Abstract
Frog sartorii were incubated in choline Ringer solution containing different amounts of the cationic dye ruthenium red, and were subsequently superfused with ruthenium red-free solution. The contraction threshold was measured during and after the incubation at different calcium and magnesium concentrations.
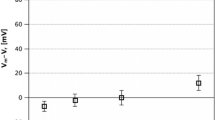
During incubation in ruthenium red the threshold potential is slowly shifted to more positive values depending on time of incubation and the ruthenium red concentration (10–300 μM). After ca. 40 min of incubation a saturation potential is reached.
The threshold shift is already maximal (−38 mV threshold potential) at 30 μM of ruthenium red regardless of the calcium concentration up to 5 mM. Omitting calcium from the incubation solution or adding 0.5 mM magnesium instead of calcium resulted in a more negative saturation potential (−48 mV).
Washing the muscle in ruthenium red-free solution for 60 min after the incubation fails to reverse the threshold shift completely. The irreversible component of the threshold shift does not depend on the divalent cation concentrationduring incubation as long as the saturation value during incubation is more positive than −50 mV.
The contraction threshold achievedafter incubation with ruthenium red is dependent on the divalent cation concentration with calcium being twice as effective as magnesium. The effect of ruthenium red is greatest at small divalent cation concentrations and not significant at 50 mM.
Incubating muscles with 5 units of neuraminidase shifted the concentration threshold to more positive potentials to the same extent as incubation with ruthenium red. Subsequent treatment of the neuraminidase-treated muscles with 30 μM of ruthenium red has no further effect on contraction threshold. The alternative experiment, first incubation with ruthenium red and then treatment with neuraminidase, gives the same results.
The results are explained by the interaction of ruthenium red with membrane-bound sialic acid. This interaction is thought to result in a decrease in negative charges which results in a shift of the surface potential and hence of the contraction threshold to more positive potentials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baux, G., Simonneau, M., Tauc, I.: Blocking action of ruthenium red on cholinergic and noncholinergic synapses: possible involvement of sialic acid-containing substrates in neurotransmission. Brain Res.152, 633–638 (1978)
Dörrscheidt-Käfer, M.: The action of Ca2+, Mg2+ and H+ on the contraction threshold of frog skeletal muscle. Evidence for surface charges controlling electro-mechanical coupling. Pflügers Arch.362, 33–41 (1976)
Dörrscheidt-Käfer, M.: Ruthenium red influences excitation-contraction coupling in frog skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch.373, R59 (1978)
Dörrscheidt-Käfer, M.: Excitation-contraction coupling in frog sartorius and the role of the surface charge due to the carboxyl group of sialic acid. Pflügers Arch380, 171–179 (1979)
Dörrscheidt-Käfer, M., Grocki K.: The effect of ruthenium red and its interaction with membrane-bound sialic acid on contraction threshold in frog skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)284, 52P (1978)
Dörrscheidt-Käfer, M., Lüttgau, H. Ch.: The effect of lanthanum ions on mechanical threshold and potassium contractures in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)242, 101–102P (1974)
Fletcher, J. M., Greenfield, B. F., Hardy, C. J., Scargill, D., Woodhead, J. L.: Ruthenium red. J. Chem. Soc. (Lond.)1961, 2000–2006
Frank, J. S., Langer, G. A., Nudd, L. M., Seraydarian, K.: The myocardial cell surface, its histochemistry, and the effect of sialic acid and calcium removal on its structure and cellular ionic exchange. Circ. Res.41, 702–714 (1977)
Hughes, R. C.: Membrane glycoproteins. London-Boston: Butterworth & Co. 1976
Luft, H. J.: Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of the use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat. Rec.171, 347–368 (1971a)
Luft, H. J.: Ruthenium red and violet. II. Fine structural localization in animal tissues. Anat. Rec.171, 369–416 (1971b)
Madeira, V. M. C., Antunes-Madeira, M. C.: Interaction of ruthenium red with isolated sarcolemma. J. Membr. Biol.17, 41–50 (1974)
Martinez-Palomo, A.: The surface coats of animal cells: Int. Rev. Cytol.29, 29–75 (1970)
Moore, C. L.: Specific inhibition of mitochondrial Ca2+ transport by ruthenium red. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.42, 298–305 (1971)
Morgan, H. R.: Ultrastructure of the surface of cells infected with avian-leukosis-sarcoma viruses. J. Virol.2, 1133–1146 (1968)
Spiro, R. G.: Basement membranes and collagens. In: Glycoproteins their compositions, structure and function, BBA Library, 2nd ed., Vol. 5 (A. Gottschalk, ed.) Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company, 1972
Vale, M. G. P., Carvalho, A.: Effects of ruthenium red on Ca2+ uptake and ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta325, 29–37 (1973)
Winzler, R. J.: Carbohydrates in cell surfaces. Int. Rev. Cytol.29, 77–125 (1970)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Bad Godesberg- SFB 114 “Bionach”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dörrscheidt-Käfer, M. The interaction of ruthenium red with surface charges controlling excitation-contraction coupling in frog sartorius. Pflugers Arch. 380, 181–187 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00582155