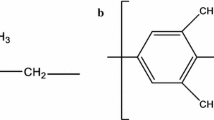
Abstract
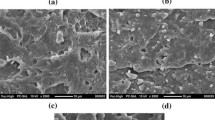
The immiscible polypropylene (PP)/polystyrene (PS) blends and theirs organoclay 10A (Cloisite10A) nanocomposites with different contents were prepared via melt blending into a co-rotating twin screw extruder and the test samples were molded by injection molding. The 10A is an anisotropic layered silicate and the effect PP/PS ratio, 10A different content on melt and crystallization enthalpy were determined by DSC. The T g , storage modulus (E’), and tanδ measurements were obtained by DMA. The domains reduction of PS in the PP with addition 10A was investigated by Scanning Electronic Microscope (SEM). There is a decrease in PS particles size in PP/PS blends containing 10A. The crystallinity degree of PP seems to reduction with the addition of PS phase and 10A. The E’ of the PP/PS 90/10/0 blends showed slightly changes between Neat PP and PP/PS/10A nonetheless the nanocomposites 3 and 5 %wt had a small rise in the storage modulus between −50 and 0 °C.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asha KK, Tresa SG, Anjana R, Newly J, Georg KE (2013) Effect of modified kaolin clays on the mechanical properties of polypropylene/polystyrene blends. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/APP.38043
Utracki LA (1989) Poymer Alloys and Blends. Thermodynamics and Rheology, New York
Yoshida K, Kawamura T, Terano M, Nitta K (2008) Effects of bulk morphology on the mechanical properties of melt-blended PP/PS blends. J A Pol Sci. doi:10.1002/app.28014
Yuan HY, Ching YL, Jui MY, Wei HL (2003) Preparation and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)–clay nanocomposite materials. Polymer. doi:10.1016/S0032–3861(03)00062–4
Silva RP, Salles CA, Mauler RS, Oliveira RVB (2010) Avaliação da morfologia e propriedades termo-mecânicas em nanocompósitos de PVC. Pol Cien Tecn. doi:10.1590/S0104–14282010005000012
Silva RP, Salles CA, Mauler RS, Oliveira RVB (2010) Investigation of the thermal, mechanical and morphological properties of poly(vinyl chloride)/polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanocomposites. Pol Int. doi:10.1002/pi.2851
Zhu Y, Xu Y, Tong L, Xu Z, Fang Z (2008) Influence of polarity on the preferential intercalation behavior of clay in immiscible polypropylene/polystyrene blend. J A Pol Sci. doi:10.1002/app.28927
Suprakas SR, Steve P, Mosto B, Leszek U (2004) Role of organically modified layered silicate as an active interfacial modifier in immiscible polystyrene/polypropylene blends. Polymer. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2004.10.009
Yurekli K, Karim A, Amis EJ, Krishnamoorti R (2003) Influence of layered silicates on the phase-separated morphology of PS − PVME blends. Macromol. doi:10.1021/ma020755l
Zhu Y, Ma H, Tong L, Fang Z (2008) Preferential intercalation behavior of clay and its effect on the thermal degradation in immiscible PP/PS blends. C J Pol Sci. doi:10.1142/S0256767908003540
Yong W, Yan X, Qin Z, Xiao LG, Qiang F (2003) The morphology and mechanical properties of dynamic packing injection molded PP/PS blends. Polymer. doi:10.1016/S0032–3861(03)00011–9
Wang Y, Zhang Q, Fu Q (2003) Compatibilization of immiscible poly(propylene)/polystyrene blends using clay. Macromol Rap Com. doi:10.1002/marc.200390026
Yan Z, Yuzhen X, Lifang T, Zhongbin X, Zhengping F (2008) Influence of polarity on the preferential intercalation behavior of clay in immiscible polypropylene/polystyrene blend. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.28927
Ray S, Suprakas P, Steve BM (2004) Role of organically modified layered silicate as an active interfacial modifier in immiscible polystyrene/polypropylene blends. Polymer. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2004.10.009
Rajkiran RT, Paul DR (2011) Effect of organoclay on the morphology, phase stability and mechanical properties of polypropylene/polystyrene blends. Polymer. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2011.01.019
Huang H, Han B, Wang L, Miao N, Mo H, Zhou NL, Ma ZM, Zhang J, Shen J (2011) Crystallization kinetics of polypropylene composites filled with nano calcium carbonate modified with maleic anhydride. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.32842
Gao J, Fu X, Ding M, Fu Q (2010) Studies on partial compatibility of PP and PS. C J Pol Sci. doi:10.1007/s10118–010–9150–6
Zhang YQ, Lee JH, Rhee JM, Rhee KY (2004) Polypropylene–clay nanocomposites prepared by in situ grafting-intercalating in melt. Comp Sci Tech. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2003.10.014
Amash A, Zugenmaier P (1997) Thermal and dynamic mechanical investigations on fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097–4628
Prasanna KS, Mural SM, Sanjay KNSA (2011) Polypropylene/high impact polystyrene blend nanocomposites obtained from E-waste: evaluation of mechanical, thermal and morphological properties. Int J Plast Technol. doi:10.1007/s12588–011–9005–1
Halimatudahliana A, Ismail H, Nasir A (2002) Morphological studies of uncompatibilized and compatibilized polystyrene/polypropylene blend. Pol Test. doi:10.1016/S0142–9418(01)00079–4
Santos KS (2011) Efeito das Condições de Processo sobre morfologia de Nanocompositos de Polipropileno com argila organofílica. UFRGS, Tese de Doutorado
Jia QM, Zheng M, Zhu YC, Li JB, Xu CZ (2007) Effects of organophilic montmorillonite on hydrogen bonding, free volume and glass transition temperature of epoxy resin/polyurethane interpenetrating polymer networks. Europ Pol J. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2006.10.016
Liv Y, Huang Y, Kong M, Li G (2013) Improved thermal oxidation stability of polypropylene films in the presence of β-nucleating agent. Pol Test. doi:10.1016/j.polymertesting.2012.10.008
Santos K, Demori R, Mauler RS, Liberman SA, Oviedo MAS (2009) The influence of screw configurations and feed mode on the dispersion of organoclay on PP. Comp Part A: App Sci Man. doi:10.1016/j.compositesa.2009.05.009
Thirtha V, Lehman R, Nosker T (2006) Morphological effects on glass transition behavior in selected immiscible blends of amorphous and semicrystalline polymers. Polymer. doi:10.1016/j.polymer. 2006.05.014
Macaúbas PHP, Demarquette N (2001) Morphology development and melt linear viscoelastic properties of (PA6/PP/PS) ternary blend systems. Polymer. doi:10.1177/0095244309104461
Asha KK, Tresa SG, Anjana R, Newly J, George KE (2013) Effect of modified kaolin clays on the mechanical properties of polypropylene/polystyrene blends. J Appl Polym Sci. doi:10.1002/app.38043
Aklonis JJ, Macknight WJ (1983) Introduction to Polymer Viscoelasticity, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 295–320
Menard KP (1999) Dynamic Mechanical Analysis. A practical Introduction CRC Press, New York
Sperling LH (2006) Introduction to Physical Polymer Science. Bethlehem, Pennsylvania
Aknowledgments
The authors thanks CAPES and CNPQ for the financial support, Braskem and Innova S.A. for supplying materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, R.P., Neto, C.P. Morphology and thermo mechanical properties of pp/ps nanocomposites. Int J Plast Technol 18, 125–134 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12588-014-9069-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12588-014-9069-9