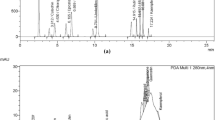
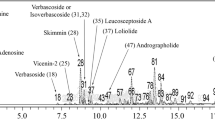
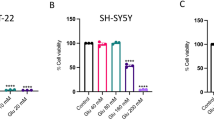
Summary.
Excitotoxicity and oxidative stress are the major mechanisms of neuronal cell death in neurodegenerative disorders that occurs in both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) that are generated extracellularly and intracellularly by various mechanisms are among the major risk factors that initiate and promote neurodegeneration.Therefore, it is important to find the compound which retard or reverse the neuronal injury. We designed this study to investigate the potential of extract of Asparagus racemosus (AR) against kainic acid (KA) – induced hippocampal and striatal neuronal damage. The dose of AR extract given to experimental animals was based on the evaluation of its total antioxidant activity. Extract of AR displayed potent reductant of Fe3+. The excitotoxic lesion in brain was produced by intra-hippocampal and intra-striatal injections of kainic acid (KA; 0.25 µg in a volume of 0.5 µl) to ketamine and xylazine (200 and 2 mg/kg b.w. respectively) anesthetized mice. The results showed impairment of hippocampus and striatal regions of brain after KA injection marked by an increase in lipid peroxidation and protein carbonyl content and decline in glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity and reduced glutathione (GSH) content. The AR extract supplemented mice displayed an improvement in GPx activity and GSH content and reduction in membranal lipid peroxidation and protein carbonyl. We show that the minimizing effect of AR extract on oxidative damage in addition to the elevation of GPx activity and GSH content could eventually result in protective effect on the KA-induced excitotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parihar, M., Hemnani, T. Experimental excitotoxicity provokes oxidative damage in mice brain and attenuation by extract of Asparagus racemosus . J Neural Transm 111, 1–12 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0069-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0069-8