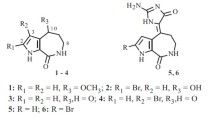
Abstract
Bioassay-guided fractionation of a collection of Moorea bouillonii from Papua New Guinea led to the isolation of a new alkyl amide, mooreamide A (1), along with the cytotoxic apratoxins A–C and E. The planar structure of 1 was elucidated by NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry analysis. Structural homology between mooreamide A and the endogenous cannabinoid ligands, anandamide, and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol inspired its evaluation against the neuroreceptors CB1 and CB2. Mooreamide A was found to possess relatively potent and selective ligand binding activity to CB1 (K 1 = 0.47 µM) versus CB2 (K 1 > 25 µM). This represents the most potent marine-derived CB1 ligand described to date and adds to the growing family of marine metabolites that exhibit cannabinomimetic activity.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2-AG:
-
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol
- AEA:
-
Anandamide
- CDCl3 :
-
Deuterated chloroform
- CH2Cl2 :
-
Dichloromethane
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- COSY:
-
Correlation spectroscopy
- ECS:
-
Endocannabinoid system
- EtOAc:
-
Ethyl acetate
- ESIMS:
-
Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- FT:
-
Fourier transform
- GPCR:
-
G protein-coupled receptor
- HMBC:
-
Heteronuclear multiple bond correlation
- HPLC:
-
High performance liquid chromatography
- HR:
-
High resolution
- HSQC:
-
Heteronuclear single quantum correlation
- IR:
-
Infrared
- LR:
-
Low resolution
- MeCN:
-
Acetonitrile
- MeOH:
-
Methanol
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy
- NP:
-
Normal phase
- OLS:
-
Olefin synthase
- RP:
-
Reverse phase
- SAM:
-
S-Adenosyl methionine
- SCUBA:
-
Self-contained underwater breathing apparatus
- SPE:
-
Solid phase extraction
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- Wt:
-
Weight
References
Nunnery JK, Mevers E, Gerwick WH (2010) Biologically active secondary metabolites from marine cyanobacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 21:787–793. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2010.09.019
Tan LT (2010) Filamentous tropical marine cyanobacteria: a rich source of natural products for anticancer drug discovery. J Appl Phycol 22:659–676. doi:10.1007/s10811-010-9506-x
Tidgewell K, Clark BR, Gerwick WH (2010) The natural products chemistry of cyaonobacteria. In: Crews P (ed) Moore, B. Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry II, Elsevier Oxford
Gerwick WH, Moore BS (2012) Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural product drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem Biol 19:85–98. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2011.12.014
Elphick MR, Egertová M (2001) The neurobiology and evolution of cannabinoid signalling. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 356:381–408. doi:10.1098/rstb.2000.0787
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (1999) Anandamide induces overeating: mediation by central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 143:315–317. doi:10.1007/s002130050953
Ramos JA, Gómez M, de Miguel R (2005) Effects on development. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Riedel G, Davies SN (2005) Cannabinoid function in learning, memory and plasticity. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Walker JM, Hohmann AG (2005) Cannabinoid mechanisms of pain suppression. In: Pertwee RG (ed) Cannabinoids. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Guzmán M (2003) Cannabinoids: potential anticancer agents. Nat Rev Cancer 3:745–755. doi:10.1038/nrc1188
Di Marzo V, Piscitelli F, Mechoulam R (2011) Cannabinoids and endocannabinoids in metabolic disorders with focus on diabetes. In: Schwanstecher M (ed) Diabetes – perspectives in drug therapy. Springer, Heidelberg
Soderstrom K, Murray TF, Yoo HD, Ketchum S, Milligan K, Gerwick WH, Ortega MJ, Salva J (1997) Discovery of Novel cannabinoid receptor ligands from diverse marine organisms. In: Sinzinger H, Samuelsson B, Vane JR, Paoletti R, Ramwell P, Wong PYK (eds) Recent advances in prostaglandin, thromboxane, and leukotriene research. Plenum Press Div, New York
Montaser R, Paul VJ, Luesch H (2012) Marine cyanobacterial fatty acid amides acting on cannabinoid receptors. Chem Bio Chem 13:2676–2681. doi:10.1002/cbic.201200502
Luesch H, Yoshida WY, Moore RE, Paul VJ, Corbett TH (2001) Total structure determination of apratoxin A, a potent novel cytotoxin from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Am Chem Soc 123:5418–5423. doi:10.1021/ja010453j
