Abstract
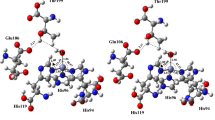
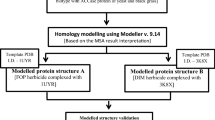
The 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) is a relevant target protein for therapeutic and agrochemical research. It is an iron-dependent enzyme, and its inhibition has very different effects on plants and animals. In animals, the enzyme has an important role in the catabolism of tyrosine, and in the plant, it operates in the cascade of photosynthesis. Potent HPPD inhibitors have been described, and all contain the 1,3-diketone group in its shape. In this research, we carried out a study of the interaction modes of HPPD enzymes from plant and rat with selective and non-selective herbicides which already available with their structures to identify the molecule groups which are essential to their activity and those that are likely to changes, mediated by molecular computations. In this theoretical investigation, methods of molecular docking, reaction mechanism (QM/MM) and AIM calculations were employed, aiming the search for new more active and selective herbicides. Modifications were performed for DAS 645 and DAS 869 inhibitors. DAS 645 presented a good selectivity for the inhibition of the plant enzyme, and the modifications to the analogs design done increased its activity. For this compound, π–π* stacking interactions seem to be important, and this fact was proven by using AIM calculations. The other prototype compound, DAS 869, a potent inhibitor for both enzymes, had its increased activity in the plant and rat enzyme after added groups capable of performing π–π* stacking interactions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhilash PC, Singh N (2009) Pesticide use and application: an Indian scenario. J Hazard Mater 165:1–12
Bader RFW (1990) Atoms in molecules: a quantum theory. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Baird C (2002) Química ambiental. Bookman, Porto Alegre
Barbosa LCA (2004) Os pesticidas, o homem e o meio ambiente. Dissertation, Federal University Viçosa
Barone V, Cossi M, Tomasi J (1998) Geometry optimization of molecular structures in solution by the polarizable continuum model. J Comput Chem 19:404–417
Battaglin WA, Thurman EM, Kalkhoff SJ, Porter SD (2003) Herbicides and transformation products in surface waters of the Midwestern United States. J American Water Res Assoc 39:743–756
Beaudegnies R, Edmunds AJF, Fraser TEM, Hall RG, Hawkes TR, Mitchell G, Schaetzer J, Wendeborn S, Wibbley J (2009) Herbicidal 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors—a review of the triketone chemistry story from a Syngenta perspective. Bioorgan Med Chem 17:4134–4152
Bizuik M, Przyjazny A, Czerwinski J, Wiergowski MJ (1996) Occurrence and determination of pesticides in natural and treated waters. J Chromatogr A 754:103–123
Bowmer KH, Korth W, Scott A, Mccorkelle G, Thomas M (1998) Pesticide monitoring in the irrigation areas of south-western NSW 1990–1995. Technical report, CSIRO Land and Water, Austrália
Braga B (2005) Introdução à Engenharia Ambiental: O desafio do desenvolvimento Sustentável. Pearson Prentice Hall, São Paulo
Caetano MS (2007) Compostos inibidores da EPSP sintase como ingredientes ativos de herbicidas. Dissertation, Federal University of Lavras
Cerone R, Holme E, Schiaffino MC, Caruso U, Maritano L, Romano C (1997) Tyrosinemia type III: diagnosis and ten-year follow-up. Acta Paediatr 86:1013–1015
Colborn T, Dumanoski D, Myers JP (1997) O futuro roubado. L&PM, Porto Alegre
Corts-Guzman F, Bader RFW (2005) Complementarity of QTAIM and MO theory in the study of bonding in donor-acceptor complexes. Coord Chem Rev 249:633–662
Coutinho CFB, Tanimoto ST, Galli A, Garbellini GS, Takayama M, Amaral RB, Mazo LH, Avaca LA, Machado SAS (2005) Pesticidas: Mecanismo de ação, degradação e toxidez. Rev Ecotox Meio Ambiente 5:65–72
Da Cunha EFF, Ramalho TC, Reynolds RC (2008) Binding mode analysis of 2,4-diamino-5-methyl-5-deaza-6-substituted pteridines with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and human dihydrofolate reductases. J Biomol Struct Dyn 25:377–385
