Abstract:
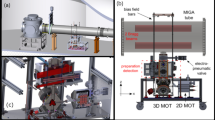
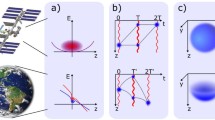
We describe the operation of a cold atom clock in reduced gravity. We have recorded the cesium hyperfine resonance signal at a frequency near 9.2 GHz in the gravity environment produced by jet plane parabolic flights. With a resonance width of 7 Hz, the device operated in a regime which is not accessible on earth. In the much lower gravity level of a satellite, our cold cesium clock would outperform the fountains with a potential accuracy of . This experiment paves the way to unprecedented performance in space applications such as tests of general relativity, global time dissemination, astronomy and geodesy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 June 1998 / Accepted: 18 June 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laurent, P., Lemonde, P., Simon, E. et al. A cold atom clock in absence of gravity. Eur. Phys. J. D 3, 201–204 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00021584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00021584