Abstract
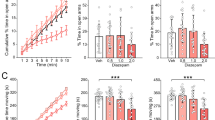
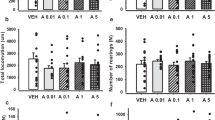
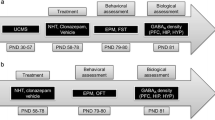
Anxiety is amongst the commonest neuropsychiatric disorders, and there is a large body of evidence to suggest that abnormalities in serotonergic function are involved in its pathogenesis. Several studies have implicated 5-HT1A receptor activation in mitigating anxiety disorders, so this study investigated the acute effects of a highly selective, potent and efficacious 5-HT1A receptor full agonist, NLX-112 (a.k.a. befiradol, F13640), in middle-aged C57bl/6 J male mice. Video tracking was used to measure several parameters including time spent in the open and closed arms of an elevated plus maze (EPM), distance travelled and thigmotaxis in an open field test (OFT). At 0.1 to 1.0 mg/kg s.c., NLX-112 markedly decreased thigmotaxis and increased exploratory behaviour in the OFT and EPM assays. Hence, at 0.3 mg/kg, NLX-112 augmented locomotor activity in the centre of an open field arena by 164% and increased the time spent in the open arms of the EPM by 119% of control. These results indicate that anxiety-like behaviours in mice are significantly diminished with low doses of NLX-112. NLX-112 may therefore possess anxiolytic properties which complement its known activity in models of movement disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All raw data and graphs are available on request. All data were generated in-house, and no “paper mill” was used.
Abbreviations
- AIMS:
-
Abnormal involuntary movements
- EPM:
-
Elevated plus maze
- LID:
-
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia
- OFT:
-
Open field test
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
References
Ahlenius S, Hillegaart V, Salmi P, Wijkström A (1993) Effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists on patterns of rat motor activity in relation to effects on forebrain monoamine synthesis. Pharmacol Toxicol 72:398–406
Akimova E, Lanzenberger R, Kasper S (2009) The serotonin-1A receptor in anxiety disorders. Biol Psych 66:627–635
Angrini M, Leslie JC, Shephard RA (1998) Effects of propranolol, buspirone, pCPA, reserpine, and chlordiazepoxide on open-field behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:387–397
Azevedo H, Ferreira M, Costa RW, Russo V, Russo E, Mascarello A et al (2019) Preclinical characterization of ACH-000029, a novel anxiolytic compound acting on serotonergic and alpha-adrenergic receptors. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psych 95:109707
Bergman J, Roof RA, Furman CA, Conroy JL, Mello NK, Sibley DR et al (2013) Modification of cocaine self-administration by buspirone (buspar®): potential involvement of D3 and D4 dopamine receptors. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:445–458
Bianchi G, Caccia S, Della Vedova F, Garattini S (1988) The α2-adrenoceptor antagonist activity of ipsapirone and gepirone is mediated by their common metabolite 1-(2-pyrimidinyl)-piperazine (PmP). Eur J Pharmacol 151:365–371
Bonhaus DW, Weinhardt KK, Taylor M, DeSouza A, McNeeley PM, Szczepanski K et al (1997) RS-102221: a novel high affinity and selective, 5-HT2C receptor antagonist. Neuropharmacol 36:621–629
Buitelaar JK, van der Hoeven J (1998) Buspirone in the management of anxiety and irritability in children with pervasive developmental disorders: results of an open-label study. J Clin Psych 59:56–59
Cervo L, Mocaer E, Bertaglia A, Samanin R (2000) Roles of 5-HT1A receptors in the dorsal raphe and dorsal hippocampus in anxiety assessed by the behavioral effects of 8-OH-DPAT and S 15535 in a modified Geller-Seifter conflict model. Neuropharmacol 39:1037–1043
Cheetham SC, Heal DJ (1993) Evidence that RU 24969-induced locomotor activity in C57/B1/6 mice is specifically mediated by the 5-HT1B receptor. Brit J Pharmacol 110:1621–1629
Colpaert FC, Tarayre JP, Koek W, Pauwels PJ, Bardin L, Xu XJ et al (2002) Large-amplitude 5-HT1A receptor activation: a new mechanism of profound, central analgesia. Neuropharmacol 43:945–958
Depoortere R, Johnston TH, Fox SH, Brotchie JM, Newman-Tancredi A (2020) The selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic effects in MPTP-treated macaques. Parkin Rel Disord 78:151–157
Depoortère R, Papp M, Gruca P, Lason-Tyburkiewicz M, Niemczyk M, Varney MA et al (2019) Cortical 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor biased agonist, NLX-101, displays rapid-acting antidepressant-like properties in the rat chronic mild stress model. J Psychopharmacol 33:1456–1466
