Abstract
In this study, the antibacterial, cytotoxic and antiproliferative activities of novel thiosemicarbazide derivatives were assessed. Our results demonstrated that some of the novel compounds possess good antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus epidermidis, Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguinis and are only slightly cytotoxic; thus, they exhibit an excellent therapeutic index, which is higher than that of ethacridine lactate. Moreover, our data showed that compounds 2 and 4 have an antiproliferative activity against human breast adenocarcinoma and human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. We expect that the novel thiosemicarbazide derivatives can be used as agents for treatment of dental caries and also for chemotherapy support.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
For many years, new drugs of an interesting structure, unknown molecular target, low toxicity and a high therapeutic index have been looked for. This is due to the impossibility of treating many serious diseases, such as bacterial infections or cancer. For a few years, the attention of researchers has been focused on thiosemicarbazide derivatives, which were investigated as a pharmacophore for antimicrobial and anticancer activity (Salgın-Gökşen et al., 2007). In vitro screening of some thiosemicarbazides demonstrated activities against Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae (recultured), methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Sheikly et al., 2012; Umadevi et al., 2012; Patel et al., 2014; Tan et al., 2012). Many of the compounds showed a good antibacterial activity against K. pneumoniae (Alagarsamy et al., 2010) and S. aureus in comparison with the standard drug—ciprofloxacin (Rane et al., 2014). Additionally, thiosemicarbazides are one of the most promising biologically active compounds which can be used in cancer treatment (Arora et al., 2014; Mohsen et al., 1981). These derivatives have been effectively used against a number of carcinoma cell lines (Perković et al., 2012; Bhata et al., 2008; Malki et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2011). It has been found that thiosemicarbazide derivatives demonstrated cytotoxic and antiproliferative activity against HeLa, HepG2, MDA-MB-231 and HT-29 cell lines (Mavrova et al., 2014).
In this study, we synthesized new thiosemicarbazide derivatives and investigated their antibacterial, cytotoxic and antiproliferative properties. We expected the presence of the pyridine ring to significantly affect the biological activity of the tested derivatives. Additionally, because the literature lacks information about the effectiveness of thiosemicarbazide derivatives against oral bacteria, we decided to perform in vitro tests against Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sanguinis. It is extremely important because bacterial infections co-occurring with dental caries may be the cause of chronic diseases such as endocarditis, myocardial infarction (Cognasse et al., 2014; Kerrigan et al., 2002) and cancer, for example, pancreatic and gastrointestinal cancer (Meurman, 2010). It is worth highlighting that cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy often suffer from oral complications.
Results and discussion
Chemistry
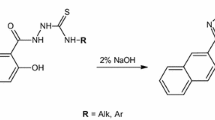
The 1-pyridinecarbonyl-4-substituted thiosemicarbazide derivatives (1–10) were prepared by the reactions of 2-, 3- or 4-pyridine carboxylic acid hydrazide with isothiocyanates. The reaction was carried out in methanol as solvent and was refluxed for 30 min. The synthesis of all compounds was accomplished using the reaction illustrated in Scheme 1.
Compounds 9 and 10 were obtained earlier (Byung et al., 2004; Goldfarb, 2009). According to the Chemical Abstracts Service (SciFinder), some of the compounds (1–4 and 7) have the CAS number, but there is no method synthesis and references.
The structures of obtained compounds were confirmed by spectral analysis (1H, 13C NMR, IR and MS). For compound 2 was performed X-ray diffraction analysis.
Figure 1 shows that this compound crystallizes in the triclinic P-1 space group. The molecule of compound 2 has an extended but not planar conformation with the dihedral angle of 47° between the mean planes of aryl rings. In this compound, molecules interact through two N–H…O hydrogen bonds (d N1…O1 = 2.860(3) Å, ∠N1–H1…O1 = 153(4)° and dN2…O1 = 2.800(4) Å, ∠N2–H2…O1 = 141(4)°) forming dimers. Between the chlorophenyl rings, there is a π…π interaction with a distance between the ring centroids of 3.728(4) Å. The molecules stack in columns along the a axis (Fig. 2).
Antibacterial activity evaluation
All synthesized compounds were initially screened for their potential in vitro antibacterial activity using the agar dilution technique. It was found that seven out of ten thiosemicarbazide derivatives (1, 2, 4–7, 10) effectively inhibited some of the tested strains (Table 1).
Two thiosemicarbazides (1, 4) showed potential activity against all tested aerobic Gram-positive, aerobic Gram-negative and microaerobic Gram-positive bacterial strains. Additionally, zones of bacterial growth inhibition of some compounds were higher compared with CLX and ethacridine lactate. Only cefepime was characterized by large zones of inhibition (29–38 mm) in comparison with thiosemicarbazide derivatives. The detailed in vitro antibacterial activity of the potentially active compounds was later determined using the broth microdilution method on the basis of minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC). Six of the compounds (especially 1, 2, 4, but also 5, 6, 10) had a potential activity against aerobic Gram-positive bacteria (MIC = 15.6–500 μg/mL). The antimicrobial activity of derivatives 1, 2 and 4 against these bacteria was greater or similar to the activity of the control ethacridine lactate. The same compounds (1, 2, 4, 5 and 6) were also found to effectively inhibit the growth of Gram-negative E. coli at a concentration between 62 and 125 μg/mL. The growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa was moderately inhibited only by compounds 1 and 4 (MIC = 500 μg/mL for both) (Table 2).
