Abstract
Rationale
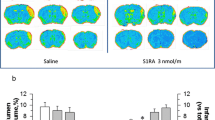
Sigma-1 receptor (Sig-1R) agonists showed anti-amnesic properties in Alzheimer’s disease models and anti-inflammatory properties in cerebrum ischaemia models. The agonist of Sig-1R was reported to up-regulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the hippocampus of mice. Here, we investigate whether the activation of Sig-1R attenuates the learning and memory impairment induced by ischaemia/reperfusion and how it affects the expression of BDNF.
Objectives
Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) was induced for 20 min in C57BL/6 mice.
Materials and methods
Sig-1R agonist, PRE084, sigma 1/2 non-selective agonist, DTG, Sig-1R antagonist and BD1047 were injected once daily throughout the experiment. Behavioural tests were performed from day 8. On day 22 after BCCAO, mice were sacrificed for biochemical analysis.
Results
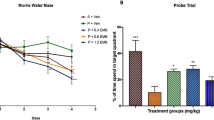
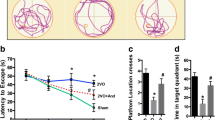
PRE084 and DTG ameliorated learning and memory impairments in the Y maze, novel object recognition, and water maze tasks and prevented the decline of synaptic proteins and BDNF expression in the hippocampus of BCCAO mice. Furthermore, PRE084 and DTG up-regulated the level of NMDA receptor 2A (NR2A), calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV (CaMKIV) and CREB-specific co-activator transducer of regulated CREB activity 1 (TORC1). Additionally, the effects of PRE084 and DTG were antagonised by the co-administration of BD1047.
Conclusions
Sig-1R activation showed an attenuation in the ischaemia/reperfusion model and the activation of Sig-1R increased the expression of BDNF, possibly through the NR2A-CaMKIV-TORC1 pathway, and Sig-1R agonists might function as neuroprotectant agents in vascular dementia.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso G, Phan V, Guillemain I, Saunier M, Legrand A, Anoal M, Maurice T (2000) Immunocytochemical localization of the sigma (1) receptor in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 97:155–170
Andsberg G, Kokaia Z, Klein RL, Muzyczka N, Lindvall O, Mandel RJ (2002) Neuropathological and behavioral consequences of adeno-associated viral vector-mediated continuous intrastriatal neurotrophin delivery in a focal ischemia model in rats. Neurobiol Dis 9:187–204
Aydar E, Palmer CP, Klyachko VA, Jackson MB (2002) The sigma receptor as a ligand-regulated auxiliary potassium channel subunit. Neuron 34:399–410
Bannerman DM, Sprengel R, Sanderson DJ, McHugh SB, Rawlins JN, Monyer H, Seeburg PH (2014) Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety. Nat Rev Neurosci 15:181–192
Bath KG, Jing DQ, Dincheva I, Neeb CC, Pattwell SS, Chao MV, Lee FS, Ninan I (2012) BDNF Val66Met impairs fluoxetine-induced enhancement of adult hippocampus plasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1297–1304
Cunha C, Brambilla R, Thomas KL (2010) Simple role for BDNF in learning and memory? Front Mol Neurosci 3:1–14
Damgaard T, Larsen DB, Hansen SL, Grayson B, Neill JC, Plath N (2010) Positive modulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors reverses sub-chronic PCP-induced deficits in the novel object recognition task in rats. Behav Brain Res 207:144–150
El-Husseini AE, Schnell E, Chetkovich DM, Nicoll RA, Bredt DS (2000) PSD-95 involvement in maturation of excitatory synapses. Science 290:1364–1368
Fujii M, Hara H, Meng W, Vonsattel JP, Huang Z, Moskowitz MA (1997) Strain-related differences in susceptibility to transient forebrain ischemia in SV-129 and C57black/6 mice. Stroke 28:1805–1810
Fujimoto M, Hayashi T, Urfer R, Mita S, Su TP (2012) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones regulate the secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Synaps 66:630–639
Hardingham GE, Bading H (2010) Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signaling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Neurosci 11:682–696
Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y, Bading H (2002) Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways. Nat Neurosci 5:405–414
