Abstract
Rationale
Anxiety-like behavior resulting from repeated withdrawals from chronic ethanol diets is counteracted by systemic administration of a 5-HT2C receptor antagonist or a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.
Objectives
This study investigated whether prior treatment with these agents into the amygdala, dorsal raphe nucleus, nucleus accumbens, or paraventricular nucleus during early withdrawals would ameliorate the social interaction deficits observed after a subsequent withdrawal.
Methods
Sprague–Dawley rats were exposed to three cycles of 5 days of forced ethanol diet (4.5%, w/v), with 2 days of control diet after the first and second cycles. Drugs were administered into one of four brain sites 4 h after removal of ethanol on the first and 2nd cycles but not the third. The social interaction test was performed 5 h after removal of ethanol on the third cycle. Drugs tested included SB-243213, a 5-HT2C receptor inverse agonist; buspirone, a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist; and Ro 60 1075, a 5-HT2C receptor agonist.
Results
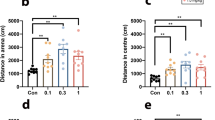
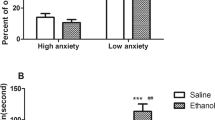
Only SB-243213 (at 3 μg, but not at 1 and 0.3 μg) counteracted the social interaction deficits after injections into the amygdala, while buspirone (at 0.3 and 1 μg but not at 0.1 μg) reduced deficits only when given into the dorsal raphe nucleus. In contrast, the 5-HT2C receptor agonist, Ro 60 1075, accentuated the behavioral deficit after two weekly injections into the amygdala.
Conclusions
These results are consistent with the involvement of 5-HT2C receptors in the amygdala and 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus in repeated ethanol withdrawal-induced sensitization of anxiety-like behavior.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews N, File SE (1993) Increased 5-HT release mediates the anxiogenic response during benzodiazepine withdrawal: a review of supported neurochemical and behavioural evidence. Psychopharmacology 112:21–25
Andrews N, Hogg S, Gonzalez LE, File SE (1994) 5-HT1A receptors in the median raphe nucleus and dorsal hippocampus may mediate anxiolytic and anxiogenic behaviour, respectively. Eur J Pharmacol 264:259–264
Bagdy G (1996) Role of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in 5-HT1A. 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor-mediated oxytocin, prolactin and ACTH/corticosterone responses. Behav Brain Res 73:277–280
Bagdy G, Graf M, Anheuer ZE, Modos EA, Kantor S (2001) Anxiety-like effects induced by acute fluoxetine, sertraline or m-CPP treatment are reversed by pretreatment with the 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB-242084 but not the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY-100635. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 4:399–408
Breese GR, Knapp DJ, Overstreet DH (2004) Stress sensitization of ethanol withdrawal-induced reduction in social interaction: inhibition by CRF-1 and benzodiazepine receptor antagonists and a 5-HT1A receptor agonists. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:470–482 DOI 10.1038/sj.npp. 1200282
Bristow LJ, O’Connor D, Watts R, Duxon MS, Hutson PH (2000) Evidence for accelerated desensitisation of 5-HT2C receptors following combined treatment with fluoxetine and the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY 100635, in the rat. Neuropharmacology 39:123–132
Campbell BM, Merchant KM (2003) Serotonin 2C receptors within the basolateral amygdala induce acute fear-like responses in an open-field environment. Brain Res 993:1–9
Carrasco GA, Van de Kar LD (2003) Neuroendocrine pharmacology of stress. Eur J Pharmacol 463:235–272
De Deurwaerdere P, Navailles S, Berg KA, Clarke WP, Spampinato U (2004) Constitutive activity of the serotonin2C receptor inhibits in vivo dopamine release in the rat striatum and nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 24:3235–3241
Eberle-Wang K, Mikeladze Z, Uryu K, Chesselet MF (1997) Pattern of expression of the serotonin2C receptor messenger RNA in the basal ganglia of adult rats. J Comp Neurol 384:233–247
File SE, Seth P (2003) A review of 25 years of the social interaction test. Eur J Pharmacol 463:35–53
File SE, Baldwin HA, Hitchcot PK (1989) Flumazenil but not nitrendipine reverses the increased anxiety during ethanol withdrawal in the rat. Psychopharmacology 98:262–264
File SE, Andrews N, al-Farhan M, Wu PY (1993) The role of 5-HT in the anxiogenic effects of acute ethanol withdrawal and in the long-lasting cognitive deficits. Alcohol 28:495–499
File SE, Gonzalez LE, Andrews N (1996) Comparative study of pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptor modulation of anxiety in two ethological animal tests. J Neurosci 16:4810–4815
Frye GD, McCown TJ, Breese GR (1983) Differential sensitivity of ethanol withdrawal signs in the rat to γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) mimetics: blockade of audiogenic seizures but not forelimb tremors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:720–725
Gonzalez LE, Andrews N, File SE (1996) 5-HT1A and benzodiazepine receptors in the basolateral amygdala modulate anxiety in the social interaction test, but not in the elevated plus-maze. Brain Res 735:145–153
Gordon JA, Hen R (2004) The serotonergic system and anxiety. Neuromolecular Med 5:27–40
Hogg S, Andrews N, File SE (1994) Contrasting behavioural effects of 8-OH-DPAT in the dorsal raphe nucleus and ventral hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 33:343–348
Irvine EE, Bagnalasta M, Marcon C, Motta C, Tessari M, File SE, Chiamulera C (2001) Nicotine self-administration and withdrawal: modulation of anxiety in the social interaction test in rats. Psychopharmacology 153:315–320
