Summary
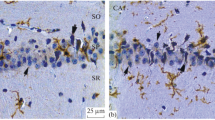
Wistar rats of both sexes and the same litter were exposed to chronic lead intoxication from birth untill sacrifice 9 months later. Lead was administered as 0.4% solution of lead nitrate in drinking water. Samples from the parietal brain cortex were examined electron microscopically following intracardiac perfusion with paraformaldehyde-glutaraldehyde solution. Similar changes were observed in the microglial cells and the vascular pericytes whereas all the other tissue elements appeared intact. Both cell types hypertrophied, the microglia assumed characteristic spindle or rod shape, the cell organelles increased, the microglial endoplasmic reticulum widened strongly and a large number of lipid inclusions appeared. The latter consisted of large lipid droplets of varying size and shape, containing multiple zones of low density, and a dense component with a coarse granular structure. The similarity in the response of both cell entities to the lesion as well as some probable functions of microglial cells and their relationship to vascular pericytes are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, E. K., Jr.: Cell division in injured spinal cord. Amer. J. Anat.123, 501–520 (1968)
Adrian, E. K., Jr., Smothermon, R. D.: Leucocytic infiltration into the hypoglossal nucleus following injury to the hypoglossal nerve. Anat. Rec.166, 99–116 (1970)
Baron, M., Gallego, A.: The relation of the microglia with the pericytes in the cat cerebral cortex. Z. Zellforsch.128, 42–57 (1972)
Barron, K. D., Doolin, P. F.: Ultrastructural observations on retrograde atrophy of lateral geniculate body. II. The environs of the neuronal somata. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.27, 401–420 (1968)
Bignami, A., Ralston, III, H. J.: The cellular reaction to Wallerian degeneration in the central nervous system of the cat. Brain Res.13, 444–461 (1969)
Blakemore, W. F.: The ultrastructure of the subependymal plate in the rat. J. Anat. (Lond.)104, 423–433 (1969)
Blakemore, W. F.: Microglial reaction following thermal necrosis of the rat cortex. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)21, 11–22 (1972)
Blinzinger, K.: Elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen bei experimentell erzeugter Randzonensiderose des Kaninchengehirns. Acta neuropath. (Berl.) Suppl.IV, 146–157 (1968)
Blinzinger, K., Hager, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen über die Feinstruktur rehender und progressiver, Mikroglialzellen im Säugetierhirn. Beitr. path. Anat.127, 173–192 (1962)
Blinzinger, K., Hager, H.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Feinstruktur ruhender und progressiver Mikrogliazellen im ZNS des Goldhamsters. In: W. Bargmann and J. P. Schadé (Eds.): Progress in brain research, vol. 6, pp. 92–112. Amsterdam-London-New York: Elsevier Publ. Comp. 1964
Blinzinger, K., Kreutzberg, G.: Displacement of synaptic terminals from regenerating motoneurons by microglial cells. Z. Zellforsch.85, 145–157 (1968)
Bodian, D.: An electron microscopic study of the monkey spinal cord. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp.114, 13–119 (1964)
Cammermeyer, J.: Juxtavascular karyokinesis and microglia cell proliferation during retrograde reaction in the mouse facial nucleus. Ergebn. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch.38, 1–22 (1965a)
Cammermeyer, J.: Endothelial and intramural karyokinesis during retrograde reaction in the facial nucleus of rabbits of varying age. Ergebn. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch.38, 23–45 (1965b)
Cammermeyer, J.: Histiocytes, juxtavascular mitotic cells and microglia cells during retrograde changes in the facial nucleus of rabbits of varying age. Ergebn. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch.38, 195–229 (1965c)
Cammermeyer, J.: Microglia cells in diffuse and granulomatous encephalitis in the rabbit. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)7, 261–274 (1967)
Cancilla, P. A., Baker, R. N., Pollock, P. S., Frommes, S. P.: The reaction of pericytes of the central nervous system to exogenous protein. Lab. Invest.26, 376–383 (1972)
Clasen, R. A., Pandolfi, S., Coogan, P. S., Laing, I., Becker, R. A., Hartmann, J. F.: Ultrastructural studies in experimental lead encephalopathy. Amer. J. Path.66, 1a-2a (1972)
Del Rio Hortega, P.: Microglia. In: W. Penfield (Ed.). Cytology and cellular pathology of the nervous system, pp. 482–534. New York: P. B. Hoeber Inc. 1932
Dimova, R. N., Markov, D. V.: Microglia and small blood vessels in proximity to a stab wound of rat brain cortex. (In preparation) (1973)
Hager, H.: Pathologie der Makro- und Mikroglia im elektronenmikroskopischen Bild. Acta neuropath. (Berl.) Suppl.IV, 86–97 (1968)
Holländer, H., Brodal, P., Walberg, F.: Electron microscopic observations on the structure of the pontine nuclei and the mode of termination of the corticopontine fibres. An experimental study in the cat. Exp. Brain. Res.7, 95–110 (1969)
Karnovsky, M. J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol27, 137A-138A (1965)
