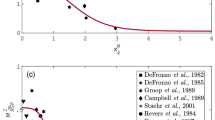
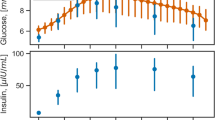
Abstract
This work discusses the physiological processes influencing the dynamics of blood glucose concentration in patients with diabetes mellitus and approaches to mathematical modeling of blood glucose metabolism are proposed to build predictive models as required for automating insulin therapy. Insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent processes occurring in the liver, kidneys, and other organs and tissues, the hormones regulating these processes, and enzymes modulating the rates of these processes are considered. A unified scheme is presented which systematizes the interaction of these substances in various processes with indications of localizations.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karpelyev VA, Filippov Y, Averin AV et al (2018) Development and testing of the operation of a PID controller for an artificial pancreas with intraperitoneal insulin administration. Sakhar Diabet 1(21):58–65
Boughton CK, Hovorka R (2019) Advances in artificial pancreas systems. Sci Transl Med 11(484):eaaw4949
Man DC, Camilleri M, Cobelli C (2006) A system model of oral glucose absorption: validation on gold standard data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(12):2472–2478
Man DC, Rizza RA, Cobelli C (2007) Meal simulation model of the glucose-insulin system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 54(10):1740–1749
Man DC, Micheletto F, Lv D, Breton M, Kovatchev B, Cobelli C (2014) The UVA/PADOVA type 1 diabetes simulator: new features. J Diabetes Sci Technol 8(1):26–34
Visentin R, Campos-Náñez E, Schiavon M, Lv D, Vettoretti M, Breton M, Kovatchev BP, Man DC, Cobelli C (2018) The UVA/Padova type 1 diabetes simulator goes from single meal to single day. J Diabetes Sci Technol 12(2):273–281
Kraegen EW, Chisholm DJ (1984) Insulin responses to varying profiles of subcutaneous insulin infusion: kinetic modelling studies. Diabetologia 26:208–213
Hovorka R, Canonico V, Chassin LJ, Haueter U, Massi-Benedetti M, Orsini Federici M, Pieber TR, Schaller HC, Schaupp L, Vering T, Wilinska ME (2004) Nonlinear model predictive control of glucose concentration in subjects with type 1 diabetes. Physiol Meas 25(4):905
Hovorka R (2006) Continuous glucose monitoring and closed-loop systems. Diabet Med 23(1):1–12
Yamamoto Noguchi CC, Furutani E, Sumi S (2014) Mathematical model of glucose-insulin metabolism in type 1 diabetes including digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Sice J Control Meas System Integr 7(6):314–320
Yamamoto Noguchi CC, Hashimoto S, Furutani E, Sumi S (2016) Model of gut absorption from carbohydrates with maximum rate of exogenous glucose appearance in type 1 diabetes. SICE J Control Meas System Integr 9(5):201–206
Nedosugova LV (2021) The role of the endocrine system in maintaining glucose homeostasis in health and pathology. Ross Med Zh Meditsinskoe Obozrenie 5(9):586
Khan A, Pessin J (2002) Insulin regulation of glucose uptake: a complex interplay of intracellular signalling pathways. Diabetologia 45:1475–1483
Mergenthaler P et al (2013) Sugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci 36(10):587–597
Dimitriadis GD et al (2021) Regulation of postabsorptive and postprandial glucose metabolism by insulin-dependent and insulin-independent mechanisms: An integrative approach. Nutrients 13(1):159
Liu W, Hsin CC, Tang F (2009) A molecular mathematical model of glucose mobilization and uptake. Math Biosci 221(2):121–129
Garg SS, Gupta J (2022) Polyol pathway and redox balance in diabetes. Pharmacol Res 182:106326
Matschinsky FM (2009) Assessing the potential of glucokinase activators in diabetes therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(5):399–416
Chandel NS (2021) Glycolysis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 13(5):a40535
Dunlop M (2000) Aldose reductase and the role of the polyol pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 58:S3–S12
Gurung P, Zubair M, Jialal I (2023) Plasma Glucose. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Paredes-Flores MA, Mohiuddin SS (2022) Biochemistry, Glycogenolysis. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Lema-Pérez L (2021) Main organs involved in glucose metabolism. In: Sugar Intake—risks and Benefits and the Global Diabetes Epidemic. InTechOpen,
Funding
This study was performed with financial support from the Russian Science Foundation (Agreement No. 23–24–00461 dated January 19, 2023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Meditsinskaya Tekhnika, Vol. 58, No. 1, pp. 44–48, January-February, 2024.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Original article submitted December 7, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Strukova, É.I., Pozhar, K.V. A structural model of glucose regulation for building prognostic algorithms for controlling insulin therapy. Biomed Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-024-10367-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-024-10367-2