Abstract
Resistance to cell death is the major cause of chemotherapy failure in most kinds of cancers, including Burkitt lymphoma (BL). When analyzing therapy resistance in Burkitt lymphoma (BL), we discovered a link between apoptosis resistance and ploidy control. We therefore studied systematically a panel of 15 BL lines for apoptosis induction upon treatment with microtubule inhibitors and compared three types of microtubule toxins, i.e., paclitaxel, nocodazole and vincristine. We found an inverse relationship between apoptosis sensitivity and ploidy control. Thus, cells resistant to paclitaxel- or nocodazole-induced apoptosis underwent mitotic catastrophe and developed polyploidy (>4N). Mechanistically, apoptosis resistance was linked to failure of caspase activation, which was most pronounced in cells lacking the pro-apoptotic multidomain Bcl-2 homologs Bax and Bak. Pharmacological caspase inhibition promoted polyploidy upon exposure to paclitaxel and nocodazole supporting the relationship between resistance to apoptosis and polyploidization. Of note, vincristine induced persistent mitotic arrest but no loss of ploidy control. Considering targets to facilitate Bax/Bak-independent cell death and to avoid drug-induced mitotic catastrophe and consecutive mitotic catastrophe should be of great importance to overcome therapy resistance and therapy-related events that result in ploidy changes and tumor progression.
Key message
-
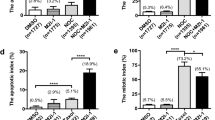
Inverse relation of apoptosis and polyploidy induction by paclitaxel or nocodazole in BL.
-
Resistant cells undergo mitotic catastrophe and develop polyploidy.
-
Lack of Bax/Bak confers resistance and leads to induction of polyploidy in BL.
-
Intact apoptosis response protects from polyploidy as a result of mitotic catastrophe.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornkamm GW (2009) Epstein-Barr virus and its role in the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma: an unresolved issue. Sem Can Biol 19:351–365
Polack A, Hortnagel K, Pajic A, Christoph B, Baier B, Falk M, Mautner J, Geltinger C, Bornkamm GW, Kempkes B (1996) c-myc activation renders proliferation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-transformed cells independent of EBV nuclear antigen 2 and latent membrane protein 1. PNAS 93:10411–10416
Prochownik EV (2008) c-Myc: linking transformation and genomic instability. Curr Mol Med 8:446–458
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
von Haefen C, Wieder T, Gillissen B, Starck L, Graupner V, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2002) Ceramide induces mitochondrial activation and apoptosis via a Bax-dependent pathway in human carcinoma cells. Oncogene 21:4009–4019
Gillissen B, Essmann F, Graupner V, Starck L, Radetzki S, Dorken B, Schulze-Osthoff K, Daniel PT (2003) Induction of cell death by the BH3-only Bcl-2 homolog Nbk/Bik is mediated by an entirely Bax-dependent mitochondrial pathway. EMBO J 22:3580–3590
Gillissen B, Essmann F, Hemmati PG, Richter A, Richter A, Oztop I, Chinnadurai G, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2007) Mcl-1 determines the Bax dependency of Nbk/Bik-induced apoptosis. J Cell Biol 179:701–715
Graupner V, Alexander E, Overkamp T, Rothfuss O, De Laurenzi V, Gillissen BF, Daniel PT, Schulze-Osthoff K, Essmann F (2012) Differential regulation of the proapoptotic multidomain protein Bak by p53 and p73 at the promoter level. Cell Death Differ 18:1130–1139
Daniel PT, Pun KT, Ritschel S, Sturm I, Holler J, Dorken B, Brown R (1999) Expression of the death gene Bik/Nbk promotes sensitivity to drug-induced apoptosis in corticosteroid-resistant T-cell lymphoma and prevents tumor growth in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Blood 94:1100–1107
Zaltsman Y, Shachnai L, Yivgi-Ohana N, Schwarz M, Maryanovich M, Houtkooper RH, Vaz FM, De Leonardis F, Fiermonte G, Palmieri F et al (2010) MTCH2/MIMP is a major facilitator of tBID recruitment to mitochondria. Nat Cell Biol 12:553–562
Krammer PH, Kaminski M, Kiessling M, Gulow K (2007) No life without death. Adv Can Res 97:111–138