The thiosemicarbazide derivatives (1, 2, 4, 5) showed significant activity (MIC = 7.81–500 μg/mL) against the tested pathogenic microaerobic bacteria (causing dental caries). The strongest antibacterial properties were exhibited by compound 4, whose MIC was 7.81 μg/mL against S. sanguinis and 31.25 μg/mL against S. mutans, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus spp. Substance 6 also showed significant activity against the pathogenic oral bacteria S. sanguinis, S. mutans but simultaneously did not limit the growth of the probiotic dental flora: L. acidophilus, Lactobacillus spp. These data suggest the possibility of using compounds especially 6 and 4 as well as 1 and 2 in the treatment of caries (Table 2). It is worth noting that among the tested pyridine derivatives, compounds 4 and 5 showed greater or equal activity against S. mutans and S. sanguinis, and compound 6 against S. sanguinis, than the commonly used antiseptic ethacridine lactate. Additionally, the activity of compound 4 against S. sanguinis was equal to that of chlorhexidine (CLX) (MIC = 7.81 μg/mL). CLX is an antiseptic drug used in the prophylaxis and treatment of dental caries (Autio-Gold 2008). However, the in vitro activity of the newly synthesized compounds against other tested bacterial strains was found to be lower compared to the controls (Cefepime, CLX and ethacridine lactate).
Cytotoxic activity evaluation
The synthesized compounds and the reference antibacterial agents were evaluated for the in vitro cytotoxic activity against the BJ cell line (normal human skin fibroblasts) using the MTT assay. The calculated response parameter was CC50, which corresponds to the concentration required for a 50 % reduction of cell viability. The in vitro cytotoxic activity of the synthesized compounds and the reference antibacterial agents is summarized in Fig. 3.
In the cytotoxic study, the novel thiosemicarbazide derivatives showed significant differences in cytotoxicity. The CC50 values of the synthesized compounds ranged from 19.5 to 917.4 μg/mL. Among all tested compounds, 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (4) exhibited the highest cytotoxic activity with a CC50 value of 19.5 μg/mL. Nevertheless, compound 4 showed lower cytotoxicity than the two reference antibacterial agents (CLX and ethacridine lactate), whose CC50 values were 8.46 μg/mL and 6.88 μg/mL, respectively. It is worth noting that 4-(4-methylthiophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (6) only slightly decreased the BJ cell viability with a CC50 value of 917.4 μg/mL. This result indicated that compound 6 showed the lowest cytotoxic activity in comparison with both the tested thiosemicarbazide derivatives and the reference antibacterial agents. Most interestingly, 4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (7 with a CC50 of 88.3 μg/mL) significantly decreased cell viability compared to compound 6. It was not possible to calculate the CC50 value for cefepime as it did not reduce cell viability by 50 % at the highest tested concentration of 1500 μg/mL (data not shown). It is widely known that all drugs applicable in the treatment of bacterial infections should exhibit high antibacterial efficiency and low toxicity toward human cells. Thus, many researchers claim that the profile of in vitro cytotoxicity of antibacterial agents may be characterized by the CC50/MIC ratio (Kashyap et al., 2012; Panchal et al., 2009; Zoraghi et al., 2011). For this reason, in the present study, we attempted to evaluate the in vitro therapeutic potential of novel thiosemicarbazide derivatives and compared them to the reference antibacterial agents (Table 3).
The TI values below 1 obtained by the tested substances correspond to the lack of therapeutic safety. Among the synthesized compounds, derivatives 1, 6 and 10 showed the highest values of therapeutic index. Compound 6 exhibited the in vitro therapeutic potential against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. coli and, which is important, against S. mutans and S. sanguinis, with the TI values of 3.67, 1.83, 14.68, 3.67 and 58.7, respectively. The essential observation is that the in vitro therapeutic indices of compound 6 were approximately 4–133 times higher than the in vitro TI values of ethacridine lactate and 58 times higher than the TI value obtained by CLX against S. mutans. Compound 1 also showed high in vitro TI values (6.82, 13.7, 3.41, 6.83 against S. aureus, S. epidermidis, E. coli and L. species, respectively). Additionally, the TI values of compound 10 against S. aureus, S. epidermidis and S. mutans were greater than those of compound 1. Nevertheless, among all the tested agents, CLX exhibited the highest in vitro TI values. It should be noted that antibacterial agents which possess a value of therapeutic index higher than 10 can be administered to perform in vivo evaluation (Kashyap et al., 2012; Ghareb et al., 2012). Our two newly synthesized compounds (1 and 6) had antibacterial activity and exhibited excellent TI values higher than 10 against some bacterial strains.
