Abstract
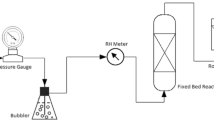
One of the promising technologies for reducing metals emission from the waste thermal process is the capture of vapor-phase metals through the use of solid sorbents. This study investigated the use of natural kaolinite for the removal of several volatile metals. The capture of cadmium and lead using a packed bed with porous kaolinite of the size range 300-400 Μm was effective. The capturing efficiency increased as the bed temperature increased. The ratio of the sorption reaction rate to the diffusion rate varied on the 10-2 order of magnitude. This suggests that the resistance of the diffusion within the pores of kaolinite particles is not significant in the selection of sorbent particle size for practice. The capturing mechanism for cadmium chloride is different from that for lead chloride. Cadmium can be reactively scavenged by CdO-Al2O3-2SiO2 as well as metakaolinite, suggesting that a unit mole of metakaolinite can ultimately capture two moles of cadmium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, H. N., “Effectiveness Factor for Two-step Consecutive Biochemical Reactions with Immobilized Biocatalysts”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,1,43 (1994).
Davison, R. L., Natusch, D. F. S. and Wallace, J. R., “Trace Elements in Fly Ash Dependence of Concentration on Particle Size,”Environ. Sci. Technol,8,1107 (1974).
Ghosh-Dastidar, A., Mahuli, S., Agnihotri, R. and Fan, L. S., “Selenium Capture Using Sorbent Powders: Mechanism of Sorption by Hydrated Lime,”Environ. Sci. Technol,30,447 (1996).
Ho, T. C, Tan, L., Chen, C. and Hopper, J. R., “Characteristics of Metal Capture during Fluidized Bed Incineration,”AIChE Symposium Series,87,118 (1991).
Ho, T. C, Chen, C, Hopper, J. R. and Oberacker, D. A., “Metal Capture during Fluidized Bed Incineration of Waste Contaminated with Lead Chloride,”Combust. Sci. & Technol.,85, 101 (1992).
Ho, T C, Wang, S. K. and Hopper, J. R., “Effects of Chlorine and Sulfur on Metal Capture by Sorbents during Fluidized Bed Incineration,” Proc. of 1996 International Conf. on IT3, Savannah, Georgia, USA, 415 (1996).
Lee, H. T, Ho, T C, Hsiao, C. C. and Bostick, W D., “Study of Metal Volatilization from Contaminated Soil in a Fluidized Bed Incinerator” Proc. of 1996 International Conf. on IT3, Savannah, Georgia, USA, 561 (1995).
Linak, W P. and Wendt, J. O. L., “Toxic Metal Emissions from Incineration: Mechanisms and Control,”Progr. Energy Combust. Sci,19,145 (1993).
Mahuli, S., Agnihotri, R., Chauk, S., Ghosh-Dastidar, A. and Fan, L. S., “Mechanisms of Arsenic Sorption by Hydrated Lime,”Environ. Sci. Technol,31, 3226 (1997).
Moon, S. K. and Won, Y. S., “Isothermal Interphase Diffusion with Consecutive Reactions,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,2,45 (1985).
Palmer, S. A. K., Breton, M. N., Nunno, T. J., Sulivan and Supreant, N. F, Thermal Destruction/Recovery Process, Metal/Cyanide Containing Wastes: Treatment Technologies, 532 (1998).
Park, H. C. and Moon, H., “Effect of Adsorptive Gaseous Reaction on Non-isothermal Behavior for Gas-Solid Reactions,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,1,165 (1994).
Perry, R. H. and Green, D., “Perry’s Chemical Engineers, Handbook,” McGraw-Hill, INC., 6, 3/285 (1984).
Satterfield, C. N., “Heterogeneous Catalysis in Industrial Practice” McGraw-Hill, INC., 2,471 (1993).
Scotto, M. A., Peterson, T. W. and Wendt, J. O. L., “Hazardous Waste Incineration: in Situ Capture of Lead by Sorbent in a Laboratory Down-Flow Combustor,” 24th International Symposium on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, Pittsburgh, 1109 (1992).
Sherwood, T. K., Pigford, R. L. and Wilke, C. R., “Mass Transfer,” McGraw-Hill Chemical Engineering Series, 319 (1975).
U. S. DOE, “Simultaneous High-Temperature Removal of Alkali and Particulates in a Pressurized Gasification System,” FE-3245-9,115 (1978-1979).
Uberoi, M. and Shadman, F., “Sorbents for Removal of Lead Compounds from Hot Flue Gases,”AIChE J.,36, 306 (1990).
Uberoi, M., Punjak, W. A. and Shadman, F., “High Temperature Adsorption of Alkali Vapors on Solid Sorbents,”AIChE J.,35, 1186 (1989).
Uberoi, M., Punjak, W. A. and Shadman, F, “The Kinetics and Mechanism of Alklali Removal from Flue Gas by Solid Sorbents,”Progr. Energy Combust. Sci.,16, 205 (1990).
Uberoi, M. and Shadman, F, “High-Temperature Removal of Cadmium Compounds Using Sorbents,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,25, 1285 (1991).
U. S. EPA, “Operational Parameters for Hazardous Waste Combustion Devices,” EPA/625/R-93/008, 62–63 (1993).
Vidic, R. D., “Removal of Mercury from the Stack Gases by Active Carbon,”21th Annual RREL Research Symposium, EPA/600/R-95/012,103 (1995).
Wouterlood, H. J. and Bowling, K. M., “Removal and Recovery of Arsenious Oxide from Flue Gases,”American Chemical Society, 13, 93 (1979).
Wu, B., Jaanu, K. K. and Shadman, F, “Multi Functional Sorbents for the Removal of Sulfur and Metallic Contaminants from High Temperature Gases,”Environ. Sci. Technol.,29,1660 (1995).
Yang, H. C, Kim, J. H., Oh, W. J., Park, H. S. and Seo, Y. C, “Behavior of Hazardous and Radioactive Metals in a Laboratory Furnace and a Demonstration-Scale Incinerator,”Environ. Eng. Sci.,15, 299 (1998).
Yang, H. C, Kim, J. H., Seo, Y. C. and Kang, Y, “Gas-phase Resistance to the Vaporization of Mercuric Halides in High-Temperature Atmospheric Gaseous Condition,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,13,261 (1996).
Yang, H. C, Kim, J. H., Seo, Y C. and Kang, Y, “Vaporization Characteristics of Heavy Metal Compounds at Elevated Temperatures,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,11, 232 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, HC., Yun, JS., Kang, MJ. et al. Capture of volatile hazardous metals using a bed of kaolinite. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 16, 646–653 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708146
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708146