Luesch H, Yoshida WY, Moore RE, Paul VJ (2002) New apratoxins of marine cyanobacterial origin from Guam and Palau. Bioorg Med Chem 10:1973–1978. doi:10.1016/S0968-0896(02)00014-7
Matthew S, Schupp PJ, Luesch H (2008) Apratoxin E, a cytotoxic peptolide from a guamanian collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya bouillonii. J Nat Prod 71:1113–1116. doi:10.1021/np700717s
Melck D, Bisogno T, De Petrocellis L, Chang H, Julius D, Bifulco M, Di Marzo V (1999) Unsaturated long-chain N-Acyl-vanillylamides (N-AVAMs): vanilloid receptor ligans that inhibit anandamide-facilitated transport and bind to cb1 cannabinoid receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:275–284. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1105
Pereira AR, McCue CF, Gerwick WH (2010) Cyanolide A, a glycosidic macrolide with potent molluscicidal activity from the Papua New Guinea cyanobacterium Lyngbya bouillonii. J Nat Prod 73:217–220. doi:10.1021/np9008128
Pretsch E, Bühlmann P, Badertscher M (2009) Structure determination of organic compounds: tables of spectral data. Springer, Berlin
Crews P, Kho-Wiseman E (1978) Stereochemical assignment in marine natural products by 13C NMR γ effects. Tetrahedron Lett 19:2483–2486. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)94806-3
Timmers MA, Dias DA, Urban S (2012) Application of HPLC-NMR in the identification of plocamenone and Isoplocamenone from the Marine Red Alga Plocamium angustum. Mar Drugs 10:2089–2102. doi:10.3390/md10092089
Gutierrez M, Pereira AR, Debonsi HM, Ligresti A, Di Marzo V, Gerwick WH (2011) Cannabinominmetic lipid from a marine cyanobacterium. J Nat Prod 74:2313–2317. doi:10.1021/np200563x
Han B, McPhail KL, Ligresti A, Di Marzo V, Gerwick WH (2003) Semiplenamides A-G, fatty acid amides from a Papua New Guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. J Nat Prod 66:1364–1368. doi:10.1021/np030242n
Sitachitta N, Gerwick WH (1998) grenadadiene and grenadamide, cyclopropyl-containing fatty acid metabolites from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J Nat Prod 61:681–684. doi:10.1021/np970576a
Dewick PM (2009) Medicinal natural products: a biosynthetic approach. Wiley, West Sussex
Edwards DJ, Marquez BL, Nogle LM, McPhail K, Goeger DE, Roberts MA, Gerwick WH (2004) Structure and biosynthesis of the jamaicamides, new mixed polyketide-peptide neurotoxins from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscule. Chem Biol 11:817–833. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.03.030
Dorrestein PC, Blackhall J, Straight PD, Fischbach MA, Garneau-Tsodikova S, Edwards DJ, McLaughlin S, Lin M, Gerwick WH, Kolter R, Walsh CT, Kelleher NL (2006) Activity screening of carrier domains within nonribosomal peptide synthetases using complex substrate mixtures and large molecule mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 45:1537–1546. doi:10.1021/bi052333k
McCarthy JG, Eisman EB, Kulkarni S, Gerwick L, Gerwick WH, Wipf P, Sherman DH, Smith JL (2012) Structural basis of functional group activation by sulfotransferases in complex metabolic pathways. ACS Chem Biol 7:1994–2003. doi:10.1021/cb300385m
Gu L, Wang B, Kulkarni A, Gehret JJ, Lloyd KR, Gerwick L, Gerwick WH, Wipf P, Håkansson K, Smith JL, Sherman DH (2009) Polyketide decarboxylative chain termination proceed by O-Sulfonation in curacin A biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 131:16033–16035. doi:10.1021/ja9071578
Chabra A, Haque AS, Pal RK, Goyal A, Rai R, Joshi S, Panjikar S, Pasha S, Sankaranarayanan R, Gokhale RS (2012) Nonprocessive [2 + 2]e− off-loading reductase domains from mycobacterial nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:5681–5686. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118680109
Grindberg RV, Ishoey T, Brinza D, Esquenazi E, Coates RC, Liu WT, Gerwick L, Dorrestein PC, Pevzner P, Lasken R, Gerwick WH (2011) Single cell genome amplification accelerates indentification of the apratoxin biosynthetic pathway from a complex microbial assemblage. PLoS One 6:e18565. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018565
Elphick MR (2012) The Evolution and comparative neurobiology of endocannabinoid signaling. Phil Trans R Soc B 367:1607–3201. doi:10.1098/rstb.2011.0394
Acknowledgments
We thank the government of Papua New Guinea for the permission to collect the cyanobacterial specimens. We thank the UCSD Chemistry and Biochemistry mass spectrometry facilities for their analytical services. The 500 MHz NMR 13C XSens cold probe was supported by NSF CHE-0741968. We also acknowledge The Growth Regulation & Oncogenesis Training Grant NