Abstract
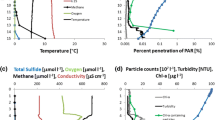
The distribution of oxygen (O2) at the oxic/anoxic interface in the water column of two Swiss lakes was measured with sub-micromolar sensitivity, high precision, and high spatial resolution. The O2 distribution was found to be highly variable and it is shown that N-cycling and the redox gradients of Mn, Fe and CH4 are controlled by O2 distributions down to the nanomolar concentration range. The profiles reveal that apparent gaps between the oxic zone and the sites of CH4 and Mn oxidation are bridged by zones with 0.01−1 µmol L–1 O2 concentrations and thus CH4 and Mn oxidation clearly occur at oxic conditions. Directly below the steep oxycline of Lake Rot a broad low O2 zone in the depth range of 6−7.5 m was now detectable. The O2 increase during daylight in this zone was comparable to the O2 flux along the oxycline. Here photosynthesis could be responsible for a substantial part of the chemotrophic oxidation processes. An even broader zone (0.8−3.8 m) with sub-micromolar O2 and evidence for methanotrophic and lithotrophic activities found at 160 m depth in the deep, dark hypolimnion of Lake Zug was maintained by transport, reaction- and mixing processes. The submicromolar zones could not have been resolved with traditional CTD-profiles. Their existence expands the oxic zone downwards and implies that substantial parts of “suboxic zones” characterized by the absence of both O2 and H2S may actually belong to the realm of oxic processes if more sensitive measurement techniques are used for their characterization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson BB, Krause D (1984) The concentration and isotopic fractionation of oxygen dissolved in fresh-water and seawater in equilibrium with the atmosphere. Limnol Oceanogr 29(3):620–632. doi:10.4319/lo.1984.29.3.0620
Berg P, Røy H, Janssen F, Meyer V, Jørgensen BB, Huettel M, de Beer D (2003) Oxygen uptake by aquatic sediments measured with a novel non-invasive eddy-correlation technique. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 261:75–83. doi:10.3354/Meps261075
Berner RA (1981) A new geochemical classification of sedimentary environments. J Sediment Petrol 51(2):359–365. doi:10.1306/212F7C7F-2B24-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Bethke CM, Sanford RA, Kirk MF, Jin QS, Flynn TM (2011) The thermodynamic ladder in geomicrobiology. Am J Sci 311(3):183–210. doi:10.2475/03.2011.01
Bonin P, Gilewicz M, Bertrand JC (1989) Effects of oxygen on each step of denitrification on Pseudomonas nautica. Can J Microbiol 35(11):1061–1064
Brand A, McGinnis DF, Wehrli B, Wüest A (2008) Intermittent oxygen flux from the interior into the bottom boundary of lakes as observed by eddy correlation. Limnol Oceanogr 53(5):1997–2006. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.5.1997
Canfield DE, Thamdrup B (2009) Towards a consistent classification scheme for geochemical environments, or, why we wish the term ‘suboxic’ would go away. Geobiology 7(4):385–392. doi:10.1111/j.1472-4669.2009.00214.x
Clement BG, Luther GW III, Tebo BM (2009) Rapid, oxygen-dependent microbial Mn(II) oxidation kinetics at sub-micromolar oxygen concentrations in the Black Sea suboxic zone. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 73(7):1878–1889. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2008.12.023
Cline JD (1969) Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural waters. Limnol Oceanogr 14:454–458
DEV (2004) Deutsche einheitsverfahren zur wasser-abwasser- und schlammuntersuchung. Wiley, Weinheim
Garcia HE, Gordon LI (1992) Oxygen solubility in seawater—better fitting equations. Limnol Oceanogr 37(6):1307–1312. doi:10.4319/lo.1992.37.6.1307
Goudsmit GH, Peeters F, Gloor M, Wüest A (1997) Boundary versus internal diapycnal mixing in stratified natural waters. J Geophys Res Oceans 102(C13):27903–27914. doi:10.1029/97JC01861
Gray JS, Wu RSS, Or YY (2002) Effects of hypoxia and organic enrichment on the coastal marine environment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 238:249–279