Kitamura, T., Hattory, H., Fujita, S.: Autoradiographic studies on histogenesis of brain macrophages in the mouse. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.31, 502–518 (1972)
Konigsmark, B. W., Sidman, R. L.: Origin of brain macrophages in the mouse. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.22, 643–675 (1963)
Kreutzberg, G. W.: Über perineuronale Mikrogliazellen. (Autoradiographische Untersuchungen.) Acta neuropath. (Berl.) Suppl.IV, 141–145 (1968)
Kruger, L., Maxwell, D. S.: Electron microscopy of oligodendrocytes in normal rat cerebrum. Amer. J. Anat.118, 411–436 (1966)
Lampert, P., Garro, F., Pentschew, A.: Lead encephalopathy in suckling rats. In: I. Klatzo and F. Seitelberger (Eds.): Brain edema, pp. 207–222 Wien-New York: Springer 1967
Markov, D.: Ultrastructure of microglia. In: G. Galabov (Ed.): The spinal cord, vol. 2, pp. 79–95 Sofia: Publishing House of Bulg. Acad. Sci. 1971 (Bulgarian text)
Maxwell, D. S., Kruger, L.: Small blood vessels and the origin of phagocytes in the rat cerebral cortex following heavy particle irradiation. Exp. Neurol.12, 33–54 (1965)
Maxwell, D. S., Kruger, L.: The reactive oligodendrocyte. An electron microscopic study of cerebral cortex following alpha particle irradiation. Amer. J. Path.118, 437–460 (1966)
Mori, S.: Cytological features and mitotic ability of microglia in the injured rat brain. Proc. VII Internat. Congress of Electron Microscopy, pp. 769–770. Grenoble 1970
Mori, S., Leblond, C. P.: Identification of microglia in light and electron microscopy. J. comp. Neurol.135, 57–80 (1969)
Oehmichen, M., Grüninger, H., Saebisch, R., Narita, Y.: Mikroglia und Pericyten als Transformationsformen der Blut-Monocyten mit erhaltener Proliferationsfähigkeit. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)23, 200–218 (1973)
Pentschew, A.: Intoxikationen. In: W. Scholz (Ed.): Handbuch der speziellen pathologischen Anatomie und Histologie, vol. 13, part 2, pp. 1929–1971. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1958
Pentschew, A.: Morphology and morphogenesis of lead encephalopathy. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)5, 133–160 (1965)
Pentschew, A., Garro, F.: Lead encephalomyelopathy of the suckling rat and its implications on the porphyrinopathic nervous diseases. With special reference to the permeability disorders of the nervous system's capillaries. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)6, 166–278 (1966)
Popoff, N., Weinberg, S., Feigin, I.: Pathological observations in lead encephalopathy with special reference to vascular changes. Neurology (Minneap.)13, 101–112 (1963)
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–213 (1963)
Sjöstrand, J.: Studies on the glial cells in the hypoglossal nucleus of the rabbit during nerve regeneration. Acta physiol. scand.67, Suppl. 270, 1–18 (1966a)
Sjöstrand, J.: Morphological changes in glial cells during nerve regeneration. Acta physiol. scand.67, Suppl. 270, 19–43 (1966b)
Sjöstrand, J.: Neuroglial proliferation in the hypoglossal nucleus after nerve injury. Exp. Neurol.30, 178–189 (1971)
Smith, B., Rubinstein, L. J.: Histochemical observations on oxidizing enzyme activity in reactive microglia and somatic macrophages. J. Path. Bact.83, 572–575 (1962)
Smith, M. L., Jr., Adrian, E. K., Jr.: On the presence of mononuclear leucocytes in dorsal root ganglia following transection of the sciatic nerve. Anat. Rec.172, 581–588 (1972)
Stensaas, R. L., Stensaas, S. S.: Astrocytic neuroglial cells, oligodendrocytes and microgliacytes in the spinal cord of the toad. II. Electron microscopy. Z. Zellforsch.86, 184–213 (1968)
Torvik, A., Skjörten, F.: Electron microscopic observations on nerve cell regeneration and degeneration after axon lesions. II. Changes in the glial cells. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)17, 265–282 (1971)
Torvik, A.: Phagocytosis of nerve cells during retrograde degeneration. An electron microscopic study. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.31, 132–146 (1972)
Vaughn, J. E.: Electron microscopic study of the vascular response to axonal degeneration in rat optic nerve. Anat. Rec.151, 428 A (1965)
Vaughn, J. E., Peters, A.: A third neuroglial cell type. An electron microscopic study. J. comp. Neurol.133, 269–287 (1968)
Vaughn, J. E.: An electron microscopic analysis of gliogenesis in rat optic nerves. Z. Zellforsch.94, 293–324 (1969)
Vaughn, J. E., Hinds, P. L., Skoff, R. P.: Electron microscopic studies of Wallerian degeneration in rat optic nerves. I. The multipotential glia. J. comp. Neurol.140, 175–206 (1970)
Wong-Riley, M. T. T.: Terminal degeneration and glial reactions in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the Squirrel Monkey after eye removal. J. comp. Neurol.144, 61–92 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markov, D.V., Dimova, R.N. Ultrastructural alterations of rat brain microglial cells and pericytes after chronic lead poisoning. Acta Neuropathol 28, 25–35 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687515
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00687515