Abstract
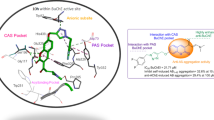
This study describes the synthesis, pharmacological evaluation, including acetylcholinesterase (AChE)/butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) inhibition, amyloid beta (Aβ) antiaggregation, and neuroprotective effects, as well as molecular modeling of novel 2-(4-substituted phenyl)-1H-benzimidazole derivatives. These derivatives were synthesized by cyclization of o-phenylenediamines with sodium hydroxy(4-substituted phenyl)methanesulfonate salts. In vitro studies indicated that the most of the target compounds showed remarkable inhibitory activity against BChE (IC50: 13.60–95.44 µM). Among them, 3d and 3g-i also exhibited high selectivity (SI ≥ 35.7) for BChE with IC50 values 39.56, 13.60, 14.45, and 15.15 µM, respectively. According to the molecular modeling studies, it may be assumed that the compounds are able to reach the catalytic site of BChE but not that of AChE. The compounds showing BChE inhibitory effects were subsequently examined for their Aβ-antiaggregating and neuroprotective activities. Among the compounds, 3d inhibited the Aβ1–40 aggregation and demonstrated significant neuroprotection against H2O2-induced and Aβ1–40-induced cell death. Collectively, compound 3d showed the best multifunctional activity (BChE; IC50 = 39.56 µM, SI > 126; Aβ self-mediated aggregation; 67.78% at 100 μM; H2O2-induced cytotoxicity with cell viability of 98% and Aβ1-40-induced cytotoxicity with cell viability of 127%). All these results suggested that 2-(4-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole (compound 3d) could be a promising multi-target lead candidate against Alzheimer’s disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alp M, Goker AH, Altanlar N (2014) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of novel 2-[4-(1H-benzimidazol-1-yl)phenyl]-1H-benzimidazoles. Turk J Chem 38:152–156
Alpan AS, Gunes HS, Topcu Z (2007) 1H-Benzimidazole derivatives as mammalian DNA topoisomerase I inhibitors. Acta Biochim Pol 54:561–565
Alpan AS, Parlar S, Carlino L, Tarikogullari AH, Alptuzun V, Gunes HS (2013) Synthesis, biological activity and molecular modeling studies on 1H-benzimidazole derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 21:4928–4937
Anand P, Singh B (2013) A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 36:375–399
Bansal Y, Silakari O (2012) The therapeutic journey of benzimidazoles: a review. Bioorg Med Chem 20(21):6208–6236
Brandl M, Weiss MS, Jabs A, Suhnel J, Hilgenfeld R (2001) C-H center dot center dot center dot pi-interactions in proteins. J Mol Biol 307:357–377
Bullock R, Touchon J, Bergman H, Gambina G, He Y, Rapatz G, Nagel J, Lane R (2005) Rivastigmine and donepezil treatment in moderate to moderately-severe Alzheimer’s disease over a 2-year period. Curr Med Res Opin 21:1317–1327
Cheung J, Rudolph MJ, Burshteyn F, Cassidy MS, Gary EN, Love J, Franklin MC, Height JJ (2012) Structures of human acetylcholinesterase in complex with pharmacologically important ligands. J Med Chem 55:10282–10286
Cui M, Ono M, Kimura H, Kawashima H, Liu BL, Saji H (2011) Radioiodinated benzimidazole derivatives as single photon emission computed tomography probes for imaging of beta-amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Nucl Med Biol 38:313–320
Cummings JL (2004) Drug therapy – Alzheimer’s disease. New Engl J Med 351:56–67
Darvesh S, Reid GA (2016) Reduced fibrillar beta-amyloid in subcortical structures in a butyrylcholinesterase-knockout Alzheimer disease mouse model. Chem Biol Interact 259(B):307–312
Dwane S, Durack E, Kiely PA (2013) Optimising parameters for the differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells to study cell adhesion and cell migration. BMC Res Notes 6:366–376
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Giacobini E (2003) Cholinesterases: new roles in brain function and in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 28:515–522
Gouras GK, Olsson TT, Hansson O (2015) Beta amyloid peptides and amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 12(1):3–11
Harada R, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Yoshikawa T, Arai H, Yanai K, Kudo Y (2014) Use of a benzimidazole derivative BF-188 in fluorescence multispectral imaging for selective visualization of tau protein fibrils in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Mol Imaging Biol 16:19–27
