Abstract
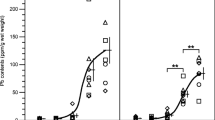
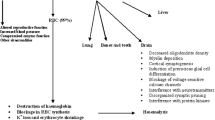
The influence of lead exposure, iron deficiency, or their combination on certain biochemical parameters in blood, plasma, and urine of rats was investigated in an attempt to identify the specific diagnostic tests of the two conditions and to draw a possible interrelationship between the two factors. The decrease in blood-glutathione peroxidase activity,-packed cell volume, plasma-ceruloplasmin, and-Fe levels and increase in urinary excretion of δ-aminolevulinic acid, plasma-cholesterol, and-total Fe binding capacity occur under Fe deficiency as well as Pb intoxication. However, increase in the activity of blood δ-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase (ALAD) without any change in blood zinc protoporphyrin (ZPP) level appears to be a specific effect of Fe deficiency that could be distinguished from Pb intoxication, a condition characterized by the inhibition in blood ALAD activity accompanied by an increase in blood ZPP level. The linear regression analysis of the data showed that the blood Pb and plasma free cholesterol levels increase with the decrease in plasma Fe level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. O. Nriagu,Nature 279, 409 (1979).
A. J. Verlangieri,Pharmac. Biochem. Behav. 11, 95 (1979).
K. M. Six and R. A. Goyer,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 79, 128 (1972).
H. A. Ragan,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 90, 700 (1977).
M. Clark, J. Royal, and R. Seeler,Pediatrics 81, 247 (1988).
A. Berlin and K. H. Schaller,Z. Klin. Chem. Klin. Biochem. 12, 389 (1974).
P. Grandjean,Brit. J. Ind. Med. 36, 52 (1979).
J. W. Clegg and E. J. King,Brit. Med. J. 2, 329 (1942).
C. A. Keele and E. Neil,Applied Physiology, 2nd edition, S. Wright, ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1966, p. 12.
D. E. Paglia and W. N. Valentine,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70, 158 (1979).
D. W. Yeager, J. Cholak, and E. W. Henderson,Environ. Sci. Technol. 5, 1020 (1971).
A. Zlalkis, B. Zak, and A. J. Boyle,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 41, 486 (1953).
G. Curzon and L. Vallet,Biochem. J. 74, 279 (1960).
T. Peters, T. J. Giovanniello, L. Apt, and J. F. Ross,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 48, 280 (1956).
J. R. Davies, R. H. Abrahams, W. I. Fishbein, and E. A. Fabrega,Arch. Environ. Hlth. 17, 164 (1968).
T. D. V. Swinscow,Statistics at Square One, British Medical Association, London, 1978, p. 62.
R. F. Labbe and C. A. Finch,Biochem. Med. 18, 323 (1977).
G. Chalevelakis, C. Lyberatos, D. Manopoulos, J. Pyrovolakis, C. Gardikas,Acta Haematol. 57, 305 (1977).
J. Onisawa and R. F. Labbe,Biochem. Biophys. Acta 56, 618 (1962).
W. Vogel, D. A. Richert, B. Q. Pixley, and M. Schulman,J. Biol. Chem. 235, 1768 (1960).
G. L. Curran,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 88, 101 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hashmi, N.S., Kachru, D.N. & Tandon, S.K. Interrelationship between iron deficiency and lead intoxication (part 1). Biol Trace Elem Res 22, 287–297 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916617
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02916617