De Beer SBA, Glattli A, Hutzler J, Vermeulen NPE, Oostenbrink C (2011) Molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations on the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. J Comp Chem 32:2160–2169
Ellis MK, Whitfield AC, Gowans LA, Auton TR, Provan WM, Lock EA, Smith LL (1995) Inhibition of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase by 2-(2-nitro-4-trifluoromethylbenzoyl)-cyclohexane-1,3-dione and 2-(2-chloro-4-methanesulfonylbenzoyl)-cyclohexane-1,3-dione. Toxicol Appl Pharm 133:12–19
Endo F, Kitano A, Uehara I, Nagata N, Matsuda I, Shinka T, Kuhara T, Matsumoto I (1983) 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid oxidase deficiency with normal fumarylacetoacetase: a new variant form of hereditary hypertyrosinemia. Pediatr Res 17:92–96
Eschenburg S, Healy ML, Priestman MA, Lushington GH, Schonbrunn E (2002) How the mutation glycine96 to alanine confers glyphosate insensitivity to 5-enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate synthase from Escherichia coli. Planta 216:129–135
Fitzpatick D (2006) Evolution and chaos in property rights systems: The Third World tragedy of contested access. Yale Law J 115:996–1048
Gehlhaar DK, Verkhivker GM, Rejto PA, Sherman CJ, Fogel DB, Fogel LJ, Freer ST (1995) Molecular recognition of the inhibitor AG-1343 by HIV-1 protease-conformationally flexible docking by evolutionary programming. Chem Biol 2:317–324
Grabowski SJ, Sokalski WA, Leszczynski J (2004) Is a pi center dot center dot center dot H+ center dot center dot center dot pi complex hydrogen bonded? J Phys Chem A 108:1806–1812
Gunsior M, Ravel J, Challis GL, Townsend CA (2004) Engineering p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase to a p-hydroxymandelate synthase and evidence for the proposed benzene oxide intermediate in homogentisate formation. Biochemistry 43:663–674
Hausinger RP (2004) Fe(II)/alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases and related enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 39:21–68
Huang MZNG, Yang DY, Shang Z, Zou J, Yu Q (2002) 3D-Qsar studies on 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors by comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:2271–2275
Huhn R, Stoermer H, Klingele B, Bausch E, Fois A, Farnetani M, Di Rocco M, Boue J, Kirk JM, Coleman R, Scherer G (1998) Novel and recurrent tyrosine aminotransferase gene mutations in tyrosinemia type II. Hum Genet 102:305–313
Kavana M, Moran GR (2003) Interaction of (4-hydroxyphenyl)pyruvate dioxygenase with the specific inhibitor 2[2-nitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]1,3-cyclohexanedione. Biochem 42:10238–10245
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg ST, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
Lin SW, Lin YL, Lin TC, Yang DY (2000) Discovery of a potent, non-triketone type inhibitor of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 10:1297–1298
Lindstedt S, Rundgren M (1982) Blue color, metal content, and substrate binding in 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase from pseudomonas SP Strain PJ 874. J Biol Chem 257:1922–1931
Lo’pez-Ramos M, Perruccio F (2010) HPPD: ligand- and target-based virtual screening on a herbicide target. J Chem Inf Model 50:801–814
Mati LK, Cockroft SL (2010) Molecular balances for quantifying non-covalent interactions. Chem Soc Rev 39:4195–4205
Michael WJ, Kratz GW (1988) Preparation of benzoylcyclohexanedione herbicides. US patent 4,780,127, filled 4 March, 1988
Mitchell G, Bartlett DW, Fraser TEM, Hawkes TR, Holt DC, Townson JK, Wichert RA (2001) Mesotrione: a new selective herbicide for use in maize. Pest Manag Sci 57:120–128
Moran GR (2005) 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 433:117–128
Norris SR, Barrette TR, DellaPenna (1995) Genetic dissection of carotenoid synthesis in arabidopsis defines plastoquinone as an essential component of phytoene desaturation. Plant Cell 7:2139–2149
Oliveira BG, Araújo RCMU, Carvalho AB, Ramos MN (2009) Small heterocyclics as hydrogen bond acceptors and donors: the case of the C2H3XS center dot center dot center dot NH3 complexes (X = H, F and CH3). Struct Chem 20:663–670