Jorgensen H, Knigge U, Kjaer A, Moller M, Warberg J (2002) Serotonergic stimulation of corticostroine-releasing hormone and pro-opiomelanocortin gene expression. J Neuroendocrinol 14:788–795
Jorgensen H, Kjaer A, Knigge U, Moller M, Warberg J (2003) Serotonin stimulates hypothalamic mRNA expression and local release of neurohypophysial peptides. J Neuroendocrinol 15:564–571
Kampov-Polevoy AB, Matthews DB, Gause L, Morrow AL, Overstreet DH (2000) P rats develop physical dependence on alcohol via voluntary drinking: Changes in seizure thresholds, anxiety, and patterns of alcohol drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:278–284
Kennett GA, Wood MD, Bright F, Trail B, Riley G, Holland V, Avenell KY, Stean T, Upton N, Bromidge S, Forbes IT, Brown AM, Middlemiss DN, Blackburn TP (1997) SB-242084, a selective and brain penetrant 5-HT2C receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacology 36:609–620
Kennett G, Lightowler S, Trail B, Bright F, Bromidge S (2000) Effects of RO 60 0175, a 5-HT2C receptor agonist, in three animal models of anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 387:197–204
Knapp DJ, Duncan GE, Crews FT, Breese GR (1998) Induction of Fos-like proteins and ultrasonic vocalizations during ethanol withdrawal: further evidence for withdrawal-induced anxiety. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:481–493
Knapp DJ, Overstreet DH, Moy SS, Breese CR (2004) SB-242084, flumazenil and CRA1000 block ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety in rats. Alcohol 32:101–111
Knapp DJ, Overstreet DH, Breese GR (2005) Modulation of ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior during later withdrawals by treatment of early withdrawals withbenzodiazepine/GABA ligands. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:553–563
Lanfumey L, Hamon M (2004) 5-HT1 receptors. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 3:1–10
Moy SS, Knapp DJ, Criswell HE, Breese GR (1997) Flumazenil blockade of anxiety following ethanol withdrawal in rats. Psychopharmacology 131:354–360
Moy SS, Knapp DJ, Duncan GE, Breese GR (2000) Enhanced ultrasonic vocalization and Fos protein expression following ethanol withdrawal: effects of flumazenil. Psychopharmacology 152:208–215
Overstreet DH, Rezvani AH, Pucilowski O, Janowsky DS (1995) 5-HT receptors: implications for the neuropharmacology of alcohol and alcoholism. Alcohol (Suppl 2):207–212
Overstreet DH, Knapp DJ, Breese GR (2002) Accentuated decrease in social interaction in rats repeatedly withdrawn from ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:1259–1269
Overstreet DH, Knapp DJ, Moy SS, Breese GR (2003) A 5-HT1A agonist and a 5-HT2C antagonist reduce social interaction deficit induced by multiple ethanol withdrawals in rats. Psychopharmacology 167:344–352
Overstreet DH, Knapp DJ, Breese G (2005) Pharmacological modulation of repeated ethanol withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior differs in alcohol-preferring P and Sprague–Dawley rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:122–130
Pandey SC, Pandey GN (1996) Modulation of serotonin2A/2C receptors and these receptor-linked phosphoinossitide system by ethanol. Behav Brain Res 73:235–238
Pandey SC, Piano MR, Schwertz DW, Davis JM, Pandey GN (1992) Effect of ethanol administration and withdrawal on serotonin receptor subtypes and receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16:1110–1116
Rioja J, Santin LJ, Garcia M, Dona A, De Pablos L, Caudrado MI, Alcalde FJ, Gonzalez-Baron S, Aguirre JA (2004) 5-HT1A receptor activation before acute stress counteracted the induced long-term behavioral effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1018:333–338
Serrats J, Mengod G, Cortes R (2005) Expression of serotonin 5-HT2C receptors in GABAergic cells of the anterior raphe nuclei. J Chem Neuroanat 29:83–91
Stefanski R, Palejko W, Bidzinski A, Kostowski W, Plaznik A (1993) Serotonergic innervation of the hippocampus and nucleus accumbens septi and the anxiolytic-like action of midazolam and 5-HT1A receptor agonists. Neuropharmacology 32:977–985
Ulrichsen J (1991) Alterations in serotonin receptor subtypes in ethanol-dependent rats. Alcohol 26:567–573
Wood MD (2003) Therapeutic potential of 5-HT2C receptor antagonists in the treatment of anxiety disorders. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 2:383–387
Wood MD, Reavill C, Trail B, Wilson A, Stean T, Kennett GA, Lightowler S, Blackburn TP, Thomas D, Gager TL, Riley G, Holland V, Bromidge SM, Forbes IT, Middlemiss DN (2001) SB-243213; a selective 5-HT2C receptor inverse agonist with improved anxiolytic profile: lack of tolerance and withdrawal anxiety. Neuropharmacology 41:186–199
Yilmazer-Hanke DM, Roskoden T, Zilles K, Schwegler H (2003) Anxiety-related behavior and densities of glutamate, GABA A, acetylcholine and serotonin receptors in the amygdala of seven inbred mouse strains. Behav Brain Res 145:145–159
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Qi Yu, Mili Senapati and Lara Marr for technical assistance and Martyn Wood of GlaxoSmithKline for supporting this project. This work was financially supported by NIAAA grants AA 14284, AA 11605, and AA 14949.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Overstreet, D.H., Knapp, D.J., Angel, R.A. et al. Reduction in repeated ethanol-withdrawal-induced anxiety-like behavior by site-selective injections of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C ligands. Psychopharmacology 187, 1–12 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0389-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0389-0