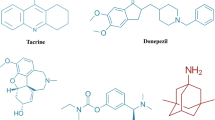
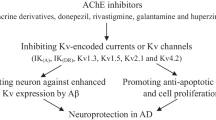
Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by the deficits in the cholinergic system and deposition of beta amyloid (Aβ) in the form of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques. Since the cholinergic system plays an important role in the regulation of learning and memory processes, it has been targetted for the design of anti-Alzheimer’s drugs. Cholinesterase inhibitors enhance cholinergic transmission directly by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) which hydrolyses acetylcholine. Furthermore, it has been also demonstrated that both acetylcholinesterase and butrylcholinesterase (BuChE) play an important role in Aβ-aggregation during the early stages of senile plaque formation. Therefore, AChE and BuChE inhibition have been documented as critical targets for the effective management of AD by an increase in the availability of acetylcholine in the brain regions and decrease in the Aβ deposition. This review discusses the different classes of cholinesterase inhibitors including tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine, galantamine, xanthostigmine, para-aminobenzoic acid, coumarin, flavonoid, and pyrrolo-isoxazole analogues developed for the treatment of AD.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuna-Castroviejo, D., G. Escames, M.I. Rodriguez, and L.C. Lopez. 2007. Melatonin role in the mitochondrial function. Frontiers in Bioscience 12: 947–963.
Alonso, D., I. Dorronsoro, L. Rubio, P. Muñoz, E. García-Palomero, M. Del Monte, A. Bidon-Chanal, M. Orozco, F.J. Luque, A. Castro, M. Medina, and A. Martínez. 2005. Donepezil-tacrine hybrid related derivatives as new dual binding site inhibitors of AChE. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 13: 6588–6597.
Anand, P., and B. Singh. 2012a. Synthesis and evaluation of novel carbamate substituted flavanone derivatives as potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amnestic agents. Medicinal Chemistry Research. doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0162-3.
Anand, P., and B. Singh. 2012b. Synthesis and evaluation of novel 4-[(3H,3aH,6aH)-3-phenyl)-4,6-dioxo-2-phenyldihydro-2H-pyrrolo[3,4-d]isoxazol-(3H,6H,6aH)-yl]benzoic acid derivatives as potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and anti-amnestic agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 20: 521–530.
Andreani, A., A. Cavalli, M. Granaiola, M. Guardigli, A. Leoni, A. Locatelli, R. Morigi, M. Rambaldi, M. Recanatini, and A. Roda. 2001. Synthesis and screening for antiacetylcholinesterase activity of (1-benzyl-4-oxopiperidin-3-ylidene) methylindoles and -pyrroles related to donepezil. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 44: 4011–4014.
Bachurin, S.O. 2003. Medicinal chemistry approaches for the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease. Medicinal Research Reviews 23: 48–88.
Barreiro, E.J., C.A. Camara, H. Verli, L. Brazil-Más, N.G. Castro, W.M. Cintra, Y. Aracava, C.R. Rodrigues, and C.A. Fraga. 2003. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological profile of novel fused pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyridine and pyrazolo[3,4-b][1,8]naphthyridine isosteres: A new class of potent and selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46: 1144–1152.
Bartolini, M., C. Bertucci, V. Cavrini, and V. Andrisano. 2003. beta-Amyloid aggregation induced by human acetylcholinesterase: Inhibition studies. Biochemical Pharmacology 65: 407–416.
Belluti, F., A. Rampa, L. Piazzi, A. Bisi, S. Gobbi, M. Bartolini, V. Andrisano, A. Cavalli, M. Recanatini, and P. Valenti. 2005. Cholinesterase inhibitors: Xanthostigmine derivatives blocking the acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 4444–4456.
Bolognesi, M.L., M. Bartolini, A. Cavalli, V. Andrisano, M. Rosini, A. Minarini, and C. Melchiorre. 2004. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of conformationally restricted rivastigmine analogues. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 47: 5945–5952.
