J, Geyer MA, Young JW (2013b) Differential effects of dopamine transporter inhibitors in the rodent Iowa gambling task : relevance to mania. Psychopharmacology 225:661–74
van Enkhuizen J, Henry BL, Minassian A, Perry W, Milienne-Petiot M, Higa KK, Geyer MA, Young JW (2014a) Reduced dopamine transporter functioning induces high-reward risk-preference consistent with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:3112–22
van Enkhuizen J, Janowsky DS, Olivier B, Minassian A, Perry W, Young JW, Geyer MA (2014b) The catecholaminergic-cholinergic balance hypothesis of bipolar disorder revisited. Eur J Pharmacol
van Enkhuizen J, Janowsky DS, Olivier B, Minassian A, Perry W, Young JW, Geyer MA (2015) The catecholaminergic-cholinergic balance hypothesis of bipolar disorder revisited. Eur J Pharmacol 753:114–26
van Enkhuizen J, Minassian A, Young JW (2013c) Further evidence for ClockDelta19 mice as a model for bipolar disorder mania using cross-species tests of exploration and sensorimotor gating. Behav Brain Res 249:44–54
Varela RB, Valvassori SS, Lopes-Borges J, Fraga DB, Resende WR, Arent CO, Zugno AI, Quevedo J (2013) Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase in an animal model of mania induced by D-amphetamine. Psychiatry Res 209:229–34
Young JW, Dulcis D (2015) Investigating the mechanism(s) underlying switching between states in bipolar disorder. Eur J Pharmacol 759:151–162
Young JW, Geyer MA (2010) Action of modafinil—increased motivation via the dopamine transporter inhibition and D1 receptors? Biol Psychiatry 67:784–7
Young JW, Goey AK, Minassian A, Perry W, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (2010a) GBR 12909 administration as a mouse model of bipolar disorder mania: mimicking quantitative assessment of manic behavior. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 208:443–54
Young JW, Goey AK, Minassian A, Perry W, Paulus MP, Geyer MA (2010b) The mania-like exploratory profile in genetic dopamine transporter mouse models is diminished in a familiar environment and reinstated by subthreshold psychostimulant administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:7–15
Young JW, Henry BL, Geyer MA (2011a) Predictive animal models of mania: hits, misses and future directions. Br J Pharmacol 164:1263–84
Young JW, van Enkhuizen J, Winstanley CA, Geyer MA (2011b) Increased risk-taking behavior in dopamine transporter knockdown mice: further support for a mouse model of mania. J Psychopharmacol 25:934–43
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Berend Olivier, William Perry, and Arpi Minassian for their support. These studies were supported by NIH grants R01-MH071916, and R01-MH104344, as well as by the U.S. Veteran’s Administration VISN 22 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center.
Conflict of interest
Dr. van Enkhuizen and Ms. Milienne-Petiot report no conflict of interest. Dr. Geyer has received consulting compensation from Abbott, Dart, Lundbeck, Neurocrine, Omeros, Otsuka, and Sunovion, and holds an equity interest in San Diego Instruments. Dr. Geyer also has research grant support from Intracellular Therapeutics, Johnson & Johnson, NIDA, NIMH, and the U.S. Veteran’s Administration VISN 22 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center. Dr. Young has received consulting compensation from Amgen and Arena Pharmaceuticals as well as research grant support from Cerca, Omeros, Lundbeck Ltd, NIMH, and the U.S. Veteran’s Administration VISN 22 Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Center. The aforementioned support did not direct any research presented here.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Enkhuizen, J., Milienne-Petiot, M., Geyer, M.A. et al. Modeling bipolar disorder in mice by increasing acetylcholine or dopamine: chronic lithium treats most, but not all features. Psychopharmacology 232, 3455–3467 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4000-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4000-4