Abstract
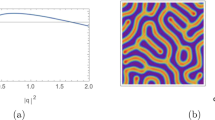
We apply the concept of marginal stability hypothesis, which has been proposed for solving the problem of dendritic crystal growth, to the pattern selection problem in the Gierer-Meinhardt models. In the case of a large system, the system selects a definite wavelength of the ultimate spatial pattern when the unstable homogeneous steady state is locally disturbed. The numerical results are analyzed theoretically by means of the marginal stability hypothesis, and they are in good agreement with it.
Biologically, these results imply why for large systems the Gierer-Meinhardt model (and presumably other reaction-diffusion schemes) have the ability to explain the observation that pattern-generating mechanisms are remarkably insensitive to a wide range of environmental and experimental conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Arcuri, P. and J. D. Murray. 1986. “Pattern Sensitivity to Boundary and Initial Conditions in Reaction-Diffusion Models”.J. math. Biol. 24, 141–165.
Ben-Jacob, E., H. Brand, G. Dee, L. Kramer and J. S. Langer. 1985. “Pattern Propagation in Nonlinear Dissipative Systems”.Physica 14D, 348–364.
Berding, C. and H. Haken. 1982. “Pattern Formation in Morphogenesis: Analytical Treatment of the Gierer-Meinhardt Model on a Sphere”.J. math. Biol. 14, 133–151.
Fife, P. C. 1979.Mathematical Aspects of Reacting and Diffusing Systems. Berlin: Springer.
Gierer, A. and H. Meinhardt. 1972. “A Theory of Biological Pattern Formation”.Kybernetik 12, 30–39.
— 1981. “Generation of Biological Patterns and Form: Some Physical, Mathematical, and Logical Aspects”.Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 37, 1–47.
Haken, H. 1981. “Synergetics and the Problem of Self-organization”. InSelf-Organizing Systems, G. Roth and H. Schwegler (Eds), pp. 9–13. Frankfurt: Campus.
Kramer, L., E. Ben-Jacob, H. Brand and M. C. Cross. 1982. “Wavelength Selection in Systems far from Equilibrium”.Phys. Rev. Lett. 49, 1891–1894.
— and R. Hermann. 1985. “Wavelength Selection in Rayleigh-Benard Convection”.Z. Phys. B59, 245–251.
Langer, J. S. 1980. “Instabilities and Pattern Formation in Crystal Growth”.Rev. Mod. Phys. 52, 1–28.
— and H. Muller-Krumbhaar. 1983. “Mode Selection in a Dendrite-Like Nonlinear System”.Phys. Rev. A27, 499–514.
Meinhardt, H. 1982.Models of Biological Pattern Formation. London: Academic Press.
Segel, L. A. 1984.Modelling dynamic phenomena in molecular and cellular biology. Cambridge.
Tarumi, K. 1987. “A Partial Differential Equation as a Model of Wavenumber Selection”. Fachberichte Physik der Universität Bremen, Report No. 38. ISSN 0724-1941.
— and H. Schwegler. 1987. “A Nonlinear Treatment of the Protocell Model by a Boundary Layer Approximation”.Bull. math. Biol. 49, 307–320.
Turing, A. M. 1952. “The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis”.Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B237, 37–72.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarumi, K., Mueller, E. Wavelength selection mechanism in the Gierer-Meinhardt model. Bltn Mathcal Biology 51, 207–216 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458442
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02458442