Abstract
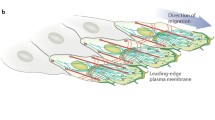
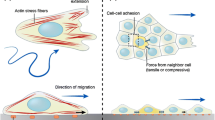
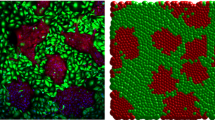
Directional cell migration is required for proper embryogenesis, immunity, and healing, and its underpinning regulatory mechanisms are often hijacked during diseases such as chronic inflammations and cancer metastasis. Studies on migratory epithelial tissues have revealed that cells can move as a collective group with shared responsibilities. First thought to be restricted to proper epithelial cell types able to maintain stable cell–cell junctions, the field of collective cell migration is now widening to include cooperative behavior of mesenchymal cells. In this review, we give an overview of the mechanisms driving collective cell migration in epithelial tissues and discuss how mesenchymal cells can cooperate to behave as a collective in the absence of bona fide cell–cell adhesions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Theveneau E, Mayor R (2011) Can mesenchymal cells undergo collective cell migration? The case of the neural crest. Cell Adh Migr 5:490–498
Rorth P (2009) Collective cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:407–429
Friedl P, Gilmour D (2009) Collective cell migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:445–457
Theveneau E, Mayor R (2012) Neural crest delamination and migration: from epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition to collective cell migration. Dev Biol 366(1):34–54
Carmona-Fontaine C, Theveneau E, Tzekou A, Tada M, Woods M, Page KM, Parsons M, Lambris JD, Mayor R (2011) Complement fragment C3a controls mutual cell attraction during collective cell migration. Dev Cell 21:1026–1037
Theveneau E, Marchant L, Kuriyama S, Gull M, Moepps B, Parsons M, Mayor R (2010) Collective chemotaxis requires contact-dependent cell polarity. Dev Cell 19:39–53
Parrinello S, Napoli I, Ribeiro S, Digby PW, Fedorova M, Parkinson DB, Doddrell RD, Nakayama M, Adams RH, Lloyd AC (2010) EphB signaling directs peripheral nerve regeneration through Sox2-dependent Schwann cell sorting. Cell 143:145–155
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 139:871–890
Duband JL (2010) Diversity in the molecular and cellular strategies of epithelium-to-mesenchyme transitions: insights from the neural crest. Cell Adh Migr 4:458–482
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP (2006) Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:131–142
Uchino M, Kojima H, Wada K, Imada M, Onoda F, Satofuka H, Utsugi T, Murakami Y (2010) Nuclear beta-catenin and CD44 upregulation characterize invasive cell populations in non-aggressive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 10:414
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R, Thompson EW (2006) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 172:973–981
Klymkowsky MW, Savagner P (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a cancer researcher’s conceptual friend and foe. Am J Pathol 174:1588–1593
Ewald AJ, Brenot A, Duong M, Chan BS, Werb Z (2008) Collective epithelial migration and cell rearrangements drive mammary branching morphogenesis. Dev Cell 14:570–581
Wheelock MJ, Shintani Y, Maeda M, Fukumoto Y, Johnson KR (2008) Cadherin switching. J Cell Sci 121:727–735
Hazan RB, Qiao R, Keren R, Badano I, Suyama K (2004) Cadherin switch in tumor progression. Ann NY Acad Sci 1014:155–163
Piloto S, Schilling TF (2010) Ovo1 links Wnt signaling with N-cadherin localization during neural crest migration. Development 137:1981–1990
Kashef J, Kohler A, Kuriyama S, Alfandari D, Mayor R, Wedlich D (2009) Cadherin-11 regulates protrusive activity in Xenopus cranial neural crest cells upstream of trio and the small GTPases. Genes Dev 23:1393–1398
Vallin J, Girault JM, Thiery JP, Broders F (1998) Xenopus cadherin-11 is expressed in different populations of migrating neural crest cells. Mech Dev 75:171–174
Chalpe AJ, Prasad M, Henke AJ, Paulson AF (2010) Regulation of cadherin expression in the chicken neural crest by the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Adh Migr 4(3):431–438
Nakagawa S, Takeichi M (1998) Neural crest emigration from the neural tube depends on regulated cadherin expression. Development 125:2963–2971
Rieger S, Senghaas N, Walch A, Koster RW (2009) Cadherin-2 controls directional chain migration of cerebellar granule neurons. PLoS Biol 7:e1000240
Ahlstrom JD, Erickson CA (2009) The neural crest epithelial-mesenchymal transition in 4D: a;tail’ of multiple non-obligatory cellular mechanisms. Development 136:1801–1812
Baum B, Georgiou M (2011) Dynamics of adherens junctions in epithelial establishment, maintenance, and remodelling. J Cell Biol 192:907–917
Nishimura T, Takeichi M (2009) Remodelling of the adherens junctions during morphogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol 89:33–54
Meng W, Takeichi M (2009) Adherens junction: molecular architecture and regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a002899
Cavey M, Lecuit T (2009) Molecular bases of cell–cell junctions stability and dynamics. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a002998
Kitt KN, Nelson WJ (2011) Rapid suppression of activated Rac1 by cadherins and Nectins during de novo cell–cell adhesion. PLoS ONE 6:e17841
Yamada S, Nelson WJ (2007) Localized zones of Rho and Rac activities drive initiation and expansion of epithelial cell–cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 178:517–527
Yonemura S (2011) Cadherin-actin interactions at adherens junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23:515–522
Miyake Y, Inoue N, Nishimura K, Kinoshita N, Hosoya H, Yonemura S (2006) Actomyosin tension is required for correct recruitment of adherens junction components and zonula occludens formation. Exp Cell Res 312:1637–1650
Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Hooper S, Chaudhry SI, Williamson P, Harrington K, Leitinger B, Sahai E (2010) Collective cell migration requires suppression of actomyosin at cell–cell contacts mediated by DDR1 and the cell polarity regulators Par3 and Par6. Nat Cell Biol 13:49–58
Weiss EE, Kroemker M, Rudiger AH, Jockusch BM, Rudiger M (1998) Vinculin is part of the cadherin-catenin junctional complex: complex formation between alpha-catenin and vinculin. J Cell Biol 141:755–764
Pokutta S, Weis WI (2007) Structure and mechanism of cadherins and catenins in cell–cell contacts. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:237–261
Harris TJ, Tepass U (2010) Adherens junctions: from molecules to morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:502–514
Benjamin JM, Kwiatkowski AV, Yang C, Korobova F, Pokutta S, Svitkina T, Weis WI, Nelson WJ (2010) AlphaE-catenin regulates actin dynamics independently of cadherin-mediated cell–cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 189:339–352
Drees F, Pokutta S, Yamada S, Nelson WJ, Weis WI (2005) Alpha-catenin is a molecular switch that binds E-cadherin-beta-catenin and regulates actin-filament assembly. Cell 123:903–915
Noren NK, Liu BP, Burridge K, Kreft B (2000) p120 catenin regulates the actin cytoskeleton via Rho family GTPases. J Cell Biol 150:567–580
Anastasiadis PZ, Moon SY, Thoreson MA, Mariner DJ, Crawford HC, Zheng Y, Reynolds AB (2000) Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin. Nat Cell Biol 2:637–644
Camand E, Peglion F, Osmani N, Sanson M, Etienne-Manneville S (2012) N-cadherin expression level modulates integrin-mediated polarity and strongly impacts on the speed and directionality of glial cell migration. J Cell Sci 125:844–857
Borghi N, Lowndes M, Maruthamuthu V, Gardel ML, Nelson WJ (2010) Regulation of cell motile behavior by crosstalk between cadherin- and integrin-mediated adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:13324–13329
Montell DJ (2006) The social lives of migrating cells in Drosophila. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:374–383
Aman A, Piotrowski T (2012) Cell–cell signaling interactions coordinate multiple cell behaviors that drive morphogenesis of the lateral line. Cell Adh Migr 5:499–508
Danjo Y, Gipson IK (1998) Actin ‘purse string’ filaments are anchored by E-cadherin-mediated adherens junctions at the leading edge of the epithelial wound, providing coordinated cell movement. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 22):3323–3332
Fredberg JJ, Tambe DT, Hardin CC, Angelini TE, Rajendran K, Park CY, Serra-Picamal X, Zhou EHH, Zaman MH, Butler JP et al (2011) Collective cell guidance by cooperative intercellular forces. Nat Mater 10:469–475
Wolf K, Wu YI, Liu Y, Geiger J, Tam E, Overall C, Stack MS, Friedl P (2007) Multi-step pericellular proteolysis controls the transition from individual to collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 9:893–904
Wacker A, Gerhardt H (2011) Endothelial development taking shape. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23:676–685
Gray RS, Cheung KJ, Ewald AJ (2010) Cellular mechanisms regulating epithelial morphogenesis and cancer invasion. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:640–650
Lu P, Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2006) Comparative mechanisms of branching morphogenesis in diverse systems. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 11:213–228
Kerstetter AE, Azodi E, Marrs JA, Liu Q (2004) Cadherin-2 function in the cranial ganglia and lateral line system of developing Zebrafish. Dev Dyn 230:137–143
Liu Q, Dalman MR, Sarmah S, Chen S, Chen Y, Hurlbut AK, Spencer MA, Pancoe L, Marrs JA (2011) Cell adhesion molecule cadherin-6 function in Zebrafish cranial and lateral line ganglia development. Dev Dyn 240:1716–1726
Liu Q, Ensign RD, Azodi E (2003) Cadherin-1, -2 and -4 expression in the cranial ganglia and lateral line system of developing Zebrafish. Gene Expr Patterns 3:653–658
Wilson AL, Shen YC, Babb-Clendenon SG, Rostedt J, Liu B, Barald KF, Marrs JA, Liu Q (2007) Cadherin-4 plays a role in the development of Zebrafish cranial ganglia and lateral line system. Dev Dyn 236:893–902
Matsuda M, Chitnis AB (2010) Atoh1a expression must be restricted by Notch signaling for effective morphogenesis of the posterior lateral line primordium in Zebrafish. Development 137:3477–3487
Aman A, Piotrowski T (2008) Wnt/beta-catenin and Fgf signaling control collective cell migration by restricting chemokine receptor expression. Dev Cell 15:749–761
Dambly-Chaudiere C, Cubedo N, Ghysen A (2007) Control of cell migration in the development of the posterior lateral line: antagonistic interactions between the chemokine receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7/RDC1. BMC Dev Biol 7:23
David NB, Sapede D, Saint-Etienne L, Thisse C, Thisse B, Dambly-Chaudiere C, Rosa FM, Ghysen A (2002) Molecular basis of cell migration in the fish lateral line: role of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 and of its ligand, SDF1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:16297–16302
Haas P, Gilmour D (2006) Chemokine signaling mediates self-organizing tissue migration in the Zebrafish lateral line. Dev Cell 10:673–680
Sapede D, Rossel M, Dambly-Chaudiere C, Ghysen A (2005) Role of SDF1 chemokine in the development of lateral line efferent and facial motor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1714–1718
Geisbrecht ER, Montell DJ (2002) Myosin VI is required for E-cadherin-mediated border cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 4:616–620
Niewiadomska P, Godt D, Tepass U (1999) DE-cadherin is required for intercellular motility during Drosophila oogenesis. J Cell Biol 144:533–547
Pacquelet A, Rorth P (2005) Regulatory mechanisms required for DE-cadherin function in cell migration and other types of adhesion. J Cell Biol 170:803–812
Duchek P, Somogyi K, Jekely G, Beccari S, Rorth P (2001) Guidance of cell migration by the Drosophila PDGF/VEGF receptor. Cell 107:17–26
Janssens K, Sung HH, Rorth P (2010) Direct detection of guidance receptor activity during border cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:7323–7328
McDonald JA, Pinheiro EM, Kadlec L, Schupbach T, Montell DJ (2006) Multiple EGFR ligands participate in guiding migrating border cells. Dev Biol 296:94–103
McDonald JA, Pinheiro EM, Montell DJ (2003) PVF1, a PDGF/VEGF homolog, is sufficient to guide border cells and interacts genetically with Taiman. Development 130:3469–3478
Nguyen TN, Uemura A, Shih W, Yamada S (2010) Zyxin-mediated actin assembly is required for efficient wound closure. J Biol Chem 285:35439–35445
Desai RA, Gao L, Raghavan S, Liu WF, Chen CS (2009) Cell polarity triggered by cell–cell adhesion via E-cadherin. J Cell Sci 122:905–911
Li L, Hartley R, Reiss B, Sun Y, Pu J, Wu D, Lin F, Hoang T, Yamada S, Jiang J et al (2012) E-cadherin plays an essential role in collective directional migration of large epithelial sheets. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:2779–2789
Leckband DE, le Duc Q, Wang N, de Rooij J (2011) Mechanotransduction at cadherin-mediated adhesions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23:523–530
Lecuit T, Lenne PF (2007) Cell surface mechanics and the control of cell shape, tissue patterns and morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:633–644
Baum B, Settleman J, Quinlan MP (2008) Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states in development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19:294–308
Saez A, Anon E, Ghibaudo M, du Roure O, Di Meglio JM, Hersen P, Silberzan P, Buguin A, Ladoux B (2011) Traction forces exerted by epithelial cell sheets. J Phys Condens Matter 22:194119
Trepat X, Fredberg JJ (2011) Plithotaxis and emergent dynamics in collective cellular migration. Trends Cell Biol 21:638–646
Tambe DT, Hardin CC, Angelini TE, Rajendran K, Park CY, Serra-Picamal X, Zhou EH, Zaman MH, Butler JP, Weitz DA et al (2011) Collective cell guidance by cooperative intercellular forces. Nat Mater 10:469–475
Angelini TE, Hannezo E, Trepat X, Marquez M, Fredberg JJ, Weitz DA (2011) Glass-like dynamics of collective cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:4714–4719
Stern CD (2004) Gastrulation : from cells to embryo. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NY
Solnica-Krezel L (2006) Gastrulation in Zebrafish—all just about adhesion? Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:433–441
Arboleda-Estudillo Y, Krieg M, Stuhmer J, Licata NA, Muller DJ, Heisenberg CP (2010) Movement directionality in collective migration of germ layer progenitors. Curr Biol 20:161–169
Ulrich F, Krieg M, Schotz EM, Link V, Castanon I, Schnabel V, Taubenberger A, Mueller D, Puech PH, Heisenberg CP (2005) Wnt11 functions in gastrulation by controlling cell cohesion through Rab5c and E-cadherin. Dev Cell 9:555–564
Winklbauer R (2012) Cadherin function during Xenopus gastrulation. Subcell Biochem 60:301–320
Weber GF, Bjerke MA, Desimone DW (2011) A mechanoresponsive cadherin–Keratin complex directs polarized protrusive behavior and collective cell migration. Dev Cell 22(1):104–115
Abercrombie M, Heaysman JE (1953) Observations on the social behaviour of cells in tissue culture. I. Speed of movement of chick heart fibroblasts in relation to their mutual contacts. Exp Cell Res 5:111–131
Abercrombie M, Dunn GA (1975) Adhesions of fibroblasts to substratum during contact inhibition observed by interference reflection microscopy. Exp Cell Res 92:57–62
