Abstract
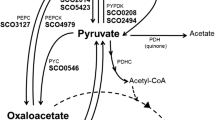
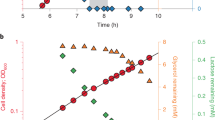
Metabolic energy in lactic streptococci can be generated by substrate level phosphorylation and by efflux of end-products in symport with protons. During growth on lactose or glucose Streptococcus cremoris maintains a high proton motive force and phosphate potential. Both energy intermediates dissipate rapidly when the energy supply stops. In the initial phase of starvation the internal phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) pool increases rapidly and this enables the organism for a prolonged period during starvation to accumulate the energy source via a PEP-dependent uptake system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelal, A. T. 1979. Arginine catabolism by microorganisms.—Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 33: 139–168.
Bragg, P. D. 1979. Electron transport and energy-transducing systems of Escherichia coli. p. 341–449. In R. A. Capaldi (ed.), Membrane Proteins in Energy Transduction.—Marcel Dekker Inc., New York.
Bruhn, J. C. and Collins, E. B. 1970. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidase of Streptococcus diacetilactis.—J. Dairy Sci. 53: 857–860.
Clarke, D. J. and Knowles, C. J. 1980. The effect of haematin and catalase on Streptococcus faecalis var. zymogenes growing on glycerol.—J. Gen. Microbiol. 121: 339–347.
Deibel, R. H. 1964. Utilization of arginine as an energy source for the growth of Streptococcus faecalis.—J. Bacteriol. 87: 988–992.
Harold, F. M. and Papineau, D. 1972. Cation transport and electrogenesis by Streptococcus faecalis. I. The membrane potential.—J. Membr. Biol. 8: 27–44.
Harold, F. M., Pavlasova, E. and Baarda, J. R. 1970. A transmembrane pH gradient in Streptococcus faecalis: origin, and dissipation by proton conductors and N, N-dicyclohexyl carbodiimide. —Biochim. Biophys. Acta 196: 235–244.
Heefner, D. L. and Harold, F. M. 1982. ATP-driven sodium pump in Streptococcus faecalis.—Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 79: 2798–2802.
Jones, D. 1978. Composition and differentiation of the genus Streptococcus. p. 1–49. In F. A. Skinner and L. B. Quesnel (eds), Streptococci.—Academic Press, London.
Kaars Sijpesteijn, A. 1970. Induction of cytochrome formation and stimulation of oxidative dissimilation by hemin in Streptococcus lactis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides.—Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 36: 335–348.
Kashket, E. R. 1981. Proton motive force in growing Streptococcus lactis and Staphylococcus aureus cells under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.—J. Bacteriol. 146: 369–376.
Kashket, E. R., Blanchard, A. G. and Metzger, W. C. 1980. Proton motive force during growth of Streptococcus lactis cells.—J. Bacteriol. 143: 128–134.
Kihara, H., Ikawa, M. and Snell, E. E. 1961. Peptides and bacterial growth X. Relation of uptake and hydrolysis to utilization of d-alanine peptides for growth of Streptococcus faecalis.—J. Biol. Chem. 236: 172–176.
Kihara, H., Klatt, O. A. and Snell, E. E. 1952. Peptides and bacterial growth III. Utilization of tyrosine and tyrosine peptides by Streptococcus faecalis.—J. Biol. Chem. 197: 801–807.
Konings, W. N. and Michels, P. A. M. 1980. Electron transfer driven solute translocation across bacterial membranes. p. 33–86. In C. J. Knowles (ed.), Diversity of Bacterial Respiratory Systems. —CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton.
Lee, R., Molskness, T., Sandine, W. E. and Elliker, P. R. 1973. Carbohydrate metabolism in lactic streptococci: fate of galactose supplied in free or disaccharide form.—Appl. Microbiol. 26: 951–958.
Mackey, J. K. and Raymond, B. W. 1968. Activities of arginine dihydrolase and phosphatase in Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium.—Appl. Microbiol. 16: 1543–1547.
Maloney, P. C. 1977. Obligatory coupling between proton entry and the synthesis of adenosine 5′-triphosphate in Streptococcus lactis.—J. Bacteriol. 132: 564–575.
Maloney, P. C. and Hansen, F. C. 1982. Stoichiometry of proton movements coupled to ATP synthesis driven by a pH gradient in Streptococcus lactis.—J. Membr. Biol. 66: 63–77.
Maloney, P. C., Kashket, E. R. and Wilson, T. H. 1974. A protonmotive force drives ATP synthesis in bacteria.—Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 71: 3896–3900.
Maloney, P. C. and Saitta, M. R. 1982. Stoichiometry of proton-adenosine 5′-triphosphate during ATP hydrolysis by the proton-translocating ATP ase of Streptococcus lactis.—Abstr. Ann. Meet. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 82: 140.
Maloney, P. C. and Wilson, T. H. 1975. ATP synthesis driven by a proton motive force in Streptococcus lactis.—J. Membr. Biol. 25: 285–310.
McKay, L., Miller III, A., Sandine, W. E. and Elliker, P. R. 1970. Mechanisms of lactose utilization by lactic acid streptococci: enzymatic and genetic analyses.—J. Bacteriol. 102: 804–809.
McKay, L. L., Walter, L. A., Sandine, W. E. and Elliker, P. R. 1969. Involvement of phosphoenolpyruvate in lactose utilization by group N-streptococci.—J. Bacteriol. 99: 603–610.
Michels, P. A. M., Michels, J. P. J., Boonstra, J. and Konings, W. N. 1979. Generation of electrochemical proton gradient in bacteria by the excretion of metabolic end products.—FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 5: 357–364.
Nisbet, T. M. and Payne, J. W. 1982. The characteristics of peptide uptake in Streptococcus faecalis: studies on the transport of natural peptides and antibacterial phosphonopeptides.—J. Gen. Microbiol. 128: 1357–1364.
Otto, R. 1981. An ecophysiological study of starter streptococci.—Ph. D. Thesis, University of Groningen.
Otto, R., Hugenholtz, J., Konings, W. N. and Veldkamp, H. 1980a. Increase of molar growth yield of Streptococcus cremoris for lactose as a consequence of lactate consumption by Pseudomonas stutzeri in mixed culture.—FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 9: 85–88.
Otto, R., Lageveen, R. G., Veldkamp, H. and Konings, W. N. 1982. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris.—J. Bacteriol. 149: 733–738.
Otto, R., Sonnenberg, A. S. M., Veldkamp, H. and Konings, W. N. 1980b. Generation of an electrochemical proton gradient in Streptococcus cremoris by lactate efflux.—Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 77: 5502–5506.
Otto, R., Ten Brink, B., Veldkamp, H. and Konings, W. N. 1983. The relation between growth rate and electrochemical proton gradient of Streptococcus cremoris.—FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 16: 69–74.
Payne, J. W. 1980. Transport and utilization of peptides by bacteria. p. 211–256. In J. W. Payne (ed.), Microorganisms and Nitrogen Sources.—John Wiley and Sons, Chichester.
Payne, J. W. and Nisbet, T. M. 1981. Continuous monitoring of substrate uptake by microorganisms using fluorescamine: application to peptide transport by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Streptococcus faecalis.—J. Appl. Biochem. 3: 447–458.
Payne, J. W., Payne, G. M. and Nisbet, T. M. 1982. An anionic peptide transport system in Streptococcus faecalis.—FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 14: 123–127.
Ritchey, T. W. and Seeley, H. W. 1976. Distribution of cytochrome-like respiration in streptococci. —J. Gen. Microbiol. 93: 195–203.
Romano, A. H., Trifone, J. D. and Brustolon, M. 1979. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in fermentative bacteria.—J. Bacteriol. 139: 93–97.
Slee, A. M. and Tanzer, J. M. 1979. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449.—Infect. Immun. 24: 821–828.
St. Martin, E. J. and Wittenberger, C. L. 1979. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans.—Infect. Immun. 24: 865–868.
Ten Brink, B. and Konings, W. N. 1982. Electrochemical proton gradient and lactate concentration gradient in Streptococcus cremoris cells grown in batch culture.—J. Bacteriol. 152: 682–686.
Thauer, R. K., Jungermann, K. and Decker, K. 1977. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria.—Bacteriol. Rev. 41: 100–180.
Thomas, T. D. and Batt, R. D. 1969. Degradation of cell constituents by starved Streptococcus lactis in relation to survival.—J. Gen. Microbiol. 58: 347–362.
Thomas, T. D., Ellwood, D. C. and Longyear, V. M. C. 1979. Change from homo-to heterolactic fermentation by Streptococcus lactis resulting from glucose limitation in anaerobic chemostat cultures.—J. Bacteriol. 138: 109–117.
Thompson, J. 1978. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis.—J. Bacteriol. 136: 465–476.
Thompson, J. 1980. Galactose transport systems in Streptococcus lactis.—J. Bacteriol. 144: 683–691.
Thompson, J. and Chassy, B. M. 1981. Uptake and metabolism of sucrose by Streptococcus lactis. —J. Bacteriol. 147: 543–551.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konings, W.N., Otto, R. Energy transduction and solute transport in streptococci. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 49, 247–257 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399501
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399501