Abstract
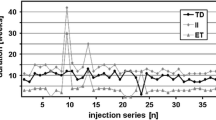
Botulinum toxin type A (BoNT/A) is the principal therapy for patients with cervical dystonia. Repeated treatments over many years are required in most cases. This retrospective review evaluates the dose of BoNT/A used to treat cervical dystonia and the interval between treatments during a 2-year observation period. Outcomes data were abstracted from the medical records of 172 patients at 3 different sites who had received BoNT/A between January and December 1998. A total of 1059 treatments were assessed. Mean per-treatment doses throughout the 2-year study ranged from 241.80 to 254.07 units. The mean interval between treatments was 108.48 days during the first year of observation and 114.14 days during the second year. These findings indicate that doses of and intervals between BoNT/A treatments for cervical dystonia were consistent throughout 2 years of observation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jahanshahi M, Marion M.H, Marsden C.D. Natural history of adult-onset idiopathic torticollis.Arch Neurol. 1990;47:548–552.
Dauer WT, Burke RE, Greene P, Fahn S. Current concepts on the clinical features, aetiology and management of idiopathic cervical dystonia.Brain. 1998;121(pt 4):547–560.
Jankovic J, Schwartz K. Response and immunoresistance to botulinum toxin injections.Neurology. 1995;45:1743–1746.
Tsui JK, Eisen A, Stoessl AJ, Calne S, Calne DB. Double-blind study of botulinum toxin in spasmodic torticollis.Lancet. 1986;2(8501):245–247.
Brans JW, Lindeboom R, Aramideh M, Speelman JD. Long-term effect of botulinum toxin on impairment and functional health in cervical dystonia.Neurology. 1998;50:1461–1463.
Naumann M, Yakovleff A, Durif F. A randomized, double-masked, crossover comparison of the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A produced from the original bulk toxin source and current bulk toxin source for the treatment of cervical dystonia.J Neurol. 2002;249:57–63.
Hilker R, Schischniaschvili M, Ghaemi M, Jacobs A, Rudolf J. Health related quality of life is improved by botulinum neurotoxin type A in long term treated patients with focal dystonia.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001;71:193–199.
Brashear A, Watts MW, Marchetti A, Magar R, Lau H, Wang L. Duration of effect of botulinum toxin type A in adult patients with cervical dystonia: a retrospective chart review.Clin Ther. 2000; 22:1516–1524.
Tan EK, Jankovic J. Botulinum toxin A in patients with oromandibular dystonia: long-term follow-up.Neurology. 1999;53:2102–2107.
Mehta RP, Goldman SN, Orloff LA. Long-term therapy for spasmodic dysphonia: acoustic and aerodynamic outcomes.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;127:393–399.
Hsiung GY, Das SK, Ranawaya R, Lafontaine AL, Suchowersky O. Long-term efficacy of botulinum toxin A in treatment of various movement disorders over a 10-year period.Mov Disord. 2002;17:1288–1293.
Defazio G, Abbruzzese G, Girlanda P, et al. Botulinum toxin A treatment for primary hemifacial spasm: a 10-year multicenter study.Arch Neurol. 2002;59:418–420.
Jankovic J, Schwartz KS. Longitudinal experience with botulinum toxin injections for treatment of blepharospasm and cervical dystonia.Neurology. 1993;43:834–836.
Greene P, Fahn S, Diamond B. Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis.Mov Disord. 1994;9:213–217.
BOTOX® (Botulinum Toxin Type A) Purified Neurotoxin Complex prescribing information. Allergan, Inc, Irvine, Calif, 2000.
Jankovic J, Ahsan J, Vuong KD. Comparison of efficacy and immunogenicity of original versus current botulinum toxin in cervical dystonia.Neurology. 2003;60:1186–1188.
Dressler D, Munchau A, Bhatia KP, Quinn NP, Bigalke H. Antibody-induced botulinum toxin therapy failure: can it be overcome by increased botulinum toxin doses?Eur Neurol. 2002;47: 118–121.
Dutton JJ, Buckley EG. Long-term results and complications of botulinum A toxin in the treatment of blepharospasm.Ophthalmology. 1988;95:1529–1534.
Dodel RC, Kirchner A, Koehne-Volland R, et al. Costs of treating dystonias and hemifacial spasm with botulinum toxin A.Pharmacoeconomics. 1997;12:695–706.
Hauser RA, Comella C, Brashear A, et al. A randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of original Botox (botulinum toxin type A) purified neurotoxin complex for the treatment of cervical dystonia [abstract].Mov Disord. 2000;15(suppl 2):30–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brashear, A., Hogan, P., Wooten-Watts, M. et al. Longitudinal assessment of the dose consistency of botulinum toxin type a (BOTOX®) for cervical dystonia. Adv Therapy 22, 49–55 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850184
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02850184