Hayashi T, Su TP (2001) Regulating ankyrin dynamics: Roles of sigma-1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:491–496
Hayashi T, Su TP (2004) Sigma-1 receptor ligands: potential in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS Drugs 18:269–284
Hayashi T, Su TP (2007) Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER mitochondrion interface regulate Ca2+ signaling and cell survival. Cell 131:596–610
Huang Y, McNamara JO (2004) Ischemic stroke: “acidotoxicity” is a perpetrator. Cell 118:665–666
Kikuchi-Utsumi K, Nakaki T (2008) Chronic treatment with a selective ligand for the sigma-1 receptor chaperone, SA4503, up-regulates BDNF protein levels in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 440:19–22
Kilic E, Kilic U, Wang Y, Bassetti CL, Marti HH, Hermann DM (2006) The phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway mediates VEGF’s neuroprotective activity and induces blood brain barrier permeability after focal cerebral ischemia. FASEB J 22:307–314
Kim DH, Li H, Yoo KY, Lee BH, Hwang IK, Won MH (2007) Effects of fluoxetine on ischemic cells and expressions in BDNF and some antioxidants in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region induced by transient ischemia. Exp Neurol 204:748–758
Kokaia Z, Zhao Q, Kokaia M, Elmer E, Metsis M, Smith ML, Siesjö BK, Lindvall O (1995) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor geneexpression after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion with and without brain damage. Exp Neurol 136:73–88
Korte M, Carroll P, Wolf E, Brem G, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T (1995) Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:8856–8860
Langa F, Codony X, Tovar V et al (2003) Generation and phenotypic analysis of sigma receptor type I (σ1) knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci 18:2188–2196
Lewin GR, Barde YA (1996) Physiology of the neurotrophins. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:289–317
Li W, Keifer J (2012) Rapid enrichment of presynaptic protein in boutons undergoing classical conditioning is mediated by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Neuroscience 203:50–58
Li Z, Cui S, Zhang Z, Zhou R, Ge Y, Sokabe M, Chen L (2009) DHEA-neuroprotection and -neurotoxicity after transient cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cerebr Blood F Met 29:287–296
Liu Y, Wang TP, Aarts M et al (2007) NMDA receptor subunits have differential roles in mediating excitotoxic neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci 27:2846–2857
Lu P, Mamiya T, Lu LL et al (2009) Silibinin prevents amyloid b peptide-induced memory impairment and oxidative stress in mice. Br J Pharmacol 157:1270–1277
Matsumoto RR, Liu Y, Lerner M, Howard EW, Brackett DJ (2003) σ receptors: Potential medications development target for anti-cocaine agents. Eur J Pharmacol 469:1–12
Maurice T (2001) Beneficial effect of the sigma1 receptor agonist PRE-084 against the spatial learning deficits in aged rats. Eur J Pharmacol 431:223–227
Maurice T, Lockhart BP (1997) Neuroprotective and anti-amnesic potentials of σ (sigma) receptor ligands. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 21:69–102
McClean PL, Parthsarathy V, Faivre E, Hölscher C (2011) The Diabetes Drug Liraglutide Prevents Degenerative Processes in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. J Neurosci 31:6587–6594
Nagahara AH, Tuszynski MH (2011) Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:209–219
Olsson T, Wieloch T, Smith M-J (2003) Brain damage in a mouse model of global cerebral ischemia Effect of NMDA receptor blockade. Brain Res 982:260–269
Pattwell SS, Bath KG, Perez-Castro R, Lee FS, Chao MV, Ninan I (2012) The BDNF Val66Met polymorphism impairs synaptic transmission and plasticity in the infralimbic medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 32:2410–2421
Peng PL, Zhong X, Tu W et al (2006) ADAR2-dependent RNA editing of AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 determines vulnerability of neurons in forebrain ischemia. Neuron 49:719–733
