Abstract
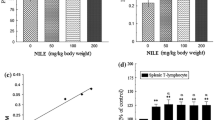
Asparagus racemosus is used in the Indian traditional system of medicine for improving the general state of health and stress-related immune disorders. Most of the synthetic chemotherapeutic agents available today are immunosuppressants and exert variety of side effects. To overcome these undesired effects of chemotherapeutic agents, botanical-based immunomodulators are often employed as adjuvant therapy. In the present study, immunomodulatory activity of two steroidal saponins shatavaroside A (1) and shatavaroside B (2), isolated from Asparagus racemosus, have been evaluated using polymorphonuclear leucocyte function test. The activity was further confirmed using more sensitive assays such as nitroblue tetrazolium, nitrous oxide, and chemiluminescence assays. Both steroidal saponins were found active at nano concentration (5 ng/ml) and can act as potent immunostimulants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatnagar M, Sisodia SS, Bhatnagar R (2005) Antiulcer and antioxidant activity of Asparagus racemosus WILLD and Withania somnifera DUNAL in rats. Ann NY Acad Sci 1056:261–278
Capasso F, Gaginella TS, Grandolini G, Izzo AA (2003) In phytotherapy: a quick reference to herbal medicine. Springer, Berlin
Chadha YR (2003) The wealth of India: a dictionary of Indian raw materials & industrial products, vol 1A, Revised edn. National Institute of Science Communication and Information Resources, Council of Scientific & Industrial Research, New Delhi, pp 470–471
Dalvi SS, Nadkarni PM, Gupta KC (1990) Effect of Asparagus racemosus on gastric emptying time in normal healthy volunteers. J Postgrad Med 36:91–94
Dhuley JN (1997) Effect of some Indian herbs on macrophage functions in ochratoxin treated mice. J Ethnopharmacol 58:15–20
Gautam M, Diwanay S, Gairola S, Shinde Y, Patki P, Patwardhan B (2004) Immunoadjubent potential of Asparagus racemosus aqueous extract in experimental system. J Ethnopharmacol 91:251–255
Handa SS, Suri OP, Gupta VN, Suri KA, Satti NK, Bhardwaj V, Bedi KL, Khajuria A, Kaul A, Parikh GG, Kuhlar P, Salunkhe U, Krishnamurthy R (2003) Oligospirostanoside, pharmaceutical composition containing novel olicospirostanoside and method for immunomodulation using said oligospirostanoside. US Patent No. 6, 649, 745, B2
Handa SS, Suri OP, Gupta VN, Suri KA, Satti NK, Bhardwaj V, Bedi KL, Khajuria A, Kaul A, Parikh GG, Kuhlar P, Salunkhe U, Krishnamurthy R (2003) Process for the isolation of novel oligospirostanoside. US Patent No. 6, 670, 459, B2
Hayes PY, Jahidin AH, Lehmann R, Penman K, Kitching W, De Voss JJ (2006a) Structural revision of shatavains I and IV, the major components from the root of A. racemosus. Tetrahedron Lett 47:6965–6969
Hayes PY, Jahidin AH, Lehmann R, Penman K, Kitching W, De Voss JJ (2006b) Asparinins, asparosides, curillins, curillosides and shavatarins: structrul clarification with the isolation of shatavarin V, a new steroidal saponins from the roots of A. racemosus. Tetrahedron Lett 47:8683–8687
Hayes PY, Jahidin AH, Lehmann R, Penman K, Kitching W, De Voss JJ (2008) Steroidal saponins from the root of A. racemosus. Phytochemistry 69:796–804
Jadhav AN, Bhutani KK (2006) Steoidal saponins from the roots of A. adscendens Roxb and A. racemosus. Indian J Chem 45B:1515–1524
Joshi J, Dev S (1988) Chemistry of ayurvedic crude drug: part VIII-Shatavari-2: structure elucidation of bioactive shatavarin-I & other glycoside. Indian J Chem 27B:12–16
Lacaille-Dubois MA (2005) Bioactive saponins with cancer related and immunomodulatory activity: recent developments. Stud Nat Prod Chem 32(12):209–246
Lehrer RI, Cline MJ (1969) Interaction of Candida albicans with human leucocytes and serum. J Bacteriol 98:996–1004
Lehrer RI, Ganz T, Selstad M, Babior B, Curmutte C (1988) Neutrophils and host defence. Ann Intern Med 109:127–132
Parihar MS, Hemnani T (2004) Experimental excitotoxicity provokes oxidative damage in mice brain and attenuation by extract of Asparagus racemosus. J Neural Transm 111:1–12
Ravikumar PR, Soman R, Chetty G, Pandey RC, Dev S (1987) Chemistry of ayurvedic crude drug: part VI-Shatavari-1: structure of shatavarin-IV. Indian J Chem 26B:1012–1017
Rege NN, Nazareth HM, Isaac A, Karandikar SM, Dahanukar SA (1989) Immunotherapeutic modulation of intraperitoneal adhesions by A. racemosus. J Postgrad Med 35:199–203
Sairam K, Priyambada S, Aryya NC, Goel RK (2003) Gastroduodenal ulcer protective activity of Asparagus racemosus: an experimental, biochemical and histological study. J Ethnopharmacol 86:1–10
Satyavati GV, Raina MK, Sharma M (1976) Medicinal plants of India, vol 1. Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, pp 167–170
Saxena VK, Chourasia S (2001) A new isoflavone from the roots of A. racemosus. Fitoterapia 72:307–309
Sharma U, Saini R, Bobita, Kumar N, Singh B (2009) Steroidal saponins from Asparagus racemosus. Chem Pharm Bull 57(8):890–893
Sharma P, Chauhan PS, Dutt P, Amina M, Suri KA, Gupta BD, Suri OP, Dhar KL, Sharma D, Gupta V, Satti NK (2011) A unique immuno-stimulant steroidal sapogenin acid from the roots of Asparagus racemosus. Steroids 74(4):358–364
Shekine T, Fukasawa N, Kashiwagi Y, Ruangrungsi N, Murakoshi I (1994) Structure of aspragamine A, a novel polycyclic alkaloids from A. racemosus. Chem Pharm Bull 42(6):1360–1362
Shekine T, Fukasawa N, Murakoshi I, Ruangrungsi N (1997) A 9,10-dihydrophenanthrene from A. racemosus. Phytochemistry 44(4):763–764
Sparg SG, Light ME, Staden JV (2004) Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J Ethnopharmacol 94:219–243
Stites DP (1987) Clinical laboratory method for detection of cellular immune function. In: Stites DP, Stobo JD, Wells JV (eds) Basics and clinical immunology. Appleton and Lange, Connecticut, pp 285–303
Thatte UM, Dahanukar SA (1988) Comparative study of immunomodulating activity of Indian medicinal plants. Lithium carbonate and glucan. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 10:639–644
Zhang HJ, Sydara K, Tan GT, Ma C, Southavong B, Soejarto DD, Pezzuto JM, Harry HS (2004) Bioactive constituents from A. cochinchinensis. J Nat Prod 67:194–200
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Dr. P. S. Ahuja, Director of the Institute, for providing the necessary facilities. Mr. Upendra Sharma is thankful to CSIR for granting Senior Research fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
IHBT Communication No. 2269.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, U., Kumar, N., Singh, B. et al. Immunomodulatory active steroidal saponins from Asparagus racemosus . Med Chem Res 22, 573–579 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0048-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-012-0048-4