Abstract
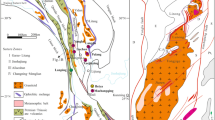
No. 22 ore of Dafulou deposit was systematically analyzed for sulfur isotopes. The results show that the δ 34S values of sulfide minerals, ranging from −0.154 to +0.218% and with an average value of +0.114 1%, are mostly positive and characterized by rich sulfur (S) content. This suggests that the sulfur of the Dafulou ore deposit is derived from magma and relates to the Longxianggai concealed granite, which points to the important role of magma during mineralization and implyies the product of the active continental margin. By comparison between the Dafulou and the Kengma tin deposit, significant differences exist in the sulfur isotope composition. In the Kengma deposit, the sulfur isotope composition is characterized by the high negative value, which is different from the Dafulou tin-polymetallic deposit. The difference of the enrichment and fractionation of the sulfur isotope is the synthesized result of the metallogenic conditions. It also has the difference in the metallogenic environment and metallogenic characteristics of the deposit in the same ore belt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
HAN F, HUTCHINSON R W. Evidence for hydrothermal exhalative sedimentary origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic deposits — Geochemistry of rare earth elements and trace elements of the host rocks [J]. Mineral Deposits, 1989, 8: 33–42. (in Chinese)
CAI Ming-hai, MAO Jing-wen, LIANG Ting, FRANCO P, HUANG Hui-lan. The origin of the Tongkeng-Changpo tin deposit, Dachang metal district, Guangxi, China: Clues from fluid inclusions and He isotope systematics [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2007, 42: 613–626.
HAN F, HUTCHINSON R W. Evidence for exhalative origin for rocks and ores of the Dachang tin polymetallic field: the ore-bearing formation and hydrothermal exhalative sedimentary rocks [J]. Mineral Deposits, 1989, 8: 25–40. (in Chinese)
CAI Ming-hai, LIANG Ting, WU De-cheng, HUANG Hui-min. Structure characteristics and mineralization controls of the Nandan-hechi metallogenic belt in Guangxi province [J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2004, 40(6): 5–10. (in Chinese)
HAN F, HUTCHINSON R W. Synthetic studies on the origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic deposits and their metallogenetic model [J]. Bull Chinese Academy Geological Sciences, 1991, 22: 61–80. (in Chinese)
JIANG Shao-yong, HAN Fa, SHEN Jian-zhong, PALMER M R. Chemical and Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd isotopic systematics of tourmaline from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposits, Guangxi Province, P.R. China [J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 157: 49–67.
FAN D, ZHANG Tao, YE Jie, PAŠAVA J, KRIBEK B, DOBES P, VARRIN I, ZAK K. Geochemistry and origin of tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits hosted by the Devonian black shale series near Dachang, Guangxi, China [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2004, 24: 103–120.
WANG Deng-hong, CHEN Yu-chuan, CHEN Wen, SANG Hai-qing, LU Yuan-fa, CHEN Kai-li, LIN Zhi-mao. Dating of the Dachang superlarge tin-polymetallic deposit in Guangxi and its implication for the genesis of the No. 100 orebody [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica: English Edition, 2004, 78(2): 452–458.
CAI Ming-hai, HE Long-qing, LIU Guo-qing, WU De-cheng, HUANG Hui-min. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of the intrusive rocks in the Dachang tin polymetallic ore field, Guangxi and their geological significance [J]. Geology Review, 2006, 52(3): 409–414. (in Chinese)
FU M, KWAK T, MERNAGH T P. Fluid inclusion studies of zoning in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore field, People’s Republic of China [J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88: 283–300.
YE Xu-sun, YAN Yun-xiu, HE Hai-zhou. The mineralization factors and tectonic evolution of Dachang super large tin deposit Guangxi, China [J]. Geochimica, 1999, 28(3): 213–221. (in Chinese)
TANELLI G, LATTANZI P. The cassiterite-polymetallic sulfide deposits of Dachang, Guangxi, People’s Republic of China [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1985, 20: 102–106.