Antiproliferative activity evaluation
The synthesized compounds were also evaluated for in vitro antiproliferative activity against various cell lines, i.e., BJ (normal human skin fibroblasts), HepG2 (human hepatocellular carcinoma) and MCF-7 (human breast adenocarcinoma). In order to evaluate cell proliferation, the cells were treated with compounds at concentrations of 0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 25, 50, 100 and 200 µg/mL for 96 h. Among the investigated compounds, only two (2 and 4) exhibited antiproliferative activity. Both compounds strongly decreased the BJ, HepG2 and MCF-7 cell proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 4).
Antiproliferative activity of the synthesized compounds against normal human skin fibroblasts (a), human hepatocellular carcinoma (b) and human breast adenocarcinoma (c). The results were expressed as mean values ± SEM from three independent experiments. The IC50 values were presented as mean values ± SD.* Statistical significance obtained at p < 0.01 compared to the control
The results were expressed as mean values ±SEM from three independent experiments. The IC50 values were presented as mean values ±SD. Statistical significance was obtained at p < 0.01 compared to the control. In the case of normal human cell line (BJ), compound 4 decreased cell proliferation more potently than compound 2. The statistical significance for compound 4 against BJ cells was even obtained at 0.1 μg/mL (Fig. 4a).
Nevertheless, it should be noted that compound 4 suppressed the HepG2 and MCF-7 cell proliferation more effectively than compound 2, with IC50 of 2.09 µg/mL (6.12 µM) and 8.63 µg/mL (25.3 µM), respectively (Fig. 4b, c).
Therefore, the IC50 value of compound 4 against the MCF-7 cell line was approximately two times lower than the IC50 value of compound 2. On the other hand, compound 2 suppressed cell division of hepatocellular carcinoma slightly more potently than that of normal skin fibroblasts. The most pronounced effect was observed with 10 μg/mL of compound 2, which reduced cell proliferation to 32 % (BJ) and to 18.9 % (HepG2) compared to the control (Fig. 4a, b). Thus, these data showed that compound 2 at 10 µg/mL is more effective against tumor than normal cells. According to the available literature data, our compounds exhibited a very high antiproliferative potential. The diarylthiosemicarbazide derivatives containing urea group and pyridine group at the para position, which also occur in the structure of our compounds, exhibited various antiproliferative activities against alveolar epithelial, lung and colorectal cell lines. After a 72-h incubation, the IC50 values of these compounds ranged from 1.8 to 82.4 μmol (Xin et al., 2013). Moreover, Ghareb and colleagues reported that the thiosemicarbazide and semicarbazide derivatives of benzimidazole hydrazides with hydrazine hydrate afforded N3-substituted-5-((2-phenyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3,4-diamines that have antiproliferative potential against the MCF-7 cell line. Two of them after a 48-h exposure inhibited cell proliferation with an IC50 of 13.7 and 16.2 μg/mL (Ghareb et al., 2012). Hence, our results indicated that the synthesized compounds 2 and 4 have a good antiproliferative potential against some tumor cells and may be promising candidates for further anticancer study.
Structure–activity analysis
An important feature of a potential drug is its bioavailability which determines how an investigated compound can penetrate a biological membrane. Thus, the physiochemical analysis of a molecule known as Lipinski’s rule of five is used (Lipinski et al., 1997). For this purpose, all thiosemicarbazides were analyzed in silico estimating their bioavailability via calculating such parameters as molecular weight (MW), partition coefficient (logP), the number of donors and acceptors of hydrogen bonds and the polar surface area (PSA). The obtained data showed that all compounds meet the criteria of Lipinski’s rule (Lipinski et al., 1997). The molecular weight of the tested derivatives ranged from 290 to 385 Da (<500 Da), and the log p values ranged from −1.43 to 2.52 (<5), respectively. All the researched compounds have no more than five hydrogen bond donors (−NH and −OH) and fewer than ten hydrogen bond acceptors (N, O). This is very important information because a decreased number of donors are known to reduce the affinity of P-glycoprotein, and the more the acceptors, the more water molecules are connected. In addition, the amount of donors and acceptors of hydrogen bonds affect the magnitude of the compound’s polar surface area (PSA), which is defined as the sum of surfaces of polar atoms (usually of oxygen, nitrogen and attached hydrogen atoms) in a molecule. This is a useful parameter for the prediction of molecular transport properties, particularly in intestinal absorption and blood–brain barrier penetration (Fernandes and Gattass, 2009). Referring to our findings (Table 4), the PSA values of the tested thiosemicarbazide derivatives ranged from 92[Å2] to 118[Å2]. Compounds 2 and 4 have demonstrated the highest antibacterial and antiproliferative activities, and their PSA values were 92.5[Å2] and 94.1[Å2], respectively.
The obtained values of topological polar surface area (TPSA) confirmed this relationship (Table 4). It seems that this may be an important parameter for searching for a relation between structure and activity for this group of compounds.
Conclusions
In this study, we reported the synthesis and antibacterial activity of new compounds with pyridinecarbonyl group connected to the thiosemicarbazide system. It should be noted that two thiosemicarbazide derivatives, i.e., 2 and 4, exhibited good or moderate inhibition of all the most common caries-associated Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains. Moreover, these compounds strongly suppressed human hepatocellular carcinoma and human breast adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. The structure–activity relationship of the compounds showed that substitution at the position 2 of the pyridine ring enhances biological activity. The prominent antibacterial and antiproliferative effect of compounds 2 and 4 may be due to changing the number of chlorine atoms in the phenyl ring. Thus, it is worth underlying that 4-(2-chloro/2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridine-2yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide derivatives will be auspicious as potential agents for caries treatment and caries-associated cancer diseases. The physicochemical analysis indicates that the polar surface area is an important parameter for biological activity of the investigated compounds. Our results will have an impact on further investigation in this field in search of thiosemicarbazide compounds as antibacterial and antiproliferative agents.
Experimental
Chemicals and instruments
The chemicals used for synthesis and analysis were purchased from Merck Co. or Alfa Aesar and used without further purification. Melting points were determined on a Fisher-Johns block and presented without any corrections. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Avance 300 MHz spectrometer in solution noted and with TMS as an internal standard. The IR spectra were recorded on a Thermo Nicolet 6700 ATR device in the range of 500–3500 cm−1. The elementary analysis was performed with the application of Perkin-Elmer analyzer (940 Winter St., Waltham, MA, USA). The obtained results were within ±0.4 % of the theoretical value. Follow-up of the reactions and the purity of the newly obtained compounds were checked using TLC on aluminum oxide 60 F254 plates (Merck) in a CHCl3/C2H5OH (10:1 and 10:2) solvent system with UV visualization. The carboxylic acid hydrazides were synthesized via the reaction of the appropriate carboxylic acid ester with 98 % hydrazine hydrate in the solution of anhydrous ethanol using the method described earlier (Idhayadhulla et al., 2013; Priebe et al., 2008; Zamani, et al., 2002).
General procedure for the synthesis of 1-pyridinecarbonyl-4-substituted thiosemicarbazide derivatives (1–10)
A mixture of 2-, 3- or 4-pyridinecarboxylic acid hydrazide (0.01 mol), isothiocyanate (0.01 mol) and methanol (15 mL) was heated in a water bath reflux temperature for 0.5 h. The product was filtered, dried and crystallized from mixture methanol–acetonitrile (1:1).
4-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (1)
Yield 87 %, m.p. 182–184 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 7.16–7.66 (m, 4H, CHphenyl), 8.01–8.69 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.52 (s, 1H, –NH exchangeable with D2O), 9.88 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.81 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 116.01, 116.14, 122.98, 124.30, 127.41, 128.34, 130.87, 138.12, 148.95, 149.92, 164.25, 182.48. FT-IR ν: 3312, 1658, 1351 cm−1. MS (Cl) m/z = 291 [M+]. Anal.: Calcd. for C13H11N4OSF (290.31): C (53.78), H (3.82), N (19.29). Found: C (53.81), H (3.87), N (19.19) (CAS: 891086-61-6).
4-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (2)
Yield 83 %, m.p. 172–174 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 7.25–7.66 (m, 4H, CHphenyl), 8.02–8.71 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.54 (s, 1H, –NH exchangeable with D2O); 9.88 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O); 10.82 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 122.99, 127.47, 128.18, 129.74, 131.00, 138.17, 149.01, 149.87, 164.27, 182.17. FT-IR ν: 3246, 1655, 1354 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z: 307 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C13H11N4OSCl (306.77): C (50.89), H (3.61), N (18.29). Found: C (50.91), H (3.64), N (18.33) (CAS: 894234-77-6).
4-(2-Morpholinoethyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (3)
Yield 90 %, m.p. 196–198 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 2.35–2.59 (m, 4H, 2xCH2 morpholine), 3.45–3.52 (4H, 2xCH2 morpholine), 3.57–3.58 (m, 2H, –NH–CH 2–CH2–), 3.74–3.76 (m, 2H, –NH–CH 2–CH2–), 7.64–8.69 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 8.69 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 9.43 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.63 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 53.22, 53.59, 53.82, 56.50, 56.89, 57.27, 66.44, 66.55, 66.68, 122.94, 127.50, 138.23, 149.03, 149.66, 181.70. FT-IR ν: 3292, 1627, 1338 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z: 308 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C13H19N5O2S (309.38): C (50.46), H (6.18), N (22.63). Found: C (50.51), H (6.22), N (22.57) (CAS: 455314-30-4).
4-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (4)
Yield 91 %, m.p. 158–160 °C. 1H (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 7.42–7.66 (m, 3H, CHphenyl), 8.02–8.69 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.57 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 9.96 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.83 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 123.06, 127.46, 127.68, 129.20, 131.72, 132.52, 136.70, 138.15, 148.97, 164.27, 182.35. FT-IR ν: 3242, 3108, 1652, 1346 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z: 342 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C13H10N4OSCl2 (341.21): C (45.75), H (2.95), N (16.41). Found: C (45.80), H (2.97), N (16.37) (CAS: 891538-65-4).
4-(4-Methylthiophenyl)-1-(pyridin-2-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (5)
Yield 88 %, m.p. 184–186 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 2.28 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.01–7.25 (m, 4H, CHphenyl), 7.51–8.25 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 8.66 (1 s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.53 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 12.01 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 14.79, 124.50, 125.47, 125.89, 129.26, 132.24, 137.81, 139.69, 145.62, 149.68, 150.00, 169.69. FT-IR ν: 3236, 3111, 1654, 1324 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z: 318 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C14H14N4OS2 (318.41): C (52.80), H (4.43), N (17.59). Found: C (52.71), H (4.38), N (17.51).