Muer A, Overkamp T, Gillissen B, Richter A, Pretzsch T, Milojkovic A, Dorken B, Daniel PT, Hemmati P (2012) p14(ARF)-induced apoptosis in p53 protein-deficient cells is mediated by BH3-only protein-independent derepression of Bak protein through down-regulation of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL proteins. J Biol Chem 287:17343–17352
Strasser A, Cory S, Adams JM (2011) Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J 30:3667–3683
Doucet JP, Hussain A, Al-Rasheed M, Gaidano G, Gutierrez MI, Magrath I, Bhatia K (2004) Differences in the expression of apoptotic proteins in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines: potential models for screening apoptosis-inducing agents. Leuk Lymphoma 45:357–362
Fan S, el-Deiry WS, Bae I, Freeman J, Jondle D, Bhatia K, Fornace AJ Jr, Magrath I, Kohn KW, O'Connor PM (1994) p53 gene mutations are associated with decreased sensitivity of human lymphoma cells to DNA damaging agents. Cancer Res 54:5824–5830
Gutierrez MI, Cherney B, Hussain A, Mostowski H, Tosato G, Magrath I, Bhatia K (1999) Bax is frequently compromised in Burkitt's lymphomas with irreversible resistance to Fas-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res 59:696–703
McIntosh JR (1984) Cell biology. Microtubule catastrophe. Nature 312:196–197
Portugal J, Bataller M, Mansilla S (2009) Cell death pathways in response to antitumor therapy. Tumori 95:409–421
Castedo M, Perfettini JL, Roumier T, Andreau K, Medema R, Kroemer G (2004) Cell death by mitotic catastrophe: a molecular definition. Oncogene 23:2825–2837
Shay JW, Wright WE (2005) Senescence and immortalization: role of telomeres and telomerase. Carcinogenesis 26:867–874
Erenpreisa J, Kalejs M, Cragg MS (2005) Mitotic catastrophe and endomitosis in tumour cells: an evolutionary key to a molecular solution. Cell Biol Int 29:1012–1018
Bhonde MR, Hanski ML, Budczies J, Cao M, Gillissen B, Moorthy D, Simonetta F, Scherubl H, Truss M, Hagemeier C et al (2006) DNA damage-induced expression of p53 suppresses mitotic checkpoint kinase hMps1: the lack of this suppression in p53MUT cells contributes to apoptosis. J Biol Chem 281:8675–8685
Bhonde MR, Hanski ML, Notter M, Gillissen BF, Daniel PT, Zeitz M, Hanski C (2006) Equivalent effect of DNA damage-induced apoptotic cell death or long-term cell cycle arrest on colon carcinoma cell proliferation and tumour growth. Oncogene 25:165–175
Hemmati PG, Normand G, Gillissen B, Wendt J, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2008) Cooperative effect of p21Cip1/WAF-1 and 14-3-3sigma on cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction by p14ARF. Oncogene 27:6707–6719
Hemmati PG, Normand G, Verdoodt B, von Haefen C, Hasenjager A, Guner D, Wendt J, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2005) Loss of p21 disrupts p14 ARF-induced G1 cell cycle arrest but augments p14 ARF-induced apoptosis in human carcinoma cells. Oncogene 24:4114–4128
Normand G, Hemmati PG, Verdoodt B, von Haefen C, Wendt J, Guner D, May E, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2005) p14ARF induces G2 cell cycle arrest in p53- and p21-deficient cells by down-regulating p34cdc2 kinase activity. J Biol Chem 280:7118–7130
Linch DC (2012) Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Br J Haematol 156:693–703
Wieder T, Essmann F, Prokop A, Schmelz K, Schulze-Osthoff K, Beyaert R, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2001) Activation of caspase-8 in drug-induced apoptosis of B-lymphoid cells is independent of CD95/Fas receptor-ligand interaction and occurs downstream of caspase-3. Blood 97:1378–1387
Jabbour AM, Daunt CP, Green BD, Vogel S, Gordon L, Lee RS, Silke N, Pearson RB, Vandenberg CJ, Kelly PN et al (2010) Myeloid progenitor cells lacking p53 exhibit delayed up-regulation of Puma and prolonged survival after cytokine deprivation. Blood 115:344–352
von Haefen C, Wieder T, Essmann F, Schulze-Osthoff K, Dorken B, Daniel PT (2003) Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in BJAB cells proceeds via a death receptor-independent, caspases-3/-8-driven mitochondrial amplification loop. Oncogene 22:2236–2247
Ferry JA (2006) Burkitt's lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Oncologist 11:375–383
