Abstract
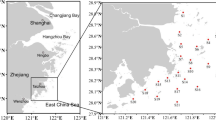
Seahorses, which have been used in Chinese traditional medicine, are poor swimmers and easily affected by regional ecological conditions. In this study, we investigated the bioaccumulation of nine metals in different tissues of four seahorse species (Hippocampus trimaculatus, H. histrix, H. kelloggi, and H. kuda) from six locations along the Chinese coast. The present study found relatively low concentrations of metals in the seahorses compared with those in other marine fishes. There was a location-dependent variation in metal concentrations in the seahorses, especially between developed and less developed cities. Results also showed metal concentrations varied among different seahorse species and tissues, with H. kelloggi having higher bioaccumulation ability compared with H. trimaculatus and higher metal levels were found in visceral mass, muscle, and skin tissues than those in brain, lips gill, endoskeleton, and exoskeleton tissues in the seahorses. Among different metals, Mg had the highest tissue concentrations in all the seahorses, followed by Al and Mn.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley-Ross MA (2002) Mechanical properties of the dorsalfin muscle of seahorse (Hippocampus) and pipefish (Syngnathus). J Exp Zool 293:561–577
Burger J, Gochfeld M (2005) Heavy metals in commercial fish in New Jersey. Environ Res 99:403–412
Caldwell IR, Vincent ACJ (2013) Asedentaryfish on the move: effects of displacementon long-snouted seahorse (Hippocampus guttulatus Cuvier) movement and habitat use. Environ Biol Fish 96:67–75
Cheung KC, Leung HM, Wong MH (2008) Metal concentrations of common freshwater and marine fish from the Pearl River delta, South China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:705–715
Choo CK, Liew HC (2003) Spatial distribution, substrate assemblages and sizecomposition of sea horses (Family Syngnathidae) in the coastal waters of Peninsular Malaysia. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 83:271–276
Falcó G, Llobet JM, Bocio A, Domingo JL (2006) Daily intake of arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead by consumption of edible marine species. J Agric Food Chem 54:6106–6112
Foster SJ, Vincent ACJ (2004) Life history and ecology of seahorses: implications for conservation and management. J Fish Biol 65:1–61
Galindo L, Hardisson A, Montelongo FG (1986) Correlation between lead, cadmium, copper, zinc and iron concentrations in frozen tuna fish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 36:595–599
Ip CCM, Li X-D, Zhang G, Wong CSC, Zhang WL (2005) Heavy metal and Pb isotopic compositions of aquatic organisms in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollut 138:494–504
IUCN (2011) IUCN red list of threatened species. http://www.iucnredlist.org/
Jaffar M, Pervais Shahid S (1989) Investigation on multi-organ heavy trace metal content of meat of selected dairy, poultry, fowl and fish species. Pak J SciInd Res 323:175–177
Kojadinovic J, Potier M, Le Corre M, Cosson RP, Bustamante P (2007) Bioaccumulation of trace elements in pelagic fish from the Western Indian Ocean. Environ Pollut 146:548–566
Kuang CC, Chark LH (2004) A record of seahorse species (Family Syngnathidae) in East Malaysia, with notes on their conservation. Malay Nat J 56:409–420
Lewis MA, Scott GI, Bearden DW, Quarles RL, Moore J, Strozier ED, Sivertsen SK, Dias AR, Sanders M (2002) Fish tissue quality in near-coastal areas of the Gulf of Mexico receiving point source discharges. Sci Total Environ 284:249–261
Lin Q, Lin JD, Wang C (2009) Biochemical composition of the wild and cultured seahorses, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker and Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach. Aquac Res 40:710–719
Lin Q, Li G, Qin G, Lin JD, Huang LM, Sun HS, Feng PY (2012) The dynamics of reproductive rate, offspring survivorship and growth in the lined seahorse, Hippocampus erectus Perry, 1810. Biol Open 1:391–396
Lourie SA, Vincent ACJ, Hall HJ (1999) Seahorses: an identification guide to the world’s species and their conservation. Project Seahorse, London
Luzzatto DC, Estalles ML, de Astarloa JMD (2013) Rafting seahorses: the presence of juvenile Hippocampus patagonicus in floating debris. J Fish Biol 83:677–681