Dubovický M, Škultétyová I, Ježová D (1999) Neonatal stress alters habituation of exploratory behavior in adult male but not female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:681–686
Dunn RW, Corbett R, Fielding S (1989) Effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists and NMDA receptor antagonists in the social interaction test and the elevated plus maze. Eur J Pharmacol 169:1–10
File SE, Gonzalez LE (1996) Anxiolytic effects in the plus-maze of 5-HT1A-receptor ligands in dorsal raphe and ventral hippocampus. Pharmacol Bioch Behav 54:123–128
File SE, Mabbutt PS, Hitchcott PK (1990) Characterisation of the phenomenon of “one-trial tolerance” to the anxiolytic effect of chlordiazepoxide in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology 102:98–101
Fisher R, Hikima A, Morris R, Jackson MJ, Rose S, Varney MA et al (2020) The selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112, exerts anti-dyskinetic and anti-parkinsonian-like effects in MPTP-treated marmosets. Neuropharmacol 167:107997
Gluch-Lutwin M, Salaciak K, Gawalska A, Jamrozik M, Sniecikowska J, Newman-Tancredi A, Kolaczkowski M, Pytka K (2021) Psychopharmacol 238:2249–2260
Gobert A, Rivet JM, Cistarelli L, Melon C, Millan MJ (1999) Buspirone modulates basal and fluoxetine-stimulated dialysate levels of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats: activation of serotonin1A receptors and blockade of α2-adrenergic receptors underlie its actions. Neurosci 93:1251–1262
Heisler LK, Chu HM, Brennan TJ, Danao JA, Bajwa P, Parsons LH et al (1998) Elevated anxiety and antidepressant-like responses in serotonin 5-HT1A receptor mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:15049–15054
Holmes A, Rodgers RJ (1999) Influence of spatial and temporal manipulations on the anxiolytic efficacy of chlordiazepoxide in mice previously exposed to the elevated plus-maze. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:971–980
Iderberg H, McCreary AC, Varney MA, Cenci MA, Newman-Tancredi A (2015) Activity of serotonin 5-HT1A receptor ‘biased agonists’ in rat models of Parkinson’s disease and L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Neuropharmacol 93:52–67
Iravani MM, Tayarani-Binazir K, Chu WB, Jackson MJ, Jenner P (2006) In 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-treated primates, the selective 5-hydroxytryptamine 1a agonist (R)-(+)-8-OHDPAT inhibits levodopa-induced dyskinesia but only with increased motor disability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1225–1234
Levigoureux E, Vidal B, Fieux S, Bouillot C, Emery S, Newman-Tancredi A et al (2018) Serotonin 5-HT1A receptor biased agonists induce different cerebral metabolic responses: a [18F]-fluorodesoxyglucose positron emission tomography study in conscious and anesthetized rats. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:3108–3119
Lister RG (1987) The Use of a plus-Maze to Measure Anxiety in the Mouse. Psychopharmacol 92:180–185
Lladó-Pelfort L, Assié MB, Newman-Tancredi A, Artigas F, Celada P (2012) In vivo electrophysiological and neurochemical effects of the selective 5-HT 1A receptor agonist, F13640, at pre-and postsynaptic 5-HT 1A receptors in the rat. Psychopharmacol 221:261–272
McCreary AC, Varney MA, Newman-Tancredi A (2016) The novel 5-HT1A receptor agonist, NLX-112 reduces l-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements in rat: a chronic administration study with microdialysis measurements. Neuropharmacol 105:651–660
Menza MA, Robertson-Hoffman DE, Bonapace AS (1993) Parkinson’s disease and anxiety: comorbidity with depression. Biol Psych 34:465–470
Mishra A, Singh S, Tiwari V, Shukla S (2019) Dopamine D1 receptor activation improves adult hippocampal neurogenesis and exerts anxiolytic and antidepressant-like effect via activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathways in rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Int 122:170–186
Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D, Ormière AM, Lestienne F, Varney MA, Martel JC (2019) Bell-shaped agonist activation of 5-HT1A receptor-coupled Gαi3 G-proteins: receptor density-dependent switch in receptor signalling. Cell Signal 63:109383
Newman-Tancredi A, Martel JC, Cosi C, Heusler P, Lestienne F, Varney MA et al (2017) Distinctive in vitro signal transduction profile of NLX-112, a potent and efficacious serotonin 5-HT 1A receptor agonist. J Pharm Pharmacol 69:1178–1190
O’Neill MF, Conway MW (2001) Role of 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(1B) receptors in the mediation of behavior in the forced swim test in mice. Neuropsychopharmacol 24:391–398