4-(4-Methylthiophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (6)
Yield 89 %, m.p. 176–177 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.23–7.57 (m, 4H, CHphenyl), 8.27–8.76 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.11 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 9.81 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.76 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 15.58, 123.90, 126.24, 127.14, 128.72, 134.96, 136.05, 136.83, 149.40, 152.84, 165.14, 181.53. FT-IR ν: 3284, 1632, 1341 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z (%): 319 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C14H14N4OS2 (318.41): C (52.80), H (4.43), N (17.59). Found: C (52.72), H (4.49), N (17.64).
4-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-3-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (7)
Yield 92 %, m.p. 196–197 °C. 1H (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 7.37–7.68 (m, 3H, CHphenyl), 8.27–9.11 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.75 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.02 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.86 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 123.96, 129.36, 135.14, 148.55, 152.23, 164.80. FT-IR ν: 3331, 3150, 1700, 1359 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z: 342 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C13H10N4OSCl2 (341.21): C (45.75), H (2.95), N (16.41). Found: C (45.98), H (2.91), N (16.52) (CAS: 475180-05-3).
4-(4-Methylthiophenyl)-1-(pyridin-4-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (8)
Yield 86 %, m.p. 197–198 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 2.47 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.23–7.86 (m, 4H, CHphenyl), 8.77–8.78 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.83 (s, 2H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.86 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 15.57, 122.15, 126.26, 127.04, 134.97, 136.79, 140.07, 150.67, 164.93, 181.45. FT-IR ν: 3097, 2936, 1667, 1378 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z (%): 319 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C14H14N4OS2 (318.41): C (52.80), H (4.43), N (17.59). Found: C (52.96), H (4.51), N (52.68).
4-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-4-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (9)
Yield 78 %, m.p. 202–204 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 7.18–7.31 (m, 4H, CHphenyl), 7.86–8.78 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.70 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 9.99 (s, 1H, exchangeable with D2O), 10.94 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 116.14, 116.27, 122.21, 124.44, 127.51, 128.74, 131.17, 140.00, 150.65, 157.08, 158.70, 165.02, 182.69. FT-IR ν: 3265, 3113, 1677, 1368 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z: 291 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C13H11N4OSF (290.31): C (53.78), H (3.82), N (19.29). Found: C (53.65), H (3.74), N (19.42) (Byung et al., 2004).
4-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-1-(pyridin-4-yl)carbonylthiosemicarbazide (10)
Yield 84 %, m.p. 164–166 °C. 1H NMR (DMSO-d6, 300 MHz) δ: 7.37–7.45 (m, 3H, CHphenyl), 7.68–8.78 (m, 4H, CHpyridine), 9.76 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.05 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O), 10.95 (s, 1H, NH exchangeable with D2O). 13C NMR (DMSO-d6, 75 MHz) δ: 122.24, 127.81, 129.30, 132.12, 132.92, 133.27, 136.55, 150.65, 165.09, 182.53. FT-IR ν: 3309, 3117, 1677, 1380 cm−1. MS (CI) m/z (%): 341 (M+). Anal.: Calcd. for C13H10N4OSCl2 (341.21): C (45.75), H (2.95), N (16.41). Found: C (45.69), H (2.90), N (17.01) (Goldfarb, 2009).
X-ray analysis
The X-ray diffraction intensities were collected at 100 K on an Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur CCD diffractometer with graphite-monochromatized MoKα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) using the ω scan technique, with an angular scan width of 1.0°. The programs CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis Red (Oxford Diffraction, Xcalibur CCD System, CRYSALIS Software System, Version 1.171, Oxford Diffraction Ltd. 2009) were used for data collection, cell refinement and data reduction. Absorption corrections were applied using the multi-scan method by Blessing (Blessing, 1995). The structures were solved via direct methods using SHELXS-97 and refined by the full-matrix least-squares on F 2 using the SHELXL-97 (Sheldrick, 2008). Non-hydrogen atoms were refined with anisotropic displacement parameters. The N-bonded H atoms were found in the difference Fourier maps and then remained fixed during the least-squares refinements. All the remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically and allowed to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C). The molecular plots were drawn with Olex2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009).
Antibacterial activity
Panel reference strains of bacteria from the American Type Culture Collection or Polish Collection of Microorganisms, including aerobic Gram-positive bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC 12228, and aerobic Gram-negative bacteria: Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, as well as microaerobic Gram-positive bacteria: Lactobacillus spp., Lactobacillus acidophilus PCM 2105, Streptococcus mutans PCM 2502 and Streptococcus sanguinis PCM 2335, were used. Microbial suspensions with an optical density of 0.5 McFarland standard at 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL (CFU: colony forming unit) were prepared in sterile 0.9 % NaCl. Mueller–Hinton (M–H) broth and M–H agar (Oxoid Ltd., England) for aerobic strains, and MRS Broth Lactobacillus, MRS Agar Lactobacillus (BioMaxima S.A., Poland), BHI Broth and BHI agar (BioMaxima S.A., Poland) for microaerobic strains were used in the microbial tests. All stock solutions of the newly synthesized compounds were prepared in DMSO (the final DMSO concentration used in bacterial tests did not inhibit microbial growth and was less than 1.5 %). The antibacterial activity of the newly synthesized compounds was compared with the controls: cefepime dihydrochloride (Maxipime, Bristol-Myers Squibb Latina), chlorhexidine digluconate ((CLX) Amara Poland) and ethacridine lactate (Rivanolum, PharmaSwiss, Czech Republic).
