Abstract
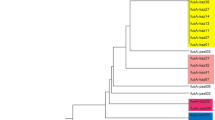
The systematics of theLactobacillus population of the intestines of 88 different rats was studied; 80 rats had been fed on fermented oat-meal soup (Molin et al. 1992). One-hundred-twenty-twoLactobacillus strains from the intestinal mucosa were phenotypically classified together with twenty-eight reference strains ofLactobacillus andLeuconostoc, using 49 unit characters. Data were examined using Jaccard coefficient, and unweighted pair group algorithm with arithmetic averages. Two major and eleven minor clusters were defined at the 76% SJ-similarity level: Cluster 1 included thirty isolates which could not be identified further, but had resemblance to the type strains ofL. jensenii, L. gasseri, L. crispatus, and to some extent toL. acidophilus. Cluster 12 including fifty-four intestinal isolates was identified asL. reuteri; and so was cluster 13 (five isolates). Isolates of the major clusters were found in all parts of the intestines. The genomic homogeneity of theL. reuteri isolates was scrutinized by endonuclease restriction analysis of the chromosomal DNA, and the isolates could be divided into six genomic strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrné S & Molin G (1991) Spontaneous mutations changing the raffinose metabolism ofLactobacillus plantarum. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 60: 87–93
Bibel DJ (1988) Elie Metchnikoff's bacillus of long life. ASM News 54: 661–665
Borch E & Molin G (1988) Numerical taxonomy of psychrotrophic lactic acid bacteria from prepacked meat and meat products. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 54: 301–323
Chassy BM, Gibson E & Guiffrida A (1976) Evidence for extrachromosomal elements in lactobacilli. J. Bacteriol. 127: 1576–1578
Conway P & Kjelleberg S (1989) Protein-mediated adhesion ofLactobacillus fermentum strain 737 to mouse stomach squamous epithelium. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135: 1175–1186
Kandler O & Weiss N (1986) Regular, non-sproing Gram-positive rods. In: Sneath PHA, Mair N, Sharpe ME & Holt JG (Eds) Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, vol 2 (pp 1208–1234) Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Lin JH-C & Savage DC (1984) Host specificity of the colonization of murine gastric epithelium by lactobacilli. REMS Microbiol. Lett. 24: 67–71
McCarthy DM, Lin JH-C, Rinckel LA & Savage DC (1988) Genetic transformation inLactobacillus sp. strain 100-33 of the capacity to colonize the nonsecreting gastric epithelium in mice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 416–422
Molin G, Andersson R, Ahrné S, Lönner C, Marklinder I, Johansson M-L, Jeppsson B & Bengmark S (1992) Effect of fermented oatmeal soup on the cholesterol level and theLactobacillus colonization in rat intestinal mucosa. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 61: 167–173 (this issue)
Norin KE, Persson A-K, Saxerholt H & Midtvedt T (1991) Establishment ofLactobacillus andBifidobacterium species in germfree mice and their influence on some microflora-associated characteristics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1850–1852
Romersburg HC (1984) Cluster Analysis for Research. Lifetime learning publications. Belmont, California
Sneath PHA (1978) Classification of microorganisms. In: Norris JR & Richmond MH (Eds) Essays in Microbiology (pp 9/1–9/13) Wiley, London
Ståhl M, Molin G, Persson A, Ahrné S & Ståhl S (1990) Restriction endonuclease patterns and multivariate analysis as a classification tool forLactobacillus spp. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 40: 189–193
Sugera N, Morotomi M, Watanabe T, Kawai Y & Mutai M (1975) Behaviour of microflora in the rat stomach: adhesion of lactobacilli to the keratinized epithelial cells of rat stomachin vitro. Infection Immunity 12: 173–179
Tannock GW & Archibald RD (1984) The derivation and use of mice which do not harbour lactobacilli in the gastrointestinal tract. Can. J. Microbiol. 30: 849–853
Tannock GW, Dashkevicz MP & Feighner SD (1989) Lactobacilli and bile salt hydrolase in murine intestinal tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 1848–1851
Tannock GW, Szylit O, Duval Y & Raibuad P (1982) Colonization of tissue surfaces in the gastrointestinal tract of gnotobotic animals by lactobacillus strains. Can. J. Microbiol. 28: 1196–1198
Webster FH (1986) Chemistry and Technology. American Association of Cereal Chemists, Inc., St. Paul, Minnesota
Wilmore DW, Smith RJ, Odwyer ST, Jacobs DO, Ziegler TR & Wang XD (1988) The gut: a central organ after surgical stress. Surgery 104: 917–923
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molin, G., Johansson, M.L., Ståhl, M. et al. Systematics of theLactobacillus population on rat intestinal mucosa with special reference toLactobacillus reuteri . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 61, 175–183 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584224
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584224