Summary
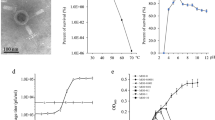
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens N produces two restriction enzymes, BamNI and BamNx. Subtilis-phage ϕ1 is strongly restricted by BamNx. We isolated ϕ1 rH, a mutant of phage ϕ1, which overcame the BamNx-restriction by producing inhibitor. This inhibitor inactivated BamNx specifically and reversibly. The inhibitor directly interacted with BamNx and the inactivation might be the result of formation of a binary complex. The inhibitory activity was sensitive to treatment with trypsin. The molecular weight of the inhibitor protein was estimated to be approximately 20,000 daltons by gel filtration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arber W (1974) DNA modification and restriction. In: Cohen WE (ed) Prog Nucleic Acid Res Molec Biol, vol 14. Academic Press, New York, p 1
Behrens B, Lüder G, Behncke M, Trautner TA, Ganesan AT (1979) The genome of B. subtilis phage SPP1, physical arrangement of phage genes. Mol Gen Genet 175:351–357
Boyer HW (1971) DNA restriction and modification mechanisms in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 25:153–176
Brunel F, Davison J (1979) Restriction insensitivity in bacteriophage T5; III. Characterization of EcoRI-sensitive mutants by restriction analysis. J Mol Biol 128:527–543
Eskin B, Lautenberger JA, Linn S (1973) Host-controlled modification and restriction of bacteriophage T7 by Escherichia coli B. J Virol 11:1020–1023
Greene PJ, Heyneker HL, Bolivar F, Rodriguez RL, Betlach MC, Covarrubias AA, Backman K, Russel DJ, Tait R, Boyer HW (1978) A general method for the purification of restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res 5:2373–2380
Hemphill HE, Whiteley HR (1975) Bacteriophages of Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev 39:257–315
Ikawa S, Shibata T, Ando T,(1979) Recognition sequence of endonuclease R. BamNx from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens N. Agric Biol Chem 43:873–875
Ikawa S, Shibata T, Ando T, Saito H (1980) Genetic studies on site-specific endodeoxyribonucleases in Bacillus subtilis. Multiple modification and restriction systems in transformants of Bacillus subtilis 168. Mol Gen Genet 177:359–368
Ito J, Spizizen J (1971) Abortive infection of sporulating Bacillus subtilis 168 by ϕ2 bacteriophage. J Virol 7:515–523
Kawamura F, Saito H, Ikeda Y, Ito J (1979) Viable deletion mutants of Bacillus subtilis phage ρ11. J Gen Appl Microbiol 25:223–236
Loening UE (1968) Molecular weights of ribosomal RNA in relation to evolution. J Mol Biol 38:355–365
Makino O, Kawamura F, Saito H, Ikeda Y (1979) Inactivation of restriction endonuclease BamNx after infection with phage ϕNR2. Nature 277:64–66
Reilly BE, Spizizen J (1965) Bacteriophage deoxyribonucleate infection of competent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 89:782–790
Roberts RJ (1976) Restriction endonucleases. In: CRC Crit. Rev Biochem 123–164 (November)
Rutberg L (1969) Mapping of a temperate bacteriophage active on Bacillus subtilis. J Virol 3:38–44
Saito H, Shibata T, Ando T (1979) Mapping of genes determining nonpermissiveness and host-specific restriction to bacteriophages in Bacillus subtilis marburg. Mol Gen Genet 170:117–122
Shibata T, Ando T (1974) Host controlled modification and restriction in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet 131:275–280
Shibata T, Ando T (1975) In vitro modification and restriction of phage ϕ105C DNA with Bacillus subtilis N cell-free extract. Mol Gen Genet 138:269–279
Shibata T, Ando T (1976) The restriction endonucleases in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens N strain. Substrate specificities. Biochim Biophys Acta 442:184–196
Shibata T, Ikawa S, Komatsu Y, Ando T, Saito H (1979) Introduction of host-controlled modification and restriction systems of Bacillus subtilis IAM 1247 into Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol 139:308–310
Spoerel N, Herrlich P, Bickle TA (1979) A novel bacteriophage defence mechanism: the anti-restriction protein. Nature 278:30–34
Studier FW, Movva NR (1976) SMAase gene of bacteriophage T3 is responsible for overcoming host restriction. J Virol 19:136–145
Sutcliffe JG, Church GM (1978) The cleavage site of the restriction endonuclease AvaII. Nucleic Acids Res 5:2313–2319
Toussaint A (1976) The DNA modification function of temperate phage Mu-1. Virology 70:17–27
Wagner EF, Auer B, Schweiger M (1979) Development of Escherichia coli virus T1: escape from host restriction. J Virol 29:1229–1231
Wilson GA, Young FE (1975) Isolation of a sequence-specific endonuclease (BamI) from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens H. J Mol Biol 97:123–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Arber
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makino, O., Saito, H. & Ando, T. Bacillus subtilis-phage φ1 overcomes host-controlled restriction by producing BamNx inhibitor protein. Molec. Gen. Genet. 179, 463–468 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271735
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271735