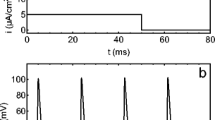
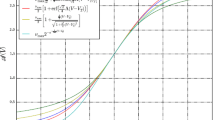
Abstract
Excitable membranes allow cells to generate and propagate electrical signals. In the nervous system these signals transmit information, in muscle they trigger contraction, and in heart they regulate spontaneous beating. A central question in excitability theory concerns the relationship between the aggregate properties of membranes (marcoscopic) and the properties of channels in the membranes (mircoscopic). Hodgkin and Huxley (1952) laid the foundations of membrane excitability, and Neher and Sakmann (1976) developed techniques to study individual channels. This article focuses on the relationship between the macroscopic domain, in which non-linear differential equations determine the electrical properties of cells, and the microscopic domain, in which the probabilistic nature of channels establishes the pattern of activity. Using nerve cell membranes as an example, we examine how information in one domain predicts behavior in the other. We conclude that the probabilistic nature of channels generates virtually all macroscopic electrical properties, including resting potentials, action potentials, spontaneous firing, and chaos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. M. Armstrong, Inactivation of the potassium conductance and related phenomena caused by quaternary ammonium ion injected in squid axons,J. Gen. Physiol. 54:553–575 (1969).
D. R. Chialvo, R. F. Gilmour, Jr., and J. Jalife, Low dimensional chaos in cardiac tissue,Nature 343:653–657 (1990).
J. R. Clay and R. L. DeHaan, Fluctuations in interbeat interval in rhythmic heart-cell clusters: Role of membrane voltage noise,Biophys. J. 28:377–390 (1979).
J. R. Clay and L. J. DeFelice, Relationship between membrane excitability and single channel open-close kinetics,Biophys. J. 42:151–157 (1983).
F. Conti, Noise analysis and single-channel recordings,Curr. Top. Membrane Trans. 22:371–105 (1984).
F. Conti and E. Wanke, Channel noise in membranes and lipid bilayers,Q. Rev. Biophys. 8:451–506 (1975).
F. Conti, L. J. DeFelice, and E. Wanke, Postassium and sodium ion current noise in the membrane of the squid giant axon,J. Physiol. (London)248:45–82 (1975).
F. Conti and E. Neher, Single channel recordings of K currents in squid axon,Nature 285:140–143 (1980).
L. J. DeFelice, Fluctuation analysís in neurobiology,Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 20:169–208 (1977).
L. J. DeFelice,Introduction to Membrane Noise (Plenum Press, New York, 1981).
L. J. DeFelice, W. J. Adelman, Jr., D. E. Clapham, and A. Mauro, Second-order admittance in squid axon, inThe Biophysical Approach to Excitable Systems, W. J. Adelman, Jr. and D. E. Goldman, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1981).
L. J. DeFelice and J. Clay, Membrane channel and membrane potential from single-current kinetics, inSingle-Channel Recording, B. Sakmann and E. Neher, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1983).
L. J. DeFelice, W. N. Goolsby, and D. Huang, Membrane noise and excitability, inNoise in Physical Systems, A. D'Amico and P. Mazzetti, eds. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1985).
L. J. DeFelice, Noise biological membranes, inNoise in Physical Systems, A. Ambrozy, ed. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1989).
L. J. DeFelice, Molecular biology and biophysics of Ca channels: A hypothesis concerning oligomeric structure, channel clustering, and macroscopic current, inNeural Engineering, Y. Kim and X. Thakor, eds. (Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, 1992).
G. Ehrenstein, H. Lecar, and R. Nossal, The nature of the negative resistance in bimolecular lipid membranes containing excitability inducing material,J. Gen. Physiol. 55:119–133 (1970).
G. Ehrenstein and H. Lecar, Electrically gated ionic channels in lipid bilayers,Q. Rev. Biophys. 10:1–34 (1977).
G. Feher, Emerging techniques: Fluctuation spectroscopy, inTrends in Biochemical Sciences (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1978), Vol. 3, pp. 111–113.
R. FitzHugh, A kinetic model of the conductance changes in nerve membrane,J. Cell Comp. Physiol. 66:111–118 (1965).
J. R. Guevara, A. C. G. van Ginneken, and H. J. Jongsma, Patterns of activity in a reduced ionic model of a cell from the rabbit sinoatrial node, inChaos in Biological Systems, H. Degn, A. V. Holde, and L. F. Olsen, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1987).
J. R. Guevara, Mathematical modeling of the electrical activity of cardiac cells, inTheory of Heart, L. Glass, P. Hunter, and A. McCullogh, eds. (Springer, New York, 1990).
T. L. Hill and Y.-D. Chen, On the theory of ion transport across nerve membrane IV: Noise from the open-close kinetics of K channels,Biophys. J. 12:948–959 (1972).
B. Hille,Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes (Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 1992).
A. L. Hodgkin and A. F. Huxley, A qualitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction in nerve,J. Physiol. 177:440–544 (1952).
T. J. Lewis and M. R. Guevara, Chaotic dynamics in an ionic model of the propagated cardiac action potential,J. Theor. Biol. 146:407–32 (1990).
L. S. Liebovitch and T. I. Toth, A model of ion channel kinetics using deterministic chaotic rather than stochastic processes,J. Theor. Biol. 148:243–267 (1991).
L. S. Liebovitch, Interpretation of protein structure and dynamics from the statistics of the open and closed times measured in a single ion-channel protein,J. Stat. Phys. 70:329–337 (1993).
I. Llano, C. K. Webb, and F. Bezanilla, Potassium conductance of the squid giant axon,J. Gen. Physiol. 92:179–196 (1988).
M. Mazzanti, L. J. DeFelice, Y. M. Liu, Gating of L-type Ca currents in embryonic chick ventricle-cells: Dependence on voltage, current, and channel density,J. Physiol. 443:307–334 (1991).
E. Neher and B. Sakmann, Single-channel currents recorded from membrane of denervated frog muscle fibres,Nature 260:779–802 (1976).
E. Neher and C. F. Stevens, Conductance fluctuations and ionic pores in membranes,Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 6:345–381 (1977).
B. Neumcke, 1/f noise in membranes,Biophys. Struct. Mech. 4:179–199 (1978).
B. Neumcke, Fluctuation of Na and K currents in excitable membranes,Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 23:35–67 (1982).
B. Sakmann and E. Neher,Single-Channel Recording (Plenum Press, New York, 1984).
F. L. Sigworth and E. Neher, Single Na channel currents observed in cultured rat muscle cells,Nature 287:447–449 (1980).
C. F. Stevens, Inferences about membrane properties from electrical noise measurements,Biophys. J. 12:1028–1047 (1972).
C. F. Stevens, Principles and applications of fluctuation analysis: A non-mathematical introduction,Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 34:1364–1370 (1975).
A. A. Verveen and L. J. DeFelice, Membrane noise,Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 28:189–265 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DeFelice, L.J., Isaac, A. Chaotic states in a random world: Relationship between the nonlinear differential equations of excitability and the stochastic properties of ion channels. J Stat Phys 70, 339–354 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053972
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053972