Bolognesi, M.L., V. Andrisano, M. Bartolini, R. Banzi, and C. Melchiorre. 2005. Propidium-based polyamine ligands as potent inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced amyloid-beta aggregation. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 24–27.
Bourne, Y., P. Taylor, Z. Radic, and P. Marchot. 2003. Structural insights into ligand interactions at the acetylcholinesterase peripheral anionic site. EMBO Journal 22: 1–12.
Brühlmann, C., F. Ooms, P.A. Carrupt, B. Testa, M. Catto, F. Leonetti, C. Altomare, and A. Carotti. 2001. Coumarins derivatives as dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 44: 3195–3198.
Campiani, G., C. Fattorusso, S. Butini, A. Gaeta, M. Agnusdei, S. Gemma, M. Persico, B. Catalanotti, L. Savini, V. Nacci, E. Novellino, H.W. Holloway, N.H. Greig, T. Belinskaya, J.M. Fedorko, and A. Saxena. 2005. Development of molecular probes for the identification of extra interaction sites in the mid-gorge and peripheral sites of butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE). Rational design of novel, selective, and highly potent BuChE inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 1919–1929.
Camps, P., X. Formosa, C. Galdeano, T. Gómez, D. Muñoz-Torrero, M. Scarpellini, E. Viayna, A. Badia, M.V. Clos, A. Camins, M. Pallàs, M. Bartolini, F. Mancini, V. Andrisano, J. Estelrich, M. Lizondo, A. Bidon-Chanal, and F.J. Luque. 2008. Novel donepezil- based inhibitors of acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51: 3588–3598.
Cappelli, A., A. Gallelli, M. Manini, M. Anzini, L. Mennuni, F. Makovec, M.C. Menziani, S. Alcaro, F. Ortuso, and S. Vomero. 2005. Further studies on the interaction of the 5-hydroxytryptamine3 (5-HT3) receptor with arylpiperazine ligands. Development of a new 5-HT3 receptor ligand showing potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 3564–3575.
Castro, A., and A. Martinez. 2001. Peripheral and dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Implications in treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 1: 267–272.
Changwong, N., C. Sabphon, K. Ingkaninan, and P. Sawasdee. 2012. Acetyl- and butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitory activities of mansorins and mansonones. Phytotherapy Research 26: 392–396.
Chen, Z., A.J. Xu, R. Li, and E.Q. Wei. 2002. Reversal of scopolamine-induced spatial memory deficits in rats by TAK-147. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 23: 355–360.
Colombres, M., J.P. Sagal, and N.C. Inestrosa. 2004. An overview of the current and novel drugs for Alzheimer’s disease with particular reference to anti-cholinesterase compounds. Current Pharmaceutical Design 10: 3121–3130.
Contreras, J.M., Y.M. Rival, S. Chayer, J.J. Bourguignon, and C.G. Wermuth. 1999. Aminopyridazines as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 42: 730–741.
Contreras, J.M., I. Parrot, W. Sippl, Y.M. Rival, and C.G. Wermuth. 2001. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of a series of 3-[2-(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)ethylamino]pyridazine derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 44: 2707–2718.
Correa-Basurto, J., I.V. Alcántara, L.M. Espinoza-Fonseca, and J.G. Trujillo-Ferrara. 2005. p-Aminobenzoic acid derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 40: 732–735.
De Ferrari, G.V., M.A. Canales, I. Shin, L.M. Weiner, I. Silman, and N.C. Inestrosa. 2001. A structural motif of acetylcholinesterase that promotes amyloid beta-peptide fibril formation. Biochemistry 40: 10447–10457.
Fallarero, A., P. Oinonen, S. Gupta, P. Blom, A. Galkin, C.G. Mohan, and P.M. Vuorela. 2008. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by coumarins: The case of coumarin 106. Pharmacological Research 58: 215–221.