WANG Deng-hong, CHEN Yu-chuan, CHEN Wen, SANG Hai-qing, LI Hua-qin, LU Yuan-fa, CHEN Kai-li, LIN Zhi-mao. Dating the Dachang giant tin-polymetallic deposit in Nandan, Guangxi [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2004, 78(1): 132–138. (in Chinese)
CAI Ming-hai, MAO Jing-wen, LIANG Ting, HUANG Hui-lan. Fluid inclusion studies of Tongkeng-Changpo deposit in Dachang polymetallic tin orefield [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2005, 24(3): 228–241. (in Chinese)
CHEN Yu-chuan, HUANG Min-zhi, XU Jue, AI Yong-de, LI Xiang-ming, TANG Shao-hua, MENG Ling-ku. Geological features and metallogenetic series of the Dachang cassiteritesulfide-polymetallic belt [J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1985, (3): 228–240. (in Chinese)
HAN F, HUTCHINSON R W. Evidence for exhalative origin of the Dachang tin-polymetallic sulfide deposits, their geological and geochemical characteristics [J]. Mineral Deposits, 1990, 9: 309–323. (in Chinese)
ZHAO Kui-dong, JIANG Shao-yong, XIAO Hong-quan, NI Pei. Origin of ore-forming fluids of the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore deposit: Evidence from helium isotopes [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(12): 1041–1045.
OHMOTO H. Systematic of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits [J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67: 551–578.
ZHAO K D, JIANG S Y, NI P, LING H F, JIANG Y H. Sulfur, lead and helium isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore district in South China: Implication for ore genesis [J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 89: 251–273.
FU M, CHANGKAKOTI A, KROUSE H R, GRAY J, KWAK T. An oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, and carbon isotope study of carbonate-replacement (skarn) tin deposits of the Dachang tin field, China [J]. Economic Geology, 1991, 86: 1683–1703.
GAO Ji-yuan. Pb isotopic evolution and its significance in ore genesis in the Dachang tin-polymetallic ore deposits [J]. Geologygeochemistry, 1999, 27(2): 38–43. (in Chinese)
LIANG Ting, WANG Deng-hong, CAI Ming-hai, CHEN Zhen-yu, GUO Chun-li, HUANG Hui-min. Sulfur and lead isotope composition tracing for the sources of ore-forming material in Dachang tin-polymetallic orefield, Guangxi [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2008, 82(7): 967–977. (in Chinese)
FAN Sen-kui, LI Xiu-dan, CHENG Yong-sheng, CHEN Cheng-zhen, HUANG Wei-hong. Geochemical features of vein rocks and their significance to structure and mineralization in the Dachang ore district, Guangxi province [J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 46(5): 828–835. (in Chinese)
LATTANZI P, CORAZZA M, CORSINI F, TANELLI G. Sulfide mineralogy in the polymetallic cassiterite deposits of Dachang, P.R. China [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1989, 24: 141–147.
LI Hua-qin, WANG Deng-hong, MEI Yu-ping, LIANG Ting, CHEN Zhen-yu, GUO Chun-li, YING Li-juan. Lithogenesis and mineralization chronology study on the lamo zinc-copper polymetallic ore deposit in Dachang orefield, Guangxi [J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2008, 82: 912–920. (in Chinese)
HE Hai-zhou, YE Xu-sun. Study on source of ore-forming materials in Dachang ore field, Guangxi [J]. Guangxi Geology, 1996, 9(4): 33–41. (in Chinese)
DING Ti-ping. Isotope geochemical study of some super-large ore deposits in China [J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 1997, 18(4): 373–381. (in Chinese)
WEI Ju-ying, WANG Guan-yu. Isotope geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988: 19–36. (in Chinese)
YE Xu-sun, YAN Yun-xiu, HE Hai-zhou. The metallogenic condition of Dachang super large tin deposit in Guangxi [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1996: 138–139. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(41202051) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2012M521721) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Project(CSUZC2013021) supported by Valuable Equipment Open Sharing Fund of Central South University, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Ys. Geology and sulfur isotope geochemistry of Dafulou tin-polymetallic deposit in Dachang orefield, Guangxi, China. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 2811–2818 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1801-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1801-7