Castedo M, Coquelle A, Vivet S, Vitale I, Kauffmann A, Dessen P, Pequignot MO, Casares N, Valent A, Mouhamad S et al (2006) Apoptosis regulation in tetraploid cancer cells. EMBO J 25:2584–2595
Davis FM, Tsao TY, Fowler SK, Rao PN (1983) Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. PNAS 80:2926–2930
Kelly GL, Strasser A (2011) The essential role of evasion from cell death in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 111:39–96
Morizane Y, Honda R, Fukami K, Yasuda H (2005) X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis functions as ubiquitin ligase toward mature caspase-9 and cytosolic Smac/DIABLO. J Biochem 137:125–132
Hecht JL, Aster JC (2000) Molecular biology of Burkitt's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 18:3707–3721
Perkins AS, Friedberg JW (2008) Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Am Soc Hematol Educ Program :341-348
Farrell PJ, Allan GJ, Shanahan F, Vousden KH, Crook T (1991) p53 is frequently mutated in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. EMBO J 10:2879–2887
Gidding CE, Kellie SJ, Kamps WA, de Graaf SS (1999) Vincristine revisited. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 29:267–287
King KL, Cidlowski JA (1995) Cell cycle and apoptosis: common pathways to life and death. J Cell Biochem 58:175–180
Miranda EI, Santana C, Rojas E, Hernandez S, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Garcia-Carranca A (1996) Induced mitotic death of HeLa cells by abnormal expression of c-H-ras. Mutat Res 349:173–182
Erenpreisa J, Kalejs M, Ianzini F, Kosmacek EA, Mackey MA, Emzinsh D, Cragg MS, Ivanov A, Illidge TM (2005) Segregation of genomes in polyploid tumour cells following mitotic catastrophe. Cell Biol Int 29:1005–1011
Eriksson D, Blomberg J, Lindgren T, Lofroth PO, Johansson L, Riklund K, Stigbrand T (2008) Iodine-131 induces mitotic catastrophes and activates apoptotic pathways in HeLa Hep2 cells. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:541–549
Wade M, Allday MJ (2000) Epstein-Barr virus suppresses a G(2)/M checkpoint activated by genotoxins. Mol Cell Biol 20:1344–1360
Jazirehi AR, Bonavida B (2004) Resveratrol modifies the expression of apoptotic regulatory proteins and sensitizes non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and multiple myeloma cell lines to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther 3:71–84
Ibrado AM, Liu L, Bhalla K (1997) Bcl-xL overexpression inhibits progression of molecular events leading to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Res 57:1109–1115
Chu R, Terrano DT, Chambers TC (2012) Cdk1/cyclin B plays a key role in mitotic arrest-induced apoptosis by phosphorylation of Mcl-1, promoting its degradation and freeing Bak from sequestration. Biochem Pharmacol 83(2):199–206
Harley ME, Allan LA, Sanderson HS, Clarke PR (2010) Phosphorylation of Mcl-1 by CDK1-cyclin B1 initiates its Cdc20-dependent destruction during mitotic arrest. EMBO J 29(14):2407–2420
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche José Carreras Leukämiestiftung e.V. to P.T.D. and the Deutsche Krebshilfe-funded MMML (molecular mechanisms in malignant lymphoma) consortium to C.P. and P.T.D. We would like to thank Dr. Georg Bornkamm, Institute of Clinical Molecular Biology and Tumor Genetics, German Research Center for Environmental Health, München, Germany, and Dr. Marina Gutierrez, King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, for the kind gift of Burkitt lymphoma cell lines and Dr. Paul Ekert, Murdoch Children's Research Institute, Royal Children's Hospital, Parkville 3052, Australia, for providing us with murine FDM cells of various genetic backgrounds.
Conflict of interest
All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript. None of the authors has any type of financial interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Cindrilla Chumduri and Bernhard Gillissen contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 522 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chumduri, C., Gillissen, B., Richter, A. et al. Apoptosis resistance, mitotic catastrophe, and loss of ploidy control in Burkitt lymphoma. J Mol Med 93, 559–572 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1242-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1242-2