Jones C, Crowe SA, Sturm A, Leslie KL, MacLean LCW, Katsev S, Henny C, Fowle DA, Canfield DE (2011) Biogeochemistry of manganese in ferruginous Lake Matano. Indonesia Biogeosciences 8(10):2977–2991. doi:10.5194/bg-8-2977-2011
Kalvelage T, Jensen MM, Contreras S, Revsbech NP, Lam P, Gunter M, LaRoche J, Lavik G, Kuypers MMM (2011) Oxygen sensitivity of anammox and coupled N-cycle processes in oxygen minimum zones. Plos One 6(12):e29299. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029299
Keeling RF, Kortzinger A, Gruber N (2010) Ocean deoxygenation in a warming world. Annu Rev Mar Sci 2:199–229. doi:10.1146/annurev.marine.010908.163855
Kirf MK, Dinkel C, Schubert C, Wehrli B (2013) Submicromolar oxygen profiles at the oxic–anoxic boundary of temperate lakes. Aquat Geochem 1−19. doi:10.1007/s10498-013-9206-7
Kohler HP, Ahring B, Albella C (1984) Bacteriological studies on the sulfur cycle in the anaerobic part of the hypolimnion and in the surface sediments of Rotsee in Switzerland. FEMS Microbiol Lett 21(3):279–286. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1984.tb00322.x
Konovalov SK, Luther GW, Friederich GE, Nuzzio DB, Tebo BM, Murray JW, Oguz T, Glazer B, Trouwborst RE, Clement B, Murray KJ, Romanov AS (2003) Lateral injection of oxygen with the Bosporus plume—fingers of oxidizing potential in the Black Sea. Limnol Oceanogr 48(6):2369–2376
Kreling J, Bravidor J, McGinnis DF, Koschorreck M, Lorke A (2014) Physical controls of oxygen fluxes at pelagic and benthic oxyclines in a lake. Limnol Oceanogr 59(5):1637–1650. doi:10.4319/lo.2014.59.5.1637
Lam P, Kuypers MMM (2011) Microbial nitrogen cycling processes in oxygen minimum zones. Annu Rev Mar Sci 3:317–345. doi:10.1146/annurev-marine-120709-142814
Lam P, Jensen MM, Lavik G, McGinnis DF, Müller B, Schubert CJ, Amann R, Thamdrup B, Kuypers MMM (2007) Linking crenarchaeal and bacterial nitrification to anammox in the Black Sea. P Natl Acad Sci USA 104(17):7104–7109
Lashof DA, Ahuja DR (1990) Relative contributions of greenhouse gas emissions to global warming. Nature 344(6266):529–531. doi:10.1038/344529a0
Lehner P, Staudinger C, Borisov SM, Klimant I (2014) Ultra-sensitive optical oxygen sensors for characterization of nearly anoxic systems. Nat Commun 5. doi:10.1038/ncomms5460
Lippitsch ME, Pusterhofer J, Leiner MJP, Wolfbeis OS (1988) Fibre-optic oxygen sensor with the fluorescence decay time as the information carrier. Anal Chim Acta 205(1–2):1–6. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)82310-7
Lorke A, Müller B, Maerki M, Wüest A (2003) Breathing sediments: the control of diffusive transport across the sediment-water interface by periodic boundary-layer turbulence. Limnol Oceanogr 48(6):2077–2085. doi:10.4319/lo.2003.48.6.2077
Maerki M, Müller B, Dinkel C, Wehrli B (2009) Mineralization pathways in lake sediments with different oxygen and organic carbon supply. Limnol Oceanogr 54(2):428–438. doi:10.4319/lo.2009.54.2.0428
Mulder A, van de Graaf AA, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1995) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized bed reactor. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 16(3):177–184. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.1995.tb00281.x
Müller B, Bryant LD, Matzinger A, Wüest A (2012) Hypolimnetic oxygen depletion in eutrophic lakes. Environ Sci Technol 46(18):9964–9971. doi:10.1021/es301422r
Peeters F, Wüest A, Piepke G, Imboden DM (1996) Horizontal mixing in lakes. J Geophys Res Oceans 101(C8):18361–18375. doi:10.1029/96JC01145
Revsbech NP, Larsen LH, Gundersen J, Dalsgaard T, Ulloa O, Thamdrup B (2009) Determination of ultra-low oxygen concentrations in oxygen minimum zones by the STOX sensor. Limnol Oceanogr Methods 7:371–381. doi:10.4319/lom.2009.7.371
Schippers A, Neretin LN, Lavik G, Leipe T, Pollehne F (2005) Manganese(II) oxidation driven by lateral oxygen intrusions in the western Black Sea. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 69(9):2241–2252. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2004.10.016