Carmona-Fontaine C, Matthews HK, Kuriyama S, Moreno M, Dunn GA, Parsons M, Stern CD, Mayor R (2008) Contact inhibition of locomotion in vivo controls neural crest directional migration. Nature 456:957–961
Mayor R, Carmona-Fontaine C (2010) Keeping in touch with contact inhibition of locomotion. Trends Cell Biol 20:319–328
Astin JW, Batson J, Kadir S, Charlet J, Persad RA, Gillatt D, Oxley JD, Nobes CD (2010) Competition amongst Eph receptors regulates contact inhibition of locomotion and invasiveness in prostate cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol 12:1194–1204
Le Douarin N, Kalcheim C (1999) The neural crest, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, UK
Hall B (2008) The neural crest and neural crest cells in vertebrate development and evolution, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Milet C, Monsoro-Burq AH (2012) Neural crest induction at the neural plate border in vertebrates. Dev Biol 366:22–33
Theveneau E, Mayor R (2011) Collective cell migration of the cephalic neural crest: the art of integrating information. Genesis 49:164–176
Kuo BR, Erickson CA (2010) Regional differences in neural crest morphogenesis. Cell Adh Migr 4:567–585
Kulesa PM, Bailey CM, Kasemeier-Kulesa JC, McLennan R (2010) Cranial neural crest migration: new rules for an old road. Dev Biol 344:543–554
Gammill LS, Roffers-Agarwal J (2010) Division of labor during trunk neural crest development. Dev Biol 344:555–565
Gao C, Chen YG (2010) Dishevelled: the hub of Wnt signaling. Cell Signal 22:717–727
Stramer B, Moreira S, Millard T, Evans I, Huang CY, Sabet O, Milner M, Dunn G, Martin P, Wood W (2010) Clasp-mediated microtubule bundling regulates persistent motility and contact repulsion in Drosophila macrophages in vivo. J Cell Biol 189:681–689
Kadir S, Astin JW, Tahtamouni L, Martin P, Nobes CD (2011) Microtubule remodelling is required for the front-rear polarity switch during contact inhibition of locomotion. J Cell Sci 124:2642–2653
Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K, Lambris JD (2010) Complement: a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat Immunol 11:785–797
Teddy JM, Kulesa PM (2004) In vivo evidence for short- and long-range cell communication in cranial neural crest cells. Development 131:6141–6151
Erickson CA, Weston JA (1983) An SEM analysis of neural crest migration in the mouse. J Embryol Exp Morphol 74:97–118
Serbedzija GN, Bronner-Fraser M, Fraser SE (1992) Vital dye analysis of cranial neural crest cell migration in the mouse embryo. Development 116:297–307
Serbedzija GN, Fraser SE, Bronner-Fraser M (1990) Pathways of trunk neural crest cell migration in the mouse embryo as revealed by vital dye labelling. Development 108:605–612
Kulesa PM, Fraser SE (2000) In ovo time-lapse analysis of chick hindbrain neural crest cell migration shows cell interactions during migration to the branchial arches. Development 127:1161–1172
Xu X, Francis R, Wei CJ, Linask KL, Lo CW (2006) Connexin 43-mediated modulation of polarized cell movement and the directional migration of cardiac neural crest cells. Development 133:3629–3639
Xu X, Li WE, Huang GY, Meyer R, Chen T, Luo Y, Thomas MP, Radice GL, Lo CW (2001) Modulation of mouse neural crest cell motility by N-cadherin and connexin 43 gap junctions. J Cell Biol 154:217–230
Xu X, Li WE, Huang GY, Meyer R, Chen T, Luo Y, Thomas MP, Radice GL, Lo CW (2001) N-cadherin and Cx43alpha1 gap junctions modulates mouse neural crest cell motility via distinct pathways. Cell Commun Adhes 8:321–324
Carmona-Fontaine C, Matthews H, Mayor R (2008) Directional cell migration in vivo: Wnt at the crest. Cell Adh Migr 2:240–242
De Calisto J, Araya C, Marchant L, Riaz CF, Mayor R (2005) Essential role of non-canonical Wnt signalling in neural crest migration. Development 132:2587–2597
Matthews HK, Marchant L, Carmona-Fontaine C, Kuriyama S, Larrain J, Holt MR, Parsons M, Mayor R (2008) Directional migration of neural crest cells in vivo is regulated by Syndecan-4/Rac1 and non-canonical Wnt signaling/RhoA. Development 135:1771–1780
Banerjee S, Gordon L, Donn TM, Berti C, Moens CB, Burden SJ, Granato M (2011) A novel role for MuSK and non-canonical Wnt signaling during segmental neural crest cell migration. Development 138:3287–3296
Rios AC, Serralbo O, Salgado D, Marcelle C (2011) Neural crest regulates myogenesis through the transient activation of NOTCH. Nature 473(7348):532–535
Kulesa P, Ellies DL, Trainor PA (2004) Comparative analysis of neural crest cell death, migration, and function during vertebrate embryogenesis. Dev Dyn 229:14–29
Breau MA, Wilson D, Wilkinson DG, Xu Q (2012) Chemokine and Fgf signalling act as opposing guidance cues in formation of the lateral line primordium. Development 139:2246–2253
Simpson MJ, Zhang DC, Mariani M, Landman KA, Newgreen DF (2007) Cell proliferation drives neural crest cell invasion of the intestine. Dev Biol 302:553–568
Hearn CJ, Murphy M, Newgreen D (1998) GDNF and ET-3 differentially modulate the numbers of avian enteric neural crest cells and enteric neurons in vitro. Dev Biol 197:93–105
Young HM, Bergner AJ, Anderson RB, Enomoto H, Milbrandt J, Newgreen DF, Whitington PM (2004) Dynamics of neural crest-derived cell migration in the embryonic mouse gut. Dev Biol 270:455–473
Thomas LA, Yamada KM (1992) Contact stimulation of cell migration. J Cell Sci 103(Pt 4):1211–1214
Kelsh RN, Harris ML, Colanesi S, Erickson CA (2009) Stripes and belly-spots—a review of pigment cell morphogenesis in vertebrates. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:90–104
Spieth J, Keller RE (1984) Neural crest cell behavior in white and dark larvae of Ambystoma mexicanum: differences in cell morphology, arrangement, and extracellular matrix as related to migration. J Exp Zool 229:91–107
Keller RE, Spieth J (1984) Neural crest cell behavior in white and dark larvae of Ambystoma mexicanum: time-lapse cinemicrographic analysis of pigment cell movement in vivo and in culture. J Exp Zool 229:109–126
Erickson CA (1985) Control of neural crest cell dispersion in the trunk of the avian embryo. Dev Biol 111:138–157
Belmadani A, Jung H, Ren D, Miller RJ (2009) The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 regulates the migration of melanocyte progenitors in mouse hair follicles. Differentiation 77:395–411
Deisboeck TS, Couzin ID (2009) Collective behavior in cancer cell populations. Bioessays 31:190–197
Friedl P, Alexander S (2011) Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 147:992–1009
Nguyen DX, Bos PD, Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ-specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9:274–284
Khalil AA, Friedl P (2010) Determinants of leader cells in collective cell migration. Integr Biol (Camb) 2:568–574
Hotary K, Li XY, Allen E, Stevens SL, Weiss SJ (2006) A cancer cell metalloprotease triad regulates the basement membrane transmigration program. Genes Dev 20:2673–2686
Wolf K, Friedl P (2011) Extracellular matrix determinants of proteolytic and non-proteolytic cell migration. Trends Cell Biol 21:736–744
Egeblad M, Werb Z (2002) New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:161–174
Murphy G (2008) The ADAMs: signalling scissors in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer 8:929–941
Bidard FC, Pierga JY, Vincent-Salomon A, Poupon MF (2008) A “class action” against the microenvironment: do cancer cells cooperate in metastasis? Cancer Metastasis Rev 27:5–10
De Wever O, Mareel M (2003) Role of tissue stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol 200:429–447
Bhowmick NA, Neilson EG, Moses HL (2004) Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature 432:332–337
Sanz-Moreno V, Gaggioli C, Yeo M, Albrengues J, Wallberg F, Viros A, Hooper S, Mitter R, Feral CC, Cook M et al (2011) ROCK and JAK1 signaling cooperate to control actomyosin contractility in tumor cells and stroma. Cancer Cell 20:229–245
Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C, Grosse R, Marshall JF, Harrington K, Sahai E (2007) Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat Cell Biol 9:1392–1400
Maeda M, Johnson KR, Wheelock MJ (2005) Cadherin switching: essential for behavioral but not morphological changes during an epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition. J Cell Sci 118:873–887
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S, Hu GF (2009) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in metastasis. Cancer Res 69:7135–7139
Lopez-Schier H, Starr CJ, Kappler JA, Kollmar R, Hudspeth AJ (2004) Directional cell migration establishes the axes of planar polarity in the posterior lateral-line organ of the Zebrafish. Dev Cell 7:401–412
Lecaudey V, Cakan-Akdogan G, Norton WH, Gilmour D (2008) Dynamic Fgf signaling couples morphogenesis and migration in the Zebrafish lateral line primordium. Development 135:2695–2705
Hava D, Forster U, Matsuda M, Cui S, Link BA, Eichhorst J, Wiesner B, Chitnis A, Abdelilah-Seyfried S (2009) Apical membrane maturation and cellular rosette formation during morphogenesis of the Zebrafish lateral line. J Cell Sci 122:687–695
Loureiro JJ, Akong K, Cayirlioglu P, Baltus AE, DiAntonio A, Peifer M (2001) Activated armadillo/beta-catenin does not play a general role in cell migration and process extension in Drosophila. Dev Biol 235:33–44
Pinheiro EM, Montell DJ (2004) Requirement for Par-6 and Bazooka in Drosophila border cell migration. Development 131:5243–5251
Bastock R, Strutt D (2007) The planar polarity pathway promotes coordinated cell migration during Drosophila oogenesis. Development 134:3055–3064
Kim SH, Yamamoto A, Bouwmeester T, Agius E, Robertis EM (1998) The role of paraxial protocadherin in selective adhesion and cell movements of the mesoderm during Xenopus gastrulation. Development 125:4681–4690
Yoder MD, Gumbiner BM (2011) Axial protocadherin (AXPC) regulates cell fate during notochordal morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 240:2495–2504
Schneider S, Herrenknecht K, Butz S, Kemler R, Hausen P (1993) Catenins in Xenopus embryogenesis and their relation to the cadherin-mediated cell–cell adhesion system. Development 118:629–640
Borchers A, David R, Wedlich D (2001) Xenopus cadherin-11 restrains cranial neural crest migration and influences neural crest specification. Development 128:3049–3060
McCusker C, Cousin H, Neuner R, Alfandari D (2009) Extracellular cleavage of cadherin-11 by ADAM metalloproteases is essential for Xenopus cranial neural crest cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 20:78–89
Ciesiolka M, Delvaeye M, Van Imschoot G, Verschuere V, McCrea P, van Roy F, Vleminckx K (2004) p120 catenin is required for morphogenetic movements involved in the formation of the eyes and the craniofacial skeleton in Xenopus. J Cell Sci 117:4325–4339
Rangarajan J, Luo T, Sargent TD (2006) PCNS: a novel protocadherin required for cranial neural crest migration and somite morphogenesis in Xenopus. Dev Biol 295:206–218
Acknowledgments
This investigation was supported by grants from MRC, BBSRC, and Wellcome Trust to RM and the Wellcome Trust Value in People award to ET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theveneau, E., Mayor, R. Collective cell migration of epithelial and mesenchymal cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 3481–3492 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1251-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1251-7