Abstract
Abnormalities in signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling, especially STAT3 and STAT5, are involved in the oncogenesis of several human cancers, including gastric cancer (GC). However, the downstream targets of STAT3 and STAT5 are not fully identified, and the precise roles and the prognostic value of STAT3 and STAT5 in GC have not been fully characterized. In this study, we used ChIP-on-chip to identify STAT3 and STAT5 target genes on a whole genome scale in AGS cells, a human GC cell line. A total of 2,514 and 1,314 genes were identified as STAT3 and STAT5 target genes, which were mainly related to cell growth, metabolism, differentiation, adhesion, immune response, and stress response. Furthermore, we depleted STAT3 and STAT5 with a small interfering RNA, respectively. Our results demonstrate that STAT3, but not STAT5, is involved in GC cell growth and cell cycle progression through regulation of gene expression, such as Bcl-2, p16ink4a and p21waf1/cip1. Moreover, expression of pSTAT3Tyr705 correlates with TNM stage, differentiation and survival, and is a significant prognostic factor in GC. Therefore, our findings provide novel evidence that STAT3 may be a potential therapeutic target for GC treatment and pSTAT3Tyr705 expression can predict prognosis in GC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bronte-Tinkew DM, Terebiznik M, Franco A, Ang M, Ahn D, Mimuro H, Sasakawa C, Ropeleski MJ, Peek RM Jr, Jones NL (2009) Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated gene A activates the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res 69:632–639
Dalwad H, Krysan K, Heuze-Vourc’h N, Dohadwala M, Elashoff D, Sharma S, Cacalano N, Lichtenstein A, Dubinett S (2005) Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 by interleukin-6 in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:7674–7682
Xiong H, Chen ZF, Liang QC, Du W, Chen HM, Su WY, Chen GQ, Han ZG, Fang JY (2009) Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase induces G2 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells via inhibition of JAK2/STAT3/STAT5 signaling. J Cell Mol Med 13(9B):3668–3679
Liang QC, Xiong H, Zhao ZW, Jia D, Li WX, Qin HZ, Deng JP, Gao L, Zhang H, Gao GD (2009) Inhibition of transcription factor STAT5b suppresses proliferation, induces G1 cell cycle arrest and reduces tumor cell invasion in human glioblastoma multiforme cells. Cancer Lett 273:164–171
Alvarez JV, Greulich H, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Frank DA (2006) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is required for the oncogenic effects of non-small-cell lung cancer-associated mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res 66:3162–3168
Zhang F, Li C, Halfter H, Liu J (2003) Delineating an oncostatin M-activated STAT3 signaling pathway that coordinates the expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation and extracellular matrix deposition of MCF-7 cells. Oncogene 22:894–905
Li H, Zhang Y, Glass A, Zellweger T, Gehan E, Bubendorf L, Gelmann EP, Nevalainen MT (2005) Activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-5 in prostate cancer predicts early recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 11:5863–5868
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, Sun DF, Liang QC, Zhang YJ, Lu R, Chen YX, Fang JY (2008) Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 10:287–297
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium. Nat Genet 25:25–29
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Nakaya A (2002) The KEGG databases at GenomeNet. Nucleic Acids Res 30:42–46
Yi M, Horton JD, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH, Stephens RM (2006) WholePathwayScope: a comprehensive pathway-based analysis tool for high-throughput data. BMC Bioinforma 7:30
Dupuy D, Bertin N, Hidalgo CA, Venkatesan K, Tu D, Lee D, Rosenberg J, Svrzikapa N, Blanc A, Carnec A et al (2007) Genome-scale analysis of in vivo spatiotemporal promoter activity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Biotechnol 25:663–668
Schlitt T, Palin K, Rung J, Dietmann S, Lappe M, Ukkonen E, Brazma A (2003) From gene networks to gene function. Genome Res 13:2568–2576
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K, Nagayasu T, Sekine I (2006) Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 15:1445–1451
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Nagayasu T, Sekine I (2005) Expression of p-STAT3 in human colorectal adenocarcinoma and adenoma; correlation with clinicopathological factors. J Clin Pathol 58:833–838
Faille-Kuyber EH, Kater L, Kooiker CJ, Dorhout Mees EJ (1973) IgA-deposits in cutaneous blood-vessel walls and mesangium in Henoch–Schonlein syndrome. Lancet 1:892–893
Darnell JE Jr (1997) STATs and gene regulation. Science 277:1630–1635
Kim DY, Cha ST, Ahn DH, Kang HY, Kwon CI, Ko KH, Hwang SG, Park PW, Rim KS, Hong SP (2009) STAT3 expression in gastric cancer indicates a poor prognosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:646–651
Akira S (1999) Functional roles of STAT family proteins: lessons from knockout mice. Stem Cells 17:138–146
Coffer PJ, Koenderman L, de Groot RP (2000) The role of STATs in myeloid differentiation and leukemia. Oncogene 19:2511–2522
Calo V, Migliavacca M, Bazan V, Macaluso M, Buscemi M, Gebbia N, Russo A (2003) STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J Cell Physiol 197:157–168
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China 973 program Grant (no. 2010CB5293), National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC, no. 30830055), grants from NSFC (no. 30900757) and Shanghai Rising-Star Program (no. 10QA1404400). The funding had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Special thanks go to Genminix Company for excellent technical assistance in microarray result analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
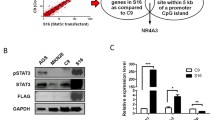
The potential STAT3 and STAT5 target genes from the ChIP-on-chip in AGS cells. The ratio value (column E, blue part) of every gene was calculated by cutting off the value in control antibody group. A total of 2,514 and 1,314 genes were identified as STAT3 and STAT5 target genes, by setting the filter for ratio values of ≥2.0. (PDF 1266 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, H., Du, W., Wang, JL. et al. Constitutive activation of STAT3 is predictive of poor prognosis in human gastric cancer. J Mol Med 90, 1037–1046 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0869-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-012-0869-0