Schubert CJ, Lucas FS, Durisch-Kaiser E, Stierli R, Diem T, Scheidegger O, Vazquez F, Müller B (2010) Oxidation and emission of methane in a monomictic lake (Rotsee, Switzerland). Aquat Sci 72(4):455–466. doi:10.1007/s00027-010-0148-5
Seitzinger SP, Nixon SW, Pilson MEQ (1984) Denitrification and nitrous-oxide production in a coastal marine ecosystem. Limnol Oceanogr 29(1):73–83
Stolper DA, Revsbech NP, Canfield DE (2010) Aerobic growth at nanomolar oxygen concentrations. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107(44):18755–18760. doi:10.1073/pnas.1013435107
Stumm W, Morgan J (1995) Aquatic chemistry: Chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters, 3rd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA
Tebo BM, Bargar JR, Clement BG, Dick GJ, Murray KJ, Parker D, Verity R, Webb SM (2004) Biogenic manganese oxides: properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu Rev Earth Pl Sc 32:287–328. doi:10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120213
Thamdrup B, Dalsgaard T, Revsbech NP (2012) Widespread functional anoxia in the oxygen minimum zone of the Eastern South Pacific. Deep Sea Res Part I 65:36–45. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2012.03.001
Tilzer MM (1988) Secchi disk—chlorophyll relationships in a lake with highly variable phytoplankton biomass. Hydrobiologia 162(2):163–171
Verbruggen F, Heiri O, Reichart GJ, Lotter AF (2010) Chironomid δ18O as a proxy for past lake water δ18O: a lateglacial record from Rotsee (Switzerland). Quaternary Sci Rev 29(17–18):2271–2279. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2010.05.030
Weiss RF, Price BA (1980) Nitrous-oxide solubility in water and seawater. Mar Chem 8(4):347–359
Wiesenburg DA, Guinasso NL (1979) Equilibrium solubilities of methane, carbon-monoxide, and hydrogen in water and sea-water. J Chem Eng Data 24(4):356–360
Wild D, von Schulthess R, Gujer W (1995) Structured modeling of denitrification intermediates. Water Sci Technol 31(2):45–54. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(95)00179-Q
Winkler LW (1888) Die Bestimmung des im Wasser gelösten Sauerstoffes. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges 21(2):2843–2854. doi:10.1002/cber.188802102122
Wright JJ, Konwar KM, Hallam SJ (2012) Microbial ecology of expanding oxygen minimum zones. Nat Rev Microbiol 10(6):381–394. doi:10.1038/Nrmicro2778
Wüest A, Lorke A (2003) Small-scale hydrodynamics in lakes. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 35:373–412. doi:10.1146/annurev.fluid.35.101101.161220
Zopfi J, Ferdelman TG, Jørgensen BB, Teske A, Thamdrup B (2001) Influence of water column dynamics on sulfide oxidation and other major biogeochemical processes in the chemocline of Mariager Fjord (Denmark). Mar Chem 74(1):29–51
Acknowledgments
We thank Eric Epping and Volker Meyer for valuable ideas supporting the measuring setup. We thank Dörte Carstens, Manuel Kunz, Gianna Battaglia, Christian Dinkel, Gijs Nobbe, Enoma Omoregie, Ruth Stierli and Alois Zwyssig for help in the laboratory and in the field and the cantonal agency Lucerne Environment and Energy for provided Secchi-data. Johny Wüest and Britta Bohnenbuck are acknowledged for comments on the text. The project was funded by Eawag and benefitted from the interaction with team members of the EU-project “Hypox” (EC grant # 22613).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
27_2014_365_MOESM1_ESM.doc
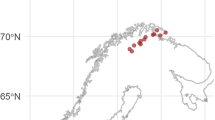
Location of Lake Rot and Lake Zug in Switzerland (middle left). Bathymetric map of Lake Zug (right) and Lake Rot (bottom). Crosses in the deepest parts indicate the sampling-areas. Modified after Verbruggen et al. (2010) (DOC 298 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirf, M.K., Røy, H., Holtappels, M. et al. Redox gradients at the low oxygen boundary of lakes. Aquat Sci 77, 81–93 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-014-0365-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-014-0365-4