Holmes C, Ballard C, Lehmann D, Smith AD, Beaumont H, Day IN, Khan MN, Lovestone S, McCulley M, Morris CM, Munoz DG, O’Brien K, Russ C, Del Ser T, Warden D (2005) Rate of progression of cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease: effect of butyrylcholinesterase K gene variation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:640–643
Huang WJ, Zhang X, Chen WW (2015) Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Rep 4(5):519–522
Jadhav GR, Shaikh MU, Kale RP, Gill CH (2009) Ammonium metavanadate: a novel catalyst for synthesis of 2-substituted benzimidazole derivatives. Chinese Chem Lett 20:292–295
Karran E, Mercken M, Strooper B (2011) The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:698–712
Kim KD, Cho ES, Um HD (2000) Caspase-dependent and -independent events in apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide. Exp Cell Res 257(1):82–88
Loo DT, Copani A, Pike CJ, Whittemore ER, Walencewicz AJ, Cotman CW (1993) Apoptosis is induced by beta-amyloid in cultured central nervous system neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(17):7951–7955
Manev H, Chen H, Dzitoyeva S, Manev R (2011) Cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:315–319
Meciarova M, Toma S, Magdolen P (2003) Ultrasound effect on the aromatic nucleophilic substitution reactions on some haloarenes. Ultrason Sonochem 10:265–270
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1-2):55–63
Muchmore SW, Edmunds JJ, Stewart KD, Hajduk PJ (2010) Cheminformatic tools for medicinal chemists. J Med Chem 53:4830–4841
Mullard A (2017) Alzheimer amyloid hypothesis lives on. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:3–5
Nicolet Y, Lockridge O, Masson P, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Nachon F (2003) Crystal structure of human butyrylcholinesterase and of its complexes with substrate and products. J Biol Chem 278:41141–41147
Oddo S, Caccamo A, Kitazawa M, Tseng BP, LaFerla FM (2003) Amyloid deposition precedes tangle formation in a triple transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:1063–1070
Pajouhesh H, Lenz GR (2005) Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs. NeuroRx 2:541–553
Perry E, Perry R, Blessed G, Tomlinson B (1978) Changes in brain cholinesterases in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol 4:273–277
Reid GA, Darvesh S (2015) Butyrylcholinesterase-knockout reduces brain deposition of fibrillar β-amyloid in an Alzheimer mouse model. Neuroscience 298:424–435
Secci D, Bolasco A, D’Ascenzio M, Sala F, Yáñez M, Carradori S (2012) Conventional and microwave-assisted synthesis of benzimidazole derivatives and their in vitro inhibition of human cyclooxygenase. J Heterocyclic Chem 49:1187–1195
Selkoe DJ, Hardy J (2016) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med 8:595–608
Sun X, Chen WD, Wang YD (2015) β-Amyloid: the key peptide in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Front Pharmacol 6:221–229
Taylor JP, Hardy J, Fischbeck KH (2002) Toxic proteins in neurodegenerative disease. Science 296:1991–1995
Yadav G, Ganguly S (2015) Structure activity relationship (SAR) study of benzimidazole scaffold for different biological activities: a mini-review. Eur J Med Chem 97:419–443
Yiannopoulou KG, Papageorgiou SG (2013) Current and future treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Ther Adv Neurol Disord 6(1):19–33
Yoon YK, Ali MA, Wei AC, Choon TS, Khaw KY, Murugaiyah V, Osman H, Masand VH (2013) Synthesis, characterization, and molecular docking analysis of novel benzimidazole derivatives as cholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorg Chem 49:33–39
Yu Z, Zheng Z, Yang M, Wang L, Tian Y, Wu J, Zhou H, Xu H, Wu Z (2013) Photon-induced intramolecular charge transfer with the influence of D/A group and mode: optical physical properties and bio-imaging. J Mater Chem C 1:7026–7033
Zhu JM, Wu CF, Li XB, Wu GS, Xie S, Hu QN, Deng ZX, Zhu MX, Luo HR, Hong XC (2013) Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling of substituted 2-aminobenzimidazoles as novel inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Bioorg Med Chem 21:4218–4224
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Turkish Scientific Research Institution (TUBITAK, 114S374).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unsal-Tan, O., Ozadali-Sari, K., Ayazgok, B. et al. Novel 2-Arylbenzimidazole derivatives as multi-targeting agents to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Med Chem Res 26, 1506–1515 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1874-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-017-1874-1