Fang, L., B. Kraus, J. Lehmann, J. Heilmann, Y. Zhang, and M. Decker. 2008. Design and synthesis of tacrine-ferulic acid hybrids as multi-potent anti-Alzheimer drug candidates. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 18: 2905–2909.
Fernández-Bachiller, M.I., C. Pérez, N.E. Campillo, J.A. Páez, G.C. González-Muñoz, P. Usán, E. García-Palomero, M.G. López, M. Villarroya, A.G. García, A. Martínez, and M.I. Rodríguez-Franco. 2009. Tacrine-melatonin hybrids as multifunctional agents for Alzheimer’s disease, with cholinergic, antioxidant, and neuroprotective properties. ChemMedChem 4: 828–841.
Geula, C., and S. Darvesh. 2004. Butyrylcholinesterase, cholinergic neurotransmission and the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Today (Barc) 40: 711–721.
Gottwald, M.D., and R.I. Rozanski. 1999. Rivastigmine, a brain-region selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor for treating Alzheimer’s disease: Review and current status. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 8: 1673–1682.
Guillou, C., A. Mary, D.Z. Renko, E. Gras, and C. Thal. 2000. Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of alkylene linked bis-galanthamine and galanthamine-galanthaminium salts. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 10: 637–639.
Hamulakova, S., L. Janovec, M. Hrabinova, P. Kristian, K. Kuca, M. Banasova, and J. Imrich. 2012. Synthesis, design and biological evaluation of novel highly potent tacrine congeners for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 55: 23–31.
Harel, M., I. Schalk, L. Ehret-Sabatier, F. Bouet, M. Goeldner, C. Hirth, P.H. Axelsen, I. Silman, and J.L. Sussman. 1993. Quaternary ligand binding to aromatic residues in the active-site gorge of acetylcholinesterase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90: 9031–9035.
Harvey, A.L. 1995. The pharmacology of galanthamine and its analogues. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 68: 113–128.
Heilmann, J., I. Calis, H. Kirmizibekmez, W. Schühly, S. Harput, and O. Sticher. 2000. Radical scavenger activity of phenylethanoid glycosides in FMLP stimulated human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: Structure-activity relationships. Planta Medica 66: 746–748.
Herlem, D., M.T. Martin, C. Thal, and C. Guillou. 2003. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of open D-Ring galanthamine analogues. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 13: 2389–2391.
Holmquist, L., G. Stuchbury, K. Berbaum, S. Muscat, S. Young, K. Hager, J. Engel, and G. Münch. 2007. Lipoic acid as a novel treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 113: 154–164.
Howlett, D.R., A.R. George, D.E. Owen, R.V. Ward, and R.E. Markwell. 1999. Common structural features determine the effectiveness of carvedilol, daunomycin and rolitetracycline as inhibitors of Alzheimer beta-amyloid fibril formation. The Biochemical Journal 343(Pt 2): 419–423.
Huang, L., T. Su, W. Shan, Z. Luo, Y. Sun, F. He, and X. Li. 2012. Inhibition of cholinesterase activity and amyloid aggregation by berberine-phenyl-benzoheterocyclic and tacrine-phenyl-benzoheterocyclic hybrids. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 20: 3038–3048.
Ismail, M.M., M.M. Kamel, L.W. Mohamed, S.I. Faggal, and M.A. Galal. 2012a. Synthesis and biological evaluation of thiophene derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Molecules 17: 7217–7231.
Ismail, M.M., M.M. Kamel, L.W. Mohamed, and S.I. Faggal. 2012b. Synthesis of new indole derivatives structurally related to donepezil and their biological evaluation as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Molecules 17: 4811–4823.
Jia, P., R. Sheng, J. Zhang, L. Fang, Q. He, B. Yang, and Y. Hu. 2009. Design, synthesis and evaluation of galanthamine derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 44: 772–784.
Jung, M., and M. Park. 2007. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by flavonoids from Agrimonia pilosa. Molecules 12: 2130–2139.
