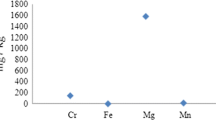
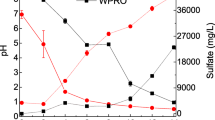
Abstract
The current global trend towards increasingly stringent environmental standards and efforts for efficient utilization and re-use of available by-products and/or wastes, favors the use of low-cost sorbent materials for the treatment of heavy metal-contaminated solid wastes. In this study, the stabilization of tannery sludge, produced from the physicochemical and biological treatment of tannery wastewaters, was examined by the addition of phosphogypsum (PG) at a ratio of 1:1. Characterization of the tannery sludge leachates showed high amounts of chromium which exceeded the acceptable level for disposal in non-hazardous waste landfills, while the dissolved organic carbon (DOC) concentrations exceeded the limits for disposal in landfills for hazardous wastes, according to the EU Decision 2003/33/EC. Leachates of the waste stabilized with PG presented chromium and DOC concentrations below the regulation limits for disposal in landfills for non-hazardous wastes. Moreover, mixing PG with tannery sludge resulted in a stabilized waste with reduced radioactivity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu M, Toffoli S (2009) Characterization of a chromium-rich tannery waste and its potential use in ceramics. Ceram Int 35:2225–2234
Council of the European Union (2003) 2003/33/EC: Council decision of 19 December 2002 establishing criteria and procedures for the acceptance of waste at landfills pursuant to Article 16 of and Annex II to Directive 1999/31/EC. Off J Eur Communities, Brussels
Garrido F, Illera V, Vizcayno C, García-González MT (2003) Evaluation of industrial by-products as soil acidity amendments: chemical and mineralogical implications. Eur J Soil Sci 54:411–422
Garrido F, Illera V, García-González MT (2005) Effect of the addition of gypsum- and lime-rich industrial by-products on Cd, Cu and Pb availability and leachability in metal-spiked acid soils. Appl Geochem 20:397–408
Illera V, Garrido F, Serrano S, García-González MT (2004) Immobilization of the heavy metals Cd, Cu and Pb in an acid soil amended with gypsum- and lime-rich industrial by-products. Eur J Soil Sci 55:135–145
Jing C, Liu S, Korfiatis G, Meng X (2006) Leaching behavior of Cr(III) in stabilized/solidified soil. Chemosphere 64:379–385
Kilic E, Font J, Puig R, Colak S, Celik D (2011) Chromium recovery from tannery sludge with saponin and oxidative remediation. J Hazard Mater 185:456–462
Moon DH, Dermatas D (2007) Arsenic and lead release from fly ash stabilised/solidified soils under modified semi-dynamic leaching conditions. J Hazard Mater 141:388–394
Papastefanou C, Stoulos S, Ioannidou A, Manolopoulou M (2006) The application of phosphogypsum in agriculture and the radiological impact. J Environ Radioact 89:188–198
Swarnalatha S, Arasakumari M, Gnanamani A, Sekaran G (2006) Solidification/stabilization of thermally-treated toxic tannery sludge. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:1307–1315
Tayibi H, Choura M, Lopez F, Alguacil F, Lopez-Delgado A (2009) Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum. J Environ Manag 90:2377–2386
Zouboulis A, Samaras P, Krestou A, Tzoupanos N (2012) Leather production modification methods towards minimization of tanning pollution: “Green tanning”. Fresenius Environ Bull 21:2406–2412
Acknowledgments
This research has been co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund – ESF) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “Education and Lifelong Learning” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF)—Research Funding Program: THALES: Reinforcement of the interdisciplinary and/or inter-institutional research and innovation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pantazopoulou, E., Zebiliadou, O., Noli, F. et al. Utilization of Phosphogypsum in Tannery Sludge Stabilization and Evaluation of the Radiological Impact. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94, 352–357 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1422-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1422-3