Summary
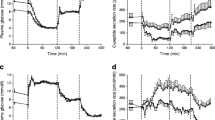
Six maturity onset diabetic patients took glibenclamide 5 mg by mouth, every morning 10 min before a standard breakfast. Serum levels of immunoreactive glibenclamide, glucose and immunoreactive insulin were measured repeatedly on the first and 15th days of treatment. Measured glibenclamide blood levels were in close agreement with an analogue computer simulation of data obtained from healthy volunteers: there was no accumulation of drug in the blood, but there was strong evidence for the existence of a slowly equilibrating “deep” compartment. Considerable insulin release and correction of the breakfast-induced hyperglycaemia were observed immediately after administration of the drug, as well as 5 h later, at lunch time. The clinical significance of blood levels of glibenclamide, as well as the correlation of pharmacokinetics with pharmacodynamics, are discussed in the light of these results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IR-:
-
immuno-reactive
- GLI:
-
glibenclamide
- IRI:
-
immuno-reactive insulin
- GLU:
-
glucose
- AK 1:
-
values obtained with patient AK on the first day of treatment
- AK 15:
-
values obtained with patient AK on the 15th day of treatment
- b:
-
serum level
- bmax :
-
maximal serum level
- t:
-
time after dose
- tmax :
-
time of maximal serum level
- G:
-
gastro-intestinal system
- B:
-
central compartment (blood)
- T:
-
peripheral compartment (tissue)
- E:
-
excreta
- M,N:
-
coefficients of the equation of a bi-exponential decay curve
- µ, v:
-
exponents of the equation of a bi-exponential decay curve
- e:
-
base of natural logarithms
- KBG KEB KTB KBT :
-
first order rate constants (e. g. KBG means: into B, from G)
- K“BG” :
-
first order rate constants
- etc.:
-
not corrected for the volume of distribution
References
Berger, W.: Achtundachtzig schwere Hypoglykämie-Zwischenfälle unter der Behandlung mit Sulfonylharnstoffen. Schweiz. med. Wschr.28, 1013–1022 (1971)
Gottesbüren, H., Gerdes, H., Littmann, K.-P., Martini, G. A.: Severe hypoglycemia after glibenclamide. Lancet1970 II, 576
Kade, H.: Gefährliche Hypoglykämien nach Glibenclamid. Hamburg. Ärztebl.24, Nr. 9 (1970)
Fabre, J.: Unpublished observation: Policlinique universitaire de médecine, Genève 1973
Balant, L., Fabre, J., Zahnd, G. R.: Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of glipizide and glibenclamide in man. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.8, 63–69 (1975)
Schmidt, H. A. E., Petrides, Pl.: Glucose- und HB 419*-Konzentration im Blut sowie HB 419*-Ausscheidung im Urin nach einmaliger oraler Applikation von HB 419−14C. Arzneimittel-Forsch.19, 1422–1428 (1969)
Rupp, W., Christ, O., Heptner, W.: Resorption, Ausscheidung und Metabolismus nach intravenöser und oraler Gabe von HB 419−14C an Menschen. Arzneimittel-Forsch.19, 1428–1434 (1969)
Rupp, W., Christ, O., Fülberth, W.: Untersuchungen zur Bioavailability von Glibenclamid. Arzneimittel-Forsch.22, 471–473 (1972)
Fucella, L. M., Tamassia, V., Valzelli, G.: Metabolism and kinetics of the hypoglycemic agent glipizide in man. Comparison with glibenclamide. J. clin. Pharmacol.13, 68–75 (1973)
Hrstka, V., Schmidt, F. H.: Eine Methode zur radioimmunologischen Bestimmung von Glibenclamide (Euglucon) in biologischen Flüssigkeiten. Arzneimittel-Forsch. (in press)
Creighton, W.D., Lambert, P.H., Miescher, P.A.: Detection of antibodies and soluble antigen-antibody complexes by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. J. Immunol.,111, 1219–1227 (1973)
Zender, R.: Une microméthode automatique pour l'analyse quantitative des aldohexoses dans les liquides biologiques par l'o-toluidine. Clin. chim. Acta8, 351–358 (1963)
Hales, C. N., Randle, P. Y.: Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem. J.88, 137–146 (1963)
Schmidt, F. H., Hrstka, V. E.: Radio-immunoassay of glibenclamide: Minimum effective dose levels and pharmacodynamics. XIIe Congrès International de Thérapeutique, Genève 1973
Raptis, S., Pfeiffer, E. F.: Sulfonylharnstoffe als orale Antidiabetica der 1. und 2. Generation. Therapiewoche21, 578–590 (1971)
Aiello, C., Turner, D., Aparicio, N. J. I., de Turner, E. A., Vazquez, A.: Nivelles plasmaticos de insulina y glucosa en diabéticos tratados con glibenclamida y clorpropamida. Acta diabet. lat.10, 30–35 (1973)
Haupt, E., Cordes, U., Petzoldt, R., Beyer, J., Schoeffling, K.: Untersuchungen zur Frage des Langzeiteffektes von blutzuckersenkenden Sulfonamiden auf Glucosetoleranz und Insulinsekretion bei erwachsenen Diabetikern. Berichte über den 79. Kongress der Gesellschaft für innere Medizin. S. 1216–1220 (1973)
Zahnd, G. R., Balant, L.: In preparation
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balant, L., Zahnd, G.R., Weber, F. et al. Behaviour of glibenclamide on repeated administration to diabetic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 11, 19–25 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561783
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00561783