Summary
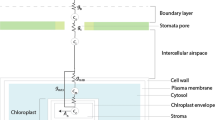
The vapor pressure difference between H2 18O and H2 16O is the reason for the accumulation of the heavy molecule in transpiring leaves. Since photosynthesis on land is the main source of atmospheric oxygen, this mechanism is important for the remarkable enrichment of18O in atmospheric O2 (Dole effect). Using a simple box model for transpiring leaves a quantitative understanding of the isotope fractionation is possible which is well confirmed by the results of model experiments as well as by measurements on trees. Maximum enrichment of H2 18O in the water of leaves (relative to soil water) is 25 ‰ (theoretically, for dry air) and was found under natural conditions to be 21 ‰ (for 28 % relative humidity); minimum theoretical enrichment is zero (observed 2.5 ‰).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baertschi, P., Thürkauf, M.: Isotopie-Eifekt bei der Trennung der Sauerstoff-Isotopen16O und18O bei der Rektifikation von leichtem und schweren Wasser. Helv. Chim. Acta43, 80–89 (1969)
Brutsaert, W.: A model for evaporation as a molecular diffusion process into a turbulent atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res.70, 5017–5024 (1965)
Craig, H.: Standard for reporting concentrations of deuterium and oxygen-18 in natural waters. Science 133, 1833–1834 (1961)
Craig, H., Gordon, L. I., Horibe, Y.: Isotopic exchange effects in the evaporation of water. J. Geophys. Res.68, 5079–5087 (1963)
Deissler, R. G.: Analysis of turbulent heat transfer, mass transfer, and friction in smooth tubes at high Prandtl and Schmidt-numbers. U.S. National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics. Report 1210 (1955)
Dongmann, G.: Die H2 18O-Anreicherung in den Blättern transpirierender Pflanzen und ihre Bedeutung für die stationäre18O-Überhöhung in der Atmosphäre. Thesis, TH Aachen 1973
Dongmann, G., Förstel, H., Wagener, K.:18O-rich oxygen from land photosynthesis. Nature (Lond.) New Biol.240, 127–128 (1972)
Ehhalt, D., Knott, K.: Kinetische Isotopentrennung bei der Verdampfung von Wasser. Tellus17, 389–397 (1965)
Gonfiantini, R., Gratziu, S., Tongiorgi, E.: Oxygen isotopic composition of water in leaves. In: Use of isotopes and radiation in soil-plant nutrition studies, p. 405. Wien: IAEA 1965
Harriot, P.: A random eddy modification of the penetration theory. Chem. Ing. Sci.17, 149–154 (1962)
Harriot, P.: A review of mass transfer to interfaces. Can. J. Chem. Eng.40, 60–69 (1962)
Lane, G. A., Dole, M.: Fractionation of oxygen isotopes during respiration. Science123, 574–576 (1956)
Merlivat, L.: L'étude quantitative de bilans de lacs à l'aide des concentrations en deuterium et oxygéne-18 dans l'eau. In: Isotopes in hydrology, p. 89. Wien: IAEA 1970
Pasquill, F.: Evaporation from a plane, free-liquid surface into a turbulent air stream. Proc. Roy. Soc. (London) A182, 75–95 (1943)
Prüger, W.: Die Verdampfungsgeschwindigkeit der Flüssigkeiten. Z. Physik115, 202–244 (1940)
Roether, W.: Estimating the tritium input to ground-water from wine samples: ground-water and direct run-off contribution to central european surface waters. In: Isotopes in hydrology, p. 73. Wien: IAEA 1967
Van den Honert, T. H.: Water transport as a catenary process. Discussions Faraday Soc.3, 146–153 (1948)
Wagener, K.: Isotopenfraktionierung im Sauerstoffzyklus der Erde. Z. Naturforsch.29A, (1974) (in press)
Zimmermann, U., Ehhalt, D., Münnich, K. O.: Soil-water movement and evapotranspiration: changes in the isotopic composition of the water. In: Isotopes in hydrology, p. 567. Wien: IAEA 1967
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dongmann, G., Nürnberg, H.W., Förstel, H. et al. On the enrichment of H2 18O in the leaves of transpiring plants. Radiat Environ Biophys 11, 41–52 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01323099
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01323099