Abstract
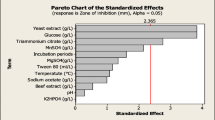
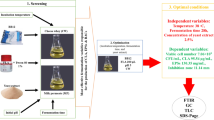
Bacteriocins are nowadays recognized as good biopreservatives that are able to contain microbial contaminant development in several food products. In this study, the goat milk isolate Lactobacillus brevis NS01 brevicin activity on common foodborne pathogenic organisms and its characterization, stability, and statistical response surface methodology (RSM) optimization of media components for enhanced production were determined. Its adsorption onto common stabilizing agent silica and applicability in apple juice preservation were also determined. The L. brevis NS01 produced 3.2 kDa common foodborne pathogen inhibitory brevicin having more polar (68.6 %) than non-polar (30.8 %) amino acids. Optimization of growth conditions by RSM demonstrated that glucose, sodium acetate, and triammonium sulfate concentration of 33.41, 8.36, and 2.22 g/L, respectively, increased its production. Brevicin activity was constant over a broad range of pH (3–8) and temperature (20–100 °C) and reached a maximum at pH 6 and 40 °C. Maximum adsorption of brevicin onto silica took place at pH 6–7, 40 °C for 240 min. The carrier silica exhibited significant Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectral changes upon brevicin adsorption and presented good biopreservative activity. This study demonstrates the potential large-scale use of brevicin adsorbed silica for shelf life increase and clarification at a same time.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebayo, C. O., & Aderiye, B. I. (2011). Suspected mode of antimycotic action of brevicin SG1 against Candida albicans and Penicillium citrinum. Food Control, 22, 1814–1820.
Ajay Pal, K., Ramana, V., & Bawa, A. S. (2010). Simplification and optimization of deMan Rogosa Sharpe (MRS) medium for enhanced production of bacteriocin by Weissella paramesenteroides DFR-8. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 47(3), 258–265.
Akelah, A. (2013). Polymers in food processing industries. In A. Akelah (ed.), Functionalized polymeric materials in agriculture and the food industry. New York: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-7061-8_4.
Castellano, P., Belfiore, C., Fadda, S., & Vignolo, G. (2008). A review of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria used as bioprotective cultures in fresh meat produced in Argentina. Meat Science, 79, 483–499.
Cindrić, I. J., Kunštić, M., Zeiner, M., Stingeder, G., & Rusak, G. (2011). Sample preparation methods for the determination of the antioxidative capacity of apple juices. Croatica chemical acta. Arhiv za kemiju, 84(3), 435–438.
Coventry, M. J., Gordon, J. B., Alexander, M., Hickey, M. W., & Wan, J. (1996). A food-grade process for isolation and partial purification of bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria that uses diatomite calcium silicate. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62(5), 1764–1769.
Crim, S. M., Iwamoto, M., Huang, J. Y., Griffin, P. M., Gilliss, D., Cronquist, A. B., Cartter, M., Tobin-D'Angelo, M., Blythe, D., Smith, K., Lathrop, S., Zansky, S., Cieslak, P. R., Dunn, J., Holt, K. G., Lance, S., Tauxe, R., & Henao, O. L. (2014). Incidence and trends of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food—Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network, 10 U.S. Sites, 2006–2013. MMWR, 63(15), 328–332.
Dawson, P. L., Harmon, L., Sotthibandhu, A., & Han, I. Y. (2005). Antimicrobial activity of nisin-adsorbed silica and corn starch powders. Food Microbiology, 22(1), 93–99.
Faheem, F., Saeed, S., & Rasool, S. A. (2007). Studies on brevicin AF01: a bacteriocin like inhibitory substance active against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 39(4), 1293–1302.
FAOSTAT-FAO Statistical Database, (2013). http://faostat.fao.org/.
Grande, M. J., Lucas, R., Abriouel, H., Omar, N. B., Maqueda, M., Martínez-Bueno, M., Martínez-Cañamero, M., Valdivia, E., & Gálvez, A. (2005). Control of Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris in fruit juices by enterocin AS-48. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 104(3), 289–297.
Han, B., Yu, Z., Liu, B., Ma, Q., & Zhang, R. (2011). Optimization of bacteriocin production by Lactobacillus plantarum YJG isolated from the mucosa of the gut of healthy chickens. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 5(10), 1147–1155.
Hillman, K., & Fox, A. (1994). Effects of porcine faecal lactobacilli on the rate of growth of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O149:K88:K91. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 19, 497–500.
Ibarguren, C., Audisio, C. M., Mónica Farfán Torres, E., & Apella, M. C. (2010). Silicates characterization as potential bacteriocin-carriers. Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 11, 197–202.
Imai, Y. N., Inoue, Y., & Yamamoto, Y. (2007). Propensities of polar and aromatic amino acids in noncanonical interactions: nonbonded contacts analysis of protein-ligand complexes in crystal structures. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 50(6), 1189–1196.
Jaganathan, H., & Godin, B. (2012). Biocompatibility assessment of Si-based nano- and micro-particles. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 64(15), 1800–1819.
Kaewklom, S., Lumlert, S., Kraikul, W., & Aunpa, R. (2013). Control of Listeria monocytogenes on sliced bologna sausage using a novel bacteriocin, amysin, produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens isolated from Thai shrimp paste (Kapi). Food Control, 32, 552–557.
Kazazic, M., Nissen-Meyer, J., & Fimland, G. (2002). Mutational analysis of the role of charged residues in target-cell binding, potency and specificity of the pediocin-like bacteriocin sakacin P. Microbiology, 148, 2019–2027.
Koyuncu, H., Kul, A. R., Calıml, A., Yıldız, N., & Ceylan, H. (2007). Adsorption of dark compounds with bentonites in apple juice. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 40, 489–497.
Ku, T. W., Tsai, R. L., & Pan, T. M. (2009). A simple and cost-saving approach to optimize the production of subtilisin NAT by submerged cultivation of Bacillus subtilis natto. Journal of Agricural and Food Chemistry, 57(1), 292–296.
Martin, R., Delgado, S., Maldonado, A., Jimenez, E., Olivares, M., Fernandez, L., Sobrino, O. J., & Rodriguez, J. M. (2009). Isolation of lactobacilli from sow milk and evaluation of their probiotic potential. Journal of Dairy Research, 76, 418–425.
Massani, M. B., Vignolo, G. M., Eisenberg, P., & Morando, P. J. (2013). Adsorption of the bacteriocins produced by Lactobacillus curvatus CRL705 on a multilayer-LLDPE film for food-packaging applications. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 53, 128–138.
Müller, D. M., Carrasco, M. S., Tonarelli, G. G., & Simonetta, A. C. (2009). Characterization and purification of a new bacteriocin with a broad inhibitory spectrum produced by Lactobacillus plantarum lp 31 strain isolated from dry-fermented sausage. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 106, 2031–2040.
Pei, J., Yuan, Y., & Yue, T. (2013). Primary characterization of bacteriocin paracin C—a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus paracasei. Food Control, 34, 168–176.
Rangel, J.M., Sparling, P.H., Crowe, C., Griffin, P.M., & Swerdlow, D.L. (2005). Epidemiology of Escherichia coli O157:H7 outbreaks, United States, 1982–2002. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 11(4),603–608.
Rojo-Bezares, B., Sáenz, Y., Navarro, L., Zarazaga, M., Ruiz-Larrea, F., & Torres, C. (2007). Coculture-inducible bacteriocin activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strain J23 isolated from grape must. Food Microbiology, 24, 482–491.
Senbagam, D., Gurusamy, R., & Senthilkumar, B. (2013). Antagonistic effect of brevicin on Gram positive and gram negative food borne pathogens and its biopreservative efficacy in milk. African Journal of Biotechnology, 12(2), 175–185.
Suárez-Jacobo, A., Gervilla, R., Guamis, B., Roig-Sagués, A. X., & Saldo, J. (2010). Effect of UHPH on indigenous microbiota of apple juice—a preliminary study of microbial shelf-life. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 136, 261–267.
Sung, H. J., Song, W. J., Kim, K. P., Ryu, S., & Kang, D. H. (2014). Combination effect of ozone and heat treatments for the inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella typhimurium, and Listeria monocytogenes in apple juice. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 171, 147–153.
Todorov, S. D., Prévost, H., Lebois, M., Dousset, X., LeBlanc, J. G., & Franco, B. D. G. M. (2011). Bacteriocinogenic Lactobacillus plantarum ST16Pa isolated from papaya (Carica papaya)—from isolation to application: characterization of a bacteriocin. Food Research International, 44(5), 1351–1363.
Vafa, M. R., Haghighatjoo, E., Shidfar, F., Afshari, S., Gohari, M. R., & Ziaee, A. (2011). Effects of apple consumption on lipid profile of hyperlipidemic and overweight men. International Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2(2), 94–100.
Wan, J., Gordon, J., Hickey, M. W., Mawson, R. F., & Coventry, M. J. (1996). Adsorption of bacteriocins by ingestible silica compounds. Journal of Applied Bacteriology, 81(2), 167–173.
Yamamoto, Y., Togawa, Y., Shimosaka, M., & Okazaki, M. (2003). Purification and characterization of a novel bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecalis strain RJ-11. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(10), 5746–5753.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by King Saud University, Deanship of Scientific Research, College of Sciences Research Center.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duraisamy, S., Kasi, M., Balakrishnan, S. et al. Optimization of Lactobacillus brevis NS01 Brevicin Production and Its Application in Apple Juice Biopreservation Using Food-Grade Clarifying Agent Silica as a Carrier. Food Bioprocess Technol 8, 1750–1761 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1536-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-015-1536-6