Martin-Smith KM, Samoilys MA, Meeuwig JJ, Vincent ACJ (2004) Collaborative development of management options for an artisanal fishery for seahorses in the central Philippines. Ocean Coast Manage 47:165–193
Michael SW (2001) Reef fishes, volume 1: a guide to their identification, behavior and captive care. T. H. F. Publications, Neptune City, NJ, pp 409–439
Nakayama SMM, Ikenaka Y, Muzandu K, Choongo K, Oroszlany B, Teraoka H, Mizuno N, Ishizuka M (2010) Heavy metal accumulation in lake sediments, fish (Oreochromisniloticus and Serranochromisthumbergi), and crayfish (Cheraxquadricarinatus) in lake Itezhi-tezhi and lake Kariba, Zambia. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 29:291–300
Onsanit S, Ke C, Wang X, Wang K-J, Wang W-X (2010) Trace elements in two marine fish cultured in fish cages in Fujian province, China. Environ Pollut 158:1334–1342
Pan K, Wang W-X (2012) Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:3–16
Pourang N, Dennis JH (2005) Distribution of trace elements in tissues of two shrimp species from the Persian Gulf and roles of metallothionein in their redistribution. Environ Int 31:325–341
Qin G, Lin Q, Huang LM, Lin JD (2012) Effect of broodstock origin, background and substrate color on skin coloration of three-spotted seahorses Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach, 1814. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 416–417:129–134
Qin G, Zhang YH, Huang LM, Lin Q (2014) Effects of water current on swimming performance, ventilation frequency, and feeding behavior of young seahorses (Hippocampus erectus). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 461:337–343
Rainbow PS (2002) Trace metal concentrations in aquatic invertebrates: why and so what? Environ Pollut 120:497–507
Tepe Y, Türkmen M, Türkmen A (2008) Assessment of heavy metals in two commercial fish species of four Turkish seas. Environ Monit Assess 146:277–284
Teske PR, Beheregaray LB (2009) Evolution of seahorses’ upright posture was linked to Oligocene expansion of seagrass habitats. Biol Lett 5:521–523
Türkmen M, Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Töre Y, Ates A (2009) Determination of metals in fish species from Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Food Chem 113:233–237
Uluozlu OD, Tuzen M, Mendil D, Soylak M (2007) Trace metal content in nine species of fish from the Black and Aegean Seas, Turkey. Food Chem 104:835–840
Vincent ACJ, Foster SJ, Koldewey HJK (2011) Conservation and management of seahorses and other Syngnathidae. J Fish Biol 78:1681–1724
Wang X-C, Feng H, Ma H-Q (2007) Assessment of metal contamination in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Clean 35:62–70
Yan CZ, Li QZ, Zhang X, Li GX (2010) Mobility and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Xiamen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Environ Earth Sci 60:1469–1479
Zhang W, Wang W-X (2012) Large-scale spatial and interspecies differences in trace elements and stable isotopes in marine wild fish from Chinese waters. J Hazard Mater 215–216:65–74
Zhang LP, Ye X, Feng H, Jing YH, Ouyang T, Yu XT, Liang RY, Gao CT, Chen WQ (2007) Heavy metal contamination in western Xiamen Bay sediments and its vicinity, China. Mar Pollut Bull 54:974–982
Zhang YH, Nancy P, Lin JD, Huang LM, Lin Q (2014) Genetic variations in two seahorse species (Hippocampus mohnikei and Hippocampus trimaculatus): evidence for middle Pleistocene population expansion. PLoS One 9:e105494
Zheng N, Wang QC, Zhang XW, Zheng DM, Zhang ZS, Zhang SQ (2007) Population health risk due to dietary intake of heavy metals in the industrial area of Huludao city, China. Sci Total Environ 387:96–104
Zhou HY, Wong MH (2000) Mercury accumulation in freshwater fish with emphasis on the dietary influence. Water Res 34:4232–4242
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Outstanding Youth Foundation in Guangdong Province (S2013050014802), the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (41322038), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41176146, 41306148), and the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (201403008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L. et al. Bioaccumulation of Metals in Tissues of Seahorses Collected from Coastal China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96, 281–288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1728-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1728-4