Disk diffusion method
The preliminary antibacterial activity of the carbazide derivatives against human pathogenic Gram-positive, Gram-negative aerobic and microaerobic bacteria was evaluated by measuring the zones of inhibition in the disk diffusion method (Murray et al., 1995). Each compound (100 µg) was placed on Petri plates with agar medium (previously inoculated with 0.5 McFarland standards with the tested bacterial strains). After 18 h of incubation at 37 °C (for aerobic strains) or 40 h at 35 °C (for microaerobic strains), zones of microbial growth produced around the tested substances were measured and recorded as the diameters of inhibition.
Broth microdilution method
A broth microdilution method was used to evaluate the minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) according to the CLSI document (CLSI performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 2008, Eighteenth International Supplement, CLSI document M7-MIC, Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne) with some modifications. The lowest concentration of the tested compound (expressed in μg/mL) which did not allow any visible growth of bacteria was considered as MIC. A serial doubling dilution of the compounds was prepared in 96-well plates (200 μL per well). A suitable medium (M-H Broth, MRS Broth Lactobacillus, BHI Broth) was used as a diluent. The final concentrations of derivatives were 1000–0.015 μg/mL. Finally, 2 μL of inoculum of the tested bacterial strain (1.5 × 108 CFU/mL) was added to each well. The tests were performed either at 36 °C for 18 h (aerobic strains) or at 40 h (microaerobic strains). After incubation, the panel was digitally analyzed at 600 nm using the microplate reader Bio Tech Synergy (USA) with a dedicated software system. The growth intensity in each well was compared with the negative and positive controls.
Cell lines
Normal human skin fibroblasts (BJ), human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) and human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, England, UK). The cells were cultured in Eagle’s minimum essential medium (EMEM, ATCC) supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum (FBS, PAA Laboratories), 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich). In the case of the MCF-7 cell line, the culture medium was additionally supplemented with 0.01 μg/mL of human recombinant insulin (Sigma-Aldrich). The cells were grown in 75-cm2 flasks and maintained at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5 % CO2 and 95 % air.
Cytotoxicity assay
In order to determine the cytotoxicity, BJ cells were seeded in flat-bottom 96-well plates in 100 μL of a complete growth medium at a concentration of 1.7 × 104 cells/well and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5 % CO2. Immediately before drug treatment, the synthesized compounds (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10) were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, Sigma-Aldrich) and then diluted in cell culture medium supplemented with 2 % FBS. Moreover, cefepime dihydrochloride (Maxipime, Bristol-Myers Squibb Latina), chlorhexidine digluconate ((CLX) Amara Poland) and ethacridine lactate (Rivanolum, PharmaSwiss, Czech Republic) were used as reference antibacterial agents. After incubation, the growth medium was replaced with 100 μL of the appropriate serial dilutions of the investigated compounds. Untreated cells were used as negative controls, and different concentrations of DMSO were used as the solvent control. The cell cultures were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The cytotoxicity was estimated using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay as described by Mosmann with some modifications (Mosmann, 1983). Briefly, the cells were incubated for 3 h with 25 μL of MTT solution (5 μg/mL in PBS buffer) per well. The MTT assay is a rapid colorimetric method based on the conversion of mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase from yellow, soluble tetrazolium salt to blue formazan crystals to determine the number of viable cells. In order to dissolve formazan crystals in live cells, 100 μL of SDS-HCl solution (10 % SDS in 0.01 N HCl) was added per well. After overnight incubation, absorbance was measured at 570 nm using microplate reader (BioTek ELx50). The MTT assay was repeated in three independent experiments performed in octuplicates. The half-maximal cytotoxic concentration (CC50) was defined as the compound concentration (μg/mL) required to reduce cell viability to 50 %. Therapeutic index (TI) is a widely accepted parameter to represent the specificity of antibacterial agents for human (Begg et al., 1999). In this study, the in vitro TI values were calculated as the ratio of CC50 (cytotoxic activity) and MIC (antibacterial activity); thus, greater values of in vitro therapeutic index indicate safer specificity for eukaryotic cells.
Cell proliferation assay
In order to evaluate cell proliferation, the cells were seeded in flat-bottom 96-well plates in 100 μL of a complete growth medium at a concentration of 2 × 103 cells/well (BJ), 1.5 × 104 cells/well (HepG2) and 2.5 × 104 cells/well (MCF-7) and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5 % CO2. Before drug exposure, the synthesized compounds (1–10) were dissolved in DMSO and then diluted in a complete culture medium supplemented with 10 % FBS. Subsequently, the growth medium was gently removed and the cells were exposed to 100 μL of serial dilutions of the investigated compounds at concentrations ranging from 0.05 to 200 μg/mL. Untreated cells were used as negative controls, and different concentrations of DMSO were used as the solvent control. After 96-h incubation at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5 % CO2, cell proliferation was assessed using the MTT test as described previously (Cytotoxicity assay). The MTT assay was repeated in three independent experiments in quadruplicates. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was defined as the compound concentration (μg/mL) required to inhibit cell proliferation to 50 %.