Pallett KE, Cramp SM, Little JP, Veerasekaran P, Crudace AJ, Slater AE (2001) Isoxaflutole: the background to its discovery and the basis of its herbicidal properties. Pest Manag Sci 57:133–142
Petitjean ARG, Khury NK, Lenh JM (2004) Dynamic devices. Shape switching and substrate binding in ion-controlled nanomechanical molecular tweezers. J Am Chem Soc 126:6637–6647
Prescott AG, Lloyd MD (2000) The iron(II) and 2-oxoaciddependent dioxygenases and their role in metabolism. Nat Prod Rep 17:367–383
Pretty J (2008) Agricultural sustainability: concepts, principles and evidence. Philos Trans R Soc B 363:447–465
Primel EG, Zanella R, Kurz MHS, Goncalves FF, Machado SD, Marcezan E (2005) Pollution of water by herbicides used in the irrigated Rice cultivation in the central area of Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil: theoretical prediction and monitoring. Chem New 28:605–609
Ramalho TC, Da Cunha EFF, Alencastro RB (2005) Solvent effects on C-13 and N-15 Shielding tensor of nitroimidazoles in the condensed phase: a sequential molecular dynamics/quantum mechanics study. J Phys Condens 17:4951
Ramalho TC, Da Cunha EFF, Peixoto FC, Figueiroa-Villar JD (2008) Computational NMR investigation of radiosensitizer in solution. J Theor Comput Chem 7:37–52
Renaud B, Edmunds AJF, Fraser TEM, Salão RG, Hawkes TR, Mitchell G, Schaetzer J, Wendborn S, Wibley J (2009) Herbicidal 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase inhibitors- A review of the triketone chemistry story from a Syngenta perspective. Bioorg Med Chem 17:4134–4152
Rice EL (1997) Allelopathy. Academic Press, London
Romagni JG, Meazza G, Nanayakkara NP, Dayan FE (2000) The phytotoxic lichen metabolite, usnic acid, is a potent inhibitor of plant p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. FEBS Lett 480:301–305
Schonbrunn E, Eschenburg S, Shuttleworth WA, Schloss JV, Amrhein N, Evans NS, Kabsch W (2000) Structural basis for the interaction of the fluorescence probe 8-anilino-1-1-naphthalene sulfonate (ANS) with the antibiotic target Mura. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6345–6349
Schulz A, Oswald OP, Beyer K (1993) SC-OO51, a 2-benzoylcyclohexane-1,3-dione herbicide, is a potent inhibitor of the enzyme p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. FEBS Lett 318:162–166
Secor J (1994) Inhibition of Barnyardgrass 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase by Sulcotrione. Plant Physiol 106:1429–1433
Sost D (1990) Substitution of Gly-96 to Ala in the 5-enolpyruvylshikimate 3-phosphate synthase of Klebsiella pneumoniae results in a greatly reduced affinity for the herbicide glyphosate. Arch Biochem Biophys 282:433–436
Thomsen R, Christensen MH (2006) MolDock: a new technique for high-accuracy molecular docking. J Med Chem 49:3315–3321
Tomoeda K, Awata H, Matsuura T, Matsuda I, Ploechl E, Milovac T, Boneh A, Scott CR, Danks DH, Endo F (2000) Mutations in the 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid dioxygenase gene are responsible for tyrosinemia type III and Hawkinsinuria. Mol Genet Metabol 71:506–510
Yang C, Pflugrath JW, Camper DL, Foster ML, Pernich DJ, Walsh TA (2004) Structural basis for herbicidal inhibitor selectivity revealed by comparison of crystal structures of plant and mammalian 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Biochemistry 43:10414–10423
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Brazilian funding agency: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior/Ministério da Defesa (CAPES/MD) for support and FAPEMIG, CNPq and the Federal University of Lavras (UFLA) for providing the physical infrastructure and working space.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, T.C., dos Santos Pires, M., de Castro, A.A. et al. Molecular insight into the inhibition mechanism of plant and rat 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase by molecular docking and DFT calculations. Med Chem Res 24, 3958–3971 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1436-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1436-3