Abstract
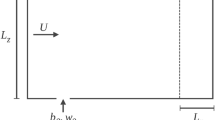
This paper presents the results of a computational study of laminar axisymmetric plumes generated by the simultaneous diffusion of thermal energy and chemical species. Species concentrations are assumed small. The plume is treated as a boundary layer. Boussinesq approximations are incorporated and the governing conservation equations of mass, momentum, energy and species are suitably non-dimensionalised. These equations are solved using one time-step-forward explicit finite-difference method. Upwind differencing is employed for convective terms. The results thus obtained are explained in terms of the basic physical mechanisms that govern these flows. They show many interesting aspects of the complex interaction of the two buoyant mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Buoyancy ratio, β*(c 0 −c ∞ )/β(t 0 −t ∞ )
- c :
-
Concentration of diffusing species
- C :
-
Concentration difference ratio, (c − c ∞ )/(c 0 −c ∞ )
- C* :
-
Concentration difference ratio based on centerline concentration, (c − c ∞ )/(c c −c ∞ )
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- p :
-
Pressure
- t :
-
Temperature
- T :
-
Temperature excess ratio, (t − t ∞ )/(t 0 − t ∞ )
- T* :
-
Temperature excess ratio based on centerline temperature, (t − t ∞ )/(t c − t ∞ )
- u, v :
-
Velocity components
- U, V :
-
Non-dimensional velocity components
- x, r :
-
Axial and radial space coordinates
- X, R :
-
Non-dimensional space coordinates
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity
- β :
-
Volumetric coefficient of thermal expansion, −1/ϱ(∂ϱ/∂t) p,c
- β* :
-
Volumetric coefficient of expansion with concentration, 1/ϱ(∂ϱ/∂c) t,p
- ϱ :
-
Density
- τ :
-
Time
- τ* :
-
Non-dimensional time
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity
- Pr:
-
Prandtl number
- Sc:
-
Schmidt number
- ∞:
-
Location far away from the axis of the plume
- 0:
-
Location indicating source
References
J.C. Mollendorf and B. Gebhart, Axisymmetric natural convection flows resulting from the combined buoyancy effects of thermal and mass diffusion, Proc. 5th Int. Heat Transfer Conference, Tokyo, Paper No. CT 1.3 (1974).
B. Gebhart and L. Pera, The nature of vertical natural convection flows resulting from the combined buoyancy effects of thermal and mass diffusion, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 14 (1971) 2025.
J. Srinivasan and D. Angirasa, Numerical study of double-diffusive free convection from a vertical surface, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer (1988), in press.
L. Pera and B. Gebhart, Natural convection flows adjacent to horizontal surfaces resulting from the combined buoyancy effects of thermal and mass diffusion, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 15, (1972) 269.
D. Angirasa and J. Srinivasan, Natural convection flows due to the combined buoyancy of heat and mass diffusion in a thermally stratified medium, submitted to Trans. ASME, J. Heat Transfer, Paper no. 87-F-445.
D.A. Anderson, J.C. Tannehill and R.H. Pletcher, Computational Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer, Hemisphere, Washington/McGraw-Hill, New York (1984).
P.J. Roache, Computational Fluid Dynamics, rev. edn., Hermosa, Albuquerque (1982).
T. Fujii, Theory of steady laminar convection above a horizontal line source and a point heat source, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 6 (1963) 597.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Angirasa, D., Sarma, P.K. A numerical study of laminar axisymmetric plumes due to the combined buoyancy of heat and mass diffusion. Appl. Sci. Res. 45, 339–352 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00457066
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00457066