Statistical analysis
The results of the in vitro cell culture experiments were presented as mean values ± standard deviation (SD) or as mean values ± standard error of the mean (SEM). The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA test followed by Dunnett’s test. Differences were considered as significant with p < 0.01 (GraphPad Prism 5, Version 5.04 Software). The values of CC50 and IC50 were calculated via 4-parameter nonlinear regression analyses using GraphPad Prism 5, version 5.04.
Molecular modeling
Molecular modeling was performed using generally available software. The LogP and PSA parameters were performed by using VEGA ZZ program (Pedretti et al., 2004). The geometry and energy of the tested compounds were optimized by AM1 semiempirical method (Dewar et al., 1985). The TPSA, miLogP and hydrogen bond donors and acceptors were calculated by Molinspiration program (http://www.molinspiration.com/cgi-bin/properties-accessed 1 February, 2015).
References
Alagarsamy V, Kumar BA, Parthiban P, Sheorey RV, Solomon VR (2010) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of some novel 1-(4-oxo-3-(3- methoxyphenyl)-3H-quinazolin-2-yl)-4-(substituted) thiosemicarbazides. AntiInfect Agents Med Chem 10(2):105–110
Arora S, Agarwal S, Singhal S (2014) Anticancer activities of thiosemicarbazides/thiosemicarbazones: a review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6:34–41
Autio-Gold J (2008) The role of chlorhexidine in caries prevention. Oper Den 33:710
Begg JE, Barclay ML, Kirkpatrick CJM (1999) The therapeutic monitoring of antimicrobial agents. Br J Clin Pharmacol 47:23–30
Bhata AR, Athar F, Van Zyl RL, Chen CT, Azam A (2008) Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-substituted 1-{[4-(10,15,20-triphenylporphyrin-5-yl)phenyl] methylidene}thiosemicarbazides as new class of potential antiprotozoal agents. Chem Biodivers 5:764–776
Blessing RH (1995) An empirical correction for absorption anisotropy. Acta Crystallogr Sect A 51:33–38
Byung H, Larsen MJ, Kubiak TM (2004) Preparation of carbonylmethylthio triazoles as anthelmintic and insecticidal agents. PCT Int. Appl. WO 2004074272 A1
Cognasse F, Hamzeh-Cognasse H, Chabert A, Jackson E, Arthaud CA, Garraud O, McNicol A (2014) Streptococcus sanguinis-induced cytokine and matrix metalloproteinase-1 release from platelets. BMC Immunol 15:1–8
Dewar MJS, Zoebisch EG, Healy EF, Stewart JJP (1985) The development and use of quantum mechanical molecular models. 76. AMI: a new general purpose quantum mechanical molecular model. J Am Chem Soc 107(13):3902–3909
Dolomanov OV, Bourhis LJ, Gildea RJ, Howard JAK, Puschmann H (2009) A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J Appl Cryst 42:339–341
Fernandes J, Gattass CR (2009) Topological polar surface area defines substrate transport by multidrug resistance associated protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1). J Med Chem 52:1214–1218
Ghareb N, Hanna PA, Said MM (2012) Synthesis and biological activities of novel indole-3-carbinol and (benzimidazolylmethyl)triazole-3,4-diamine derivatives. Afr J Pharm Sci Pharm 3:41–65
Goldfarb DC (2009) Method using lifespan-altering compounds for altering the lifespan of eukaryotic organisms, and screening for such compounds. U.S. Patent No. 20090163545 A1
Idhayadhulla A, Kumar RS, Nasser AJA, Manilal A (2013) Synthesis of some new pyrrole and pyridine derivatives and their antimicrobial, anticancer activities. Int J Biol Chem 7:15–26
Kashyap VK, Gupta RK, Shirivastava R, Srivastava BS, Srivastava R, Parai MK, Singh P, Bera S, Panda GJ (2012) In vivo activity of thiophene-containing trisubstituted methanes against acute and persistent infection of non-tubercular Mycobacterium fortuitum in a murine infection model. Antimicrob Chemother 67:1188–1197
Kerrigan SW, Douglas I, Wray A, Heath J, Byrne MF, Fitzgerald D, Cox D (2002) A role for glycoprotein Ib in Streptococcus sanguis-induced platelet aggregation. Blood 100:509–516
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (1997) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 23:3–25
Malki A, Elbayaa RY, Ashour HMA, Loffredo CA, Yousse AM (2014) Novel thiosemicarbazides induced apoptosis in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells via JNK signaling. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 3:1–10
Mavrova AT, Wesselinova D, Tsenov JA, Lubenov LA (2014) Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of some new thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4(3H)-ones containing 1,2,4-triazole and 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety. Eur J Med Chem 86:676–683