Penton-Rol G, Marin-Prida J, Pardo-Andreu G et al (2011) C-phycocyanin is neuroprotective against global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in gerbils. Brain Res Bull 86:42–52
Phan VL, Urani A, Sandillon F, Privat A, Maurice T (2003) Preserved sigma1 (sigma1) receptor expression and behavioral efficacy in the aged C57BL/6 mouse. Neurobiol Aging 24:865–881
Robinet C, Pellerin L (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances the hippocampal expression of key postsynaptic proteins < i > in vivo</i > including the monocarboxylate transporter MCT2. Neuroscience 192:155–163
Su TP, Hayashi T, Maurice T, Buch S, Ruoho AE (2010) The sigma-1 receptor chaperone as an interorganelle signaling modulator. Trends Pharmaco Sci 31:557–566
Takebayashi M, Hayashi T, Su TP (2004) A Perspective on the new mechanism of antidespressants: neuritogenesis through Sigma-1 receptor. Pharmacopsychiatry 37:208–213
Tao X, Finkbeiner S, Arnold DB, Shaywitz AJ, Greenberg ME (1998) Ca2+ influx regulates BDNF transcription by a CREB family transcription factor-dependent mechanism. Neuron 20:709–726
Tyler WJ, Pozzo-Miller L (2003) Miniature synaptic transmission and BDNF modulate dendritic spine growth and form in rat CA1 neurones. J Physiol 553:497–509
Villard V, Espallergues J, Keller E et al (2009) Antiamnesic and neuroprotective effects of the aminotetrahydrofuran derivative ANAVEX1-41 against amyloid beta (25-35)-induced toxicity in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1552–1566
Walton MR, Dragunow M (2000) Is CREB a key to neuronal survival? Trends Neurosci 23:48–53
Watanabe S, Utsuki N (2011) Effect of ischemia on spatial learning in mice. In: CARLS series of advanced study of logic and sensibility. Keio Univserty Press, Tokyo, pp 7-14
Wu C, Zhan RZ, Qi S, Fujihara H, Taga K, Shimoji K (2001) A forebrain ischemic preconditioning model established in C57Black/Crj6 mice. J Neurosci Methods 107:101–106
Yagasaki Y, Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Hayashi T, Su TP, Kunugi H (2006) Chronic antidepressants potentiate via sigma-1 receptors the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced signaling for glutamate release. J Biol Chem 281:12941–12949
Yamamoto Y, Shioda N, Han F et al (2009) Nobiletin improves brain ischemia-induced learning and memory deficits through stimulation of CaMKII and CREB phosphorylation. Brain Res 1295:218–229
Yang G, Kitagawa K, Matsushita K, Mabuchi T, Yagita Y, Yanagihara T, Matsumoto M (1997) C57BL/6 strain is most susceptible to cerebral ischemia following bilateral common carotid occlusion among seven mouse strains: selective neuronal death in the murine transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res 752:209–218
Zhang LM, Fu FH, Zhang XM, Zhu M, Wang T, Fan HY (2010) Escin attenuates cognitive deficits and hippocampal injury after transient global cerebral ischemia in mice via regulating certain inflammatory genes. Neurochem Int 57:119–127
Zhao Q, Murakami Y, Tohda M, Watanabe H, Matsumoto K (2005) Preventive Effect of Chotosan, a Kampo Medicine, on Transient Ischemia-Induced Learning Deficit Is Mediated by Stimulation of Muscarinic M1 But Not Nicotinic Receptor. Biol Pharm Bull 28:1873–1878
Zou LB, Yamada K, Sasa M, Nakata Y, Nabeshima T (2000) Effects of σ1 receptor agonist SA4503 and neuroactive steroids on performance in a radial arm maze task in mice. Neuropharmacology 39:1617–1627
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Science and Technology Major Special Project on Major New Drug Innovation of China (No. 2009ZX09103-119 and No. 2009ZX09301-012).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Ji, XF., Chi, TY. et al. Sigma 1 receptor activation regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor through NR2A-CaMKIV-TORC1 pathway to rescue the impairment of learning and memory induced by brain ischaemia/reperfusion. Psychopharmacology 232, 1779–1791 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3809-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3809-6