Pae CU, Serretti A, Patkar AA, Masand PS (2008) Aripiprazole in the treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders. CNS Drugs 22:367–388
Prut L, Belzung C (2003) The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol 463:3–33
Ramboz S, Oosting R, Amara DA, Kung HF, Blier P, Mendelsohn M et al (1998) Serotonin receptor 1A knockout: an animal model of anxiety-related disorder. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:14476–14481
Richard IH, Schiffer RB, Kurlan R (1996) Anxiety and Parkinson’s disease. J Neuropsych Clin Neurosci 8:383–392
Rodgers RJ, Cole JC (1994) Anxiolytic-like effect of (S)-WAY 100135, a 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, in the murine elevated plus-maze test. Eur J Pharm 261:321–325
Rodgers RJ, Nikulina EM, Cole JC (1994) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor ligands modulate the behaviour of mice in the elevated plus-maze. Pharmacol Bioch Behav 49:985–995
Sałat K, Kołaczkowski M, Furgała A, Rojek A, Śniecikowska J, Varney MA, Newman-Tancredi A (2017) Antinociceptive, antiallodynic and antihyperalgesic effects of the 5-HT 1A receptor selective agonist, NLX-112 in mouse models of pain. Neuropharmacol 125:181–188
Shoji H, Takao K, Hattori S, Miyakawa T (2016) Age-related changes in behaviour in C57BL/6J mice from young adulthood to middle age. Mol Brain 9:1–18
Simon P, Dupuis R, Costentin J (1994) Thigmotaxis as an index of anxiety in mice. Influence of dopaminergic transmissions. Behav Brain Res 61:59–64
Teri L, Ferretti LE, Gibbons LE, Logsdon RG, McCurry SM, Kukull WA et al (1999) Anxiety in Alzheimer’s disease: prevalence and comorbidity. J Geront Series A Biomed Sci Med Sci 54:M348–M352
Toth M (2003) 5-HT1A receptor knockout mouse as a genetic model of anxiety. Eur J Pharmacol 463:177–184
Vaidya AH, Rosenthal DI, Lang W, Crooke JJ, Benjamin D, Ilyin SE, Reitz AB (2005) Oral buspirone causes a shift in the dose-response curve between the elevated-plus maze and Vogel conflict tests in Long-Evans rats: relation of brain levels of buspirone and 1-PP to anxiolytic action. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 27:245–255
Vicente MA, Zangrossi H Jr, dos Santos L, de Macedo CE, Andrade TGC (2008) Involvement of median raphe nucleus 5-HT1A receptors in the regulation of generalized anxiety-related defensive behaviours in rats. Neurosci Lett 445:204–208
Vidal B, Bolbos R, Redouté J, Langlois JB, Costes N, Newman-Tancredi A et al (2020) Pharmacological MRI to investigate the functional selectivity of 5-HT1A receptor biased agonists. Neuropharmacol 172:107867
Walsh K, Bennett G (2001) Parkinson’s disease and anxiety. Postgrad Med J 77:89–93
Funding
This work was supported through the collaborative venture of the Hertfordshire Science Partnership, Neurolixis and the European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The contribution of co-authors were as follows: WHP, in vivo investigation, data collection and curation, preparation of figures, writing original draft and data analysis; LEA, editing, reviewing and provision of equipment; RD, editing, reviewing and statistical analysis oversight and data interpretation; AN-T, supervision, data interpretation, editing and reviewing; MMI, in vivo experimental design, supervision; manuscript revisions, and reviewing data validation. We declare that all authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The studies undertaken here were approved under knowledge and approval of local Animal Welfare Ethical Review Body and were carried out in accordance with the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986 and associated guidelines, EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments.
Consent to participate
Not applicable. No human participants took part in this study.
Consent for publication
We have the consent of all co-authors and the institution to publish this research article.
Competing interests
A. Newman-Tancredi and R. Depoortere are employees and shareholders of Neurolixis. The other authors declare no competing interest in respect to the research, authorship and publication of this research article.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Powell, W.H., Annett, L.E., Depoortere, R. et al. The selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist NLX-112 displays anxiolytic-like activity in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 149–157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02183-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02183-2