Katalinić, M., G. Rusak, J. Domaćinović Barović, G. Sinko, D. Jelić, R. Antolović, and Z. Kovarik. 2010. Structural aspects of flavonoids as inhibitors of human butyrylcholinesterase. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 45: 186–192.
Kato, K., H. Hayako, Y. Ishihara, S. Marui, M. Iwane, and M. Miyamoto. 1999. TAK-147, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, increases choline acetyltransferase activity in cultured rat septal cholinergic neurons. Neuroscience Letters 260: 5–8.
Kim, J.Y., W.S. Lee, Y.S. Kim, M.J. Curtis-Long, B.W. Lee, Y.B. Ryu, and K.H. Park. 2011. Isolation of cholinesterase-inhibiting flavonoids from Morus lhou. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry 59: 4589–4596.
Knapp, M.J., D.S. Knopman, P.R. Solomon, W.W. Pendlebury, C.S. Davis, and S.I. Gracon. 1994. A 30-week randomized controlled trial of high-dose tacrine in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. The Tacrine Study Group. JAMA 271: 985–991.
Kryger, G., I. Silman, and J.L. Sussman. 1999. Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept): Implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Structure 7: 297–307.
Ladner, C.J., and J.M. Lee. 1998. Pharmacological drug treatment of Alzheimer disease: The cholinergic hypothesis revisited. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 57: 719–731.
León, R., J. Marco-Contelles, A.G. García, and M. Villarroya. 2005. Synthesis, acetylcholinesterase inhibition and neuroprotective activity of new tacrine analogues. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 13: 1167–1175.
León, R., C. De los Ríos, J. Marco-Contelles, O. Huertas, X. Barril, F.J. Luque, M.G. López, A.G. García, and M. Villarroya. 2008. New tacrine-dihydropyridine hybrids that inhibit acetylcholinesterase, calcium entry, and exhibit neuroprotection properties. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 16: 7759–7769.
Leonetti, F., M. Catto, O. Nicolotti, L. Pisani, A. Cappa, A. Stefanachi, and A. Carotti. 2008. Homo-and hetero-bivalent edrophonium-like ammonium salts as highly potent, dual binding site AChE inhibitors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 16: 7450–7456.
Lin, G., C.Y. Lai, and W.C. Liao. 1999. Molecular recognition by acetylcholinesterase at the peripheral anionic site: Structure-activity relationships for inhibitions by aryl carbamates. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 7: 2683–2689.
Lin, G., H.C. Tseng, A.C. Chio, T.M. Tseng, and B.Y. Tsai. 2005. A rate determining step change in the pre-steady state of acetylcholinesterase inhibitions by 1, n-alkane-di-N-butylcarbamates. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 15: 951–955.
Liu, J., W. Qu, J.E. Saavedra, and M.P. Waalkes. 2004. The nitric oxide donor, O2-vinyl 1-(pyrrolidin-1-l)diazen-1-ium-1,2-diolate (V-PYRRO/NO), protects against cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 310: 18–24.
Malinski, T. 2007. Nitric oxide and nitroxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimers Disease 11: 207–218.
Mao, F., L. Huang, Z. Luo, A. Liu, C. Lu, Z. Xie, and X. Li. 2012. o-Hydroxyl- or o-amino benzylamine-tacrine hybrids: Multifunctional biometals chelators, antioxidants, and inhibitors of cholinesterase activity and amyloid-b aggregation. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 20: 5884–5892.
Marco, J.L., C. De los Ríos, M.C. Carreiras, J.E. Baños, A. Badía, and N.M. Vivas. 2001. Synthesis and acetylcholinesterase/butyrylcholinesterase inhibition activity of new tacrine-like analogues. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 9: 727–732.
Marco, J.L., C. De los Ríos, A.G. García, M. Villarroya, M.C. Carreiras, C. Martins, A. Eleutério, A. Morreale, M. Orozco, and F.J. Luque. 2004. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modelling of diversely functionalized heterocyclic derivatives as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase/butyrylcholinesterase and modulators of Ca2+ channels and nicotinic receptors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 12: 2199–2218.