Meurman JH (2010) Oral microbiota and cancer. J Oral Microbiol 2:1–10
Mohsen ME, Omar AM, Farghaly AAB, Hazzai NH, Eshba FM, Sharabi TT (1981) Daabees, Thiourea and thiosemicarbazide derivatives structurally related to hexestrol: synthesis and anticancer and other pharmacological properties. J Pharm Sci 70(9):1075–1079
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Murray PR, Baron EJ, Pfaller MA, Tenover FC, Yolke RH (1995) Manual of Clinical Microbiology, 7th ed., Washington: 1773
Panchal RG, Ulrich RL, Lane D, Butler MM, Houseweart C, Opperman T, Williams JD, Peet NP, Moir DT, Nguyen T, Gussio R, Bowlin T, Bavari S (2009) Novel broad-spectrum bis-(imidazolinylindole) derivatives with potent antibacterial activities against antibiotic-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:4283–4291
Patel SR, Gangwal R, Sangamwar AT, Jain R (2014) Synthesis, biological evaluation and 3D-QSAR study of hydrazide, semicarbazide and thiosemicarbazide derivatives of 4-(adamantan-1-yl)quinoline as anti-tuberculosis agents. Eur J Med Chem 6(85):255–267
Pedretti A, Villa L, Vistoli G (2004) VEGA—an open platform to develop chemo-bio-informatics applications using plug in architecture and script programming. JCAMD. 18:167–173
Perković I, Butula I, Kralj M, Martin-Kleiner I, Balzarini J, Hadjipavlou-Litina D, Katsori AM, Zorc B (2012) Novel NSAID 1-acyl-4-cycloalkyl/arylsemicarbazides and 1-acyl-5-benzyloxy/hydroxy carbamoylcarbazides as potential anticancer agents and antioxidants. Eur J Med Chem 51:227–238
Priebe JP, Mello RS, Nome F, Bortoluzzi AJ (2008) Nicotinohydrazide. Acta Cryst E64:302–303
Rane RA, Naphade SS, Bangalore PK, Palkar MB, Shaikh MS, Karpoormath R (2014) Synthesis of novel 4-nitropyrrole-based semicarbazide and thiosemicarbazide hybrids with antimicrobial and anti-tubercular activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:3079–3083
Salgın-Gökşen U, Gökhan-Kelekçi N, Göktas Ö, Köysal Y, Kılıç E, Işık Ş, Aktay G, Özalp M (2007) 1-Acylthiosemicarbazides, 1,2,4-triazole-5(4H)-thiones, 1,3,4-thiadiazoles and hydrazones containing 5-methyl-2-benzoxazolinones: synthesis, analgesic-anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities. Bioorg Med Chem 15:5738–5751
Sheikhy M, Jalilian AR, Novinrooz A, Motamedi-Sedeh F (2012) Synthesis and in vitro antibacterial evaluation of some thiosemicarbazides and thiosemicarbazones. J Biomed Sci Eng 5:39–42
Sheldrick GM (2008) A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst A64:112–122
Tan OU, Ozadali K, Yogeeswari P, Sriram D, Balkan A (2012) Synthesis and antimycobacterial activities of some new N-acylhydrazone and thiosemicarbazide derivatives of 6-methyl-4,5-dihydropyridazin-3(2H)-one. Med Chem Res 21:2388–2394
Umadevi P, Deepti K, Srinath I, Vijayalakshmi G, Tarakamji M (2012) Synthesis and in vitro antibacterial activity of some urea, thiourea and thiosemicarbazide derivatives. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4(3):379–383
Xin Z, Ying H, Zhen Y, Ping G (2013) Syntheses and antiproliferative activities of novel diarylthiosemicarbazide derivatives. Chem Res Chin Univ 29(1):62–66
Zamani K, Faghihi K, Iqbal R (2002) Synthesis and structure determination of some new N-glycosides of 4,5-disubstituted-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiones. J Chin Chem Soc 49:1041–1044
Zhang HJ, Qian Y, Zhu DD, Yang XG, Zhu HL (2011) Synthesis, molecular modeling and biological evaluation of chalcone thiosemicarbazide derivatives as novel anticancer agents. Eur J Med Chem 46:4702–4708
Zoraghi R, Worrall L, See RH, Strangman W, Popplewell WL, Gong H, Samaai T, Swayze RD, Kaur S, Vuckovic M, Finlay BB, Brunham RC, McMaster WR, Davies-Coleman MT, Strynadka NC, Andersen RJ, Reiner NE (2011) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pyruvate kinase as a target for bis-indole alkaloids with antibacterial activities. J Biol Chem 286:44716–44725
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by a DS2 grant (Medical University in Lublin, Poland). The paper was developed using the equipment purchased within agreement No. PORPW.01.03.00-06-010/09-00 Operational Program Development of Eastern Poland 2007-2013, Priority Axis I, Modern Economy, Operations 1.3. Innovations Promotion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Pitucha, M., Woś, M., Miazga-Karska, M. et al. Synthesis, antibacterial and antiproliferative potential of some new 1-pyridinecarbonyl-4-substituted thiosemicarbazide derivatives. Med Chem Res 25, 1666–1677 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1599-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1599-6