Marco-Contelles, J., R. León, C. De Los Ríos, A. Guglietta, J. Terencio, M.G. López, A.G. García, and M. Villarroya. 2006. Novel multipotent tacrine-dihydropyridine hybrids with improved acetylcholinesterase inhibitory and neuroprotective activities as potential drugs for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 49: 7607–7610.
Marco-Contelles, J., R. León, C. De los Ríos, A. Samadi, M. Bartolini, V. Andrisano, O. Huertas, X. Barril, F.J. Luque, M.I. Rodríguez-Franco, B. López, M.G. López, A.G. García, C. Carreiras Mdo, and M. Villarroya. 2009. Tacripyrines, the first tacrine-dihydropyridine hybrids, as multitarget-directed ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 52: 2724–2732.
Martinez, A., E. Fernandez, A. Castro, S. Conde, I. Rodriguez-Franco, J.E. Baños, and A. Badia. 2000. N-Benzylpiperidine derivatives of 1,2,4-thiadiazolidinone as new acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 35: 913–922.
Mary, A., D.Z. Renko, C. Guillou, and C. Thal. 1998. Potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of bis-interacting ligands in the galanthamine series. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 6: 1835–1850.
Masilamoni, J.G., E.P. Jesudason, S. Dhandayuthapani, B.S. Ashok, S. Vignesh, W.C. Jebaraj, S.F. Paul, and R. Jayakumar. 2008. The neuroprotective role of melatonin against amyloid beta peptide injected mice. Free Radical Research 42: 661–673.
Melchiorre, C., V. Andrisano, M.L. Bolognesi, R. Budriesi, A. Cavalli, V. Cavrini, M. Rosini, V. Tumiatti, and M. Recanatini. 1998. Acetylcholinesterase noncovalent inhibitors based on a polyamine backbone for potential use against Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 41: 4186–4189.
Meng, F.C., F. Mao, W.J. Shan, F. Qin, L. Huang, and X.S. Li. 2012. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of indanone derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and metal-chelating agents. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 22: 4462–4466.
Mesulam, M.M., A. Guillozet, P. Shaw, A. Levey, E.G. Duysen, and O. Lockridge. 2002. Acetylcholinesterase knockouts establish central cholinergic pathways and can use butyrylcholinesterase to hydrolyze acetylcholine. Neuroscience 110: 627–639.
Muñoz-Ruiz, P., L. Rubio, E. García-Palomero, I. Dorronsoro, M. del Monte-Millán, R. Valenzuela, P. Usán, C. de Austria, M. Bartolini, V. Andrisano, A. Bidon-Chanal, M. Orozco, F.J. Luque, M. Medina, and A. Martínez. 2005. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: New disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 7223–7233.
Musial, A., and B. Malawska. 2006. The fifth multidisciplinary conference on drug research, Warszawa, Vol. 77.
Mustazza, C., A. Borioni, M.R. Del Giudice, F. Gatta, R. Ferretti, A. Meneguz, M.T. Volpe, and P. Lorenzini. 2002. Synthesis and cholinesterase activity of phenylcarbamates related to Rivastigmine, a therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 37: 91–109.
Nagabukuro, H., S. Okanishi, and T. Doi. 2004. Effects of TAK-802, a novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, and various cholinomimetics on the urodynamic characteristics in anesthetized guinea pigs. European Journal of Pharmacology 494: 225–232.
Pang, Y.P., P. Quiram, T. Jelacic, F. Hong, and S. Brimijoin. 1996. Highly potent, selective, and low cost bis-tetrahydroaminacrine inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Steps toward novel drugs for treating Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry 271: 23646–23649.
Petroianu, G., K. Arafat, B.C. Sasse, and H. Stark. 2006. Multiple enzyme inhibitions by histamine H3 receptor antagonists as potential procognitive agents. Die Pharmazie 61: 179–182.
Piazzi, L., A. Rampa, A. Bisi, S. Gobbi, F. Belluti, A. Cavalli, M. Bartolini, V. Andrisano, P. Valenti, and M. Recanatini. 2003. 3-(4-[[Benzyl(methyl)amino]methyl]phenyl)-6,7-dimethoxy-2H-2-chromenone (AP2238) inhibits both acetylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation: A dual function lead for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46: 2279–2282.
Piazzi, L., F. Belluti, A. Bisi, S. Gobbi, S. Rizzo, M. Bartolini, V. Andrisano, M. Recanatini, and A. Rampa. 2007a. Cholinesterase inhibitors: SAR and enzyme inhibitory activity of 3-[omega-(benzylmethylamino)alkoxy]xanthen-9-ones. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 15: 575–585.
Piazzi, L., A. Cavalli, F. Belluti, A. Bisi, S. Gobbi, S. Rizzo, M. Bartolini, V. Andrisano, M. Recanatini, and A. Rampa. 2007b. Extensive SAR and computational studies of 3-{4-[(benzylmethylamino)methyl]phenyl}-6,7-dimethoxy-2H-2-chromenone (AP2238) derivatives. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 50: 4250–4254.
Piazzi, L., A. Cavalli, F. Colizzi, F. Belluti, M. Bartolini, F. Mancini, M. Recanatini, V. Andrisano, and A. Rampa. 2008. Multi-target-directed coumarin derivatives: hAChE and BACE1 inhibitors as potential anti-Alzheimer compounds. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 18: 423–426.
Pisani, L., M. Catto, I. Giangreco, F. Leonetti, O. Nicolotti, A. Stefanachi, S. Cellamare, and A. Carotti. 2010. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of coumarin derivatives tethered to an edrophonium-like fragment as highly potent and selective dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. ChemMedChem 5: 1616–1630.
Radić, Z., and P. Taylor. 1999. The influence of peripheral site ligands on the reaction of symmetric and chiral organophosphates with wildtype and mutant acetylcholinesterases. Chemico-Biological Interactions 119–120: 111–117.
Radić, Z., and P. Taylor. 2001. Peripheral site ligands accelerate inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by neutral organophosphates. Journal of Applied Toxicology 21(Suppl 1): S13–S14.
Rees, T., P.I. Hammond, H. Soreq, S. Younkin, and S. Brimijoin. 2003. Acetylcholinesterase promotes beta-amyloid plaques in cerebral cortex. Neurobiology of Aging 24: 777–787.
Richetti, S.K., M. Blank, K.M. Capiotti, A.L. Piato, M.R. Bogo, M.R. Vianna, and C.D. Bonan. 2011. Quercetin and rutin prevent scopolamine-induced memory impairment in zebrafish. Behavioural Brain Research 217: 10–15.
Rodríguez-Franco, M.I., M.I. Fernández-Bachiller, C. Pérez, B. Hernández-Ledesma, and B. Bartolomé. 2006. Novel tacrine-melatonin hybrids as dual-acting drugs for Alzheimer disease, with improved acetylcholinesterase inhibitory and antioxidant properties. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 49: 459–462.
Rosini, M., V. Andrisano, M. Bartolini, M.L. Bolognesi, P. Hrelia, A. Minarini, A. Tarozzi, and C. Melchiorre. 2005. Rational approach to discover multipotent anti-Alzheimer drugs. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48: 360–363.
Rosini, M., E. Simoni, M. Bartolini, A. Cavalli, L. Ceccarini, N. Pascu, D.W. McClymont, A. Tarozzi, M.L. Bolognesi, A. Minarini, V. Tumiatti, V. Andrisano, I.R. Mellor, and C. Melchiorre. 2008. Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, beta-amyloid aggregation, and NMDA receptors in Alzheimer’s disease: A promising direction for the multi-target-directed ligands gold rush. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51: 4381–4384.
Savini, L., G. Campiani, A. Gaeta, C. Pellerano, C. Fattorusso, L. Chiasserini, J.M. Fedorko, and A. Saxena. 2001. Novel and potent tacrine-related hetero- and homobivalent ligands for acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 11: 1779–1782.
Savini, L., A. Gaeta, C. Fattorusso, B. Catalanotti, G. Campiani, L. Chiasserini, C. Pellerano, E. Novellino, D. McKissic, and A. Saxena. 2003. Specific targeting of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase recognition sites. Rational design of novel, selective, and highly potent cholinesterase inhibitors. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46: 1–4.
Schalk, I., L. Ehret-Sabatier, Y. Le Feuvre, S. Bon, J. Massoulie, and M. Goeldner. 1995. 6-Coumarin diazonium salt: a specific affinity label of the Torpedo acetylcholinesterase peripheral site. Molecular Pharmacology 48: 1063–1067.
Selkoe, D.J. 2002. Deciphering the genesis and fate of amyloid beta-protein yields novel therapies for Alzheimer disease. Journal of Clinical Investigatio 110: 1375–1381.
Shao, D., C. Zou, C. Luo, X. Tang, and Y. Li. 2004. Synthesis and evaluation of tacrine-E2020 hybrids as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 14: 4639–4642.
Shen, Q., Q. Peng, J. Shao, X. Liu, Z. Huang, X. Pu, L. Ma, Y.M. Li, A.S. Chan, and L. Gu. 2005. Synthesis and biological evaluation of functionalized coumarins as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 40: 1307–1315.
Shen, Y., J. Zhang, R. Sheng, X. Dong, Q. He, B. Yang, and Y. Hu. 2009. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel flavonoid derivatives as dual binding acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry 24: 372–380.
Sheng, R., X. Lin, J. Li, Y. Jiang, Z. Shang, and Y. Hu. 2005. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of 2-phenoxy-indan-1-one derivatives as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 15: 3834–3837.
Sheng, R., X. Lin, J. Zhang, K.S. Chol, W. Huang, B. Yang, Q. He, and Y. Hu. 2009. Design, synthesis and evaluation of flavonoid derivatives as potent AChE inhibitors. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 17: 6692–6698.
Sippl, W., J.M. Contreras, I. Parrot, Y.M. Rival, and C.G. Wermuth. 2001. Structure-based 3D QSAR and design of novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design 15: 395–410.
Sobrado, M., M.G. López, F. Carceller, A.G. García, and J.M. Roda. 2003. Combined nimodipine and citicoline reduce infarct size, attenuate apoptosis and increase bcl-2 expression after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 118: 107–113.
Sterling, J., Y. Herzig, T. Goren, N. Finkelstein, D. Lerner, W. Goldenberg, I. Miskolczi, S. Molnar, F. Rantal, T. Tamas, G. Toth, A. Zagyva, A. Zekany, J. Finberg, G. Lavian, A. Gross, R. Friedman, M. Razin, W. Huang, B. Krais, M. Chorev, M.B. Youdim, and M. Weinstock. 2002. Novel dual inhibitors of AChE and MAO derived from hydroxy aminoindan and phenethylamine as potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 45: 5260–5279.
Thatcher, G.R., B.M. Bennett, and J.N. Reynolds. 2005. Nitric oxide mimetic molecules as therapeutic agents in Alzheimer’s disease. Current Alzheimer Research 2: 171–182.
Thomsen, T., and H. Kewitz. 1990. Selective inhibition of human acetylcholinesterase by galanthamine in vitro and in vivo. Life Sciences 46: 1553–1558.
Thomsen, T., U. Bickel, J.P. Fischer, and H. Kewitz. 1990. Stereoselectivity of cholinesterase inhibition by galanthamine and tolerance in humans. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 39: 603–605.
Toda, N., K. Tago, S. Marumoto, K. Takami, M. Ori, N. Yamada, K. Koyama, S. Naruto, K. Abe, R. Yamazaki, T. Hara, A. Aoyagi, Y. Abe, T. Kaneko, and H. Kogen. 2003. A conformational restriction approach to the development of dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and serotonin transporter as potential agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 11: 4389–4415.
Tomas-Zapico, C., and A. Coto-Montes. 2005. A proposed mechanism to explain the stimulatory effect of melatonin on antioxidative enzymes. Journal of Pineal Research 39: 99–104.
Trujillo-Ferrara, J., L. Montoya Cano, and M. Espinoza-Fonseca. 2003a. Synthesis, anticholinesterase activity and structure-activity relationships of m-Aminobenzoic acid derivatives. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 13: 1825–1827.
Trujillo-Ferrara, J., I. Vázquez, J. Espinosa, R. Santillan, N. Farfán, and H. Höpfl. 2003b. Reversible and irreversible inhibitory activity of succinic and maleic acid derivatives on acetylcholinesterase. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 18: 313–322.
Ucar, G., N. Gokhan, A. Yesilada, and A.A. Bilgin. 2005. 1-N-Substituted thiocarbamoyl-3-phenyl-5-thienyl-2-pyrazolines: A novel cholinesterase and selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitors for the treatment of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. Neuroscience Letters 382: 327–331.
Vidaluc, J.L., F. Calmel, D. Bigg, E. Carilla, A. Stenger, P. Chopin, and M. Briley. 1994. Novel [2-(4-piperidinyl)ethyl](thio)ureas: Synthesis and antiacetylcholinesterase activity. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 37: 689–695.
Villalobos, A., J.F. Blake, C.K. Biggers, T.W. Butler, D.S. Chapin, Y.L. Chen, J.L. Ives, S.B. Jones, D.R. Liston, A.A. Nagel, D.M. Nasan, J.A. Nielson, I.A. Shalaby, and W.F. White. 1994. Novel benzisoxazole derivatives as potent and selective inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 37: 2721–2734.
Villalobos, A., T.W. Butler, D.S. Chapin, Y.L. Chen, S.B. DeMattos, J.L. Ives, S.B. Jones, D.R. Liston, A.A. Nagel, D.M. Nason, J.A. Nielson, A.D. Ramirez, I.A. Shalaby, and W.F. White. 1995. 5,7-dihydro-3-[2-[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6H-pyrrolo[3,2-f]-1,2 benzisoxazol-6-one: a potent and centrally-selective inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase with an improved margin of safety. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 38: 2802–2808.
Watkins, P.B., H.J. Zimmerman, M.J. Knapp, S.I. Gracon, and K.W. Lewis. 1994. Hepatotoxic effects of tacrine administration in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA 271: 992–998.
Winker, M.A. 1994. Tacrine for Alzheimer’s disease. Which patient, what dose? JAMA 271: 1023–1024.
Wu, C.R., C.L. Chang, P.Y. Hsieh, L.W. Lin, and H. Ching. 2007. Psoralen and isopsoralen, two coumarins of Psoraleae Fructus, can alleviate scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Planta Medica 73: 275–278.
Yan, J.J., J.Y. Cho, H.S. Kim, K.L. Kim, J.S. Jung, S.O. Huh, H.W. Suh, Y.H. Kim, and D.K. Song. 2001. Protection against beta-amyloid peptide toxicity in vivo with long-term administration of ferulic acid. British Journal of Pharmacology 133: 89–96.
Zafrilla, P., J. Mulero, J.M. Xandri, E. Santo, G. Caravaca, and J.M. Morillas. 2006. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer patients in different stages of the disease. Current Medicinal Chemistry 13: 1075–1083.
Zhou, X., X.B. Wang, T. Wang, and L.Y. Kong. 2008. Design, synthesis, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of novel coumarin analogues. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 16: 8011–8021.
Acknowledgments
The authors duly acknowledge the financial support from UGC New Delhi, India, through the research scheme no. 39-716/2010 (SR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand, P., Singh, B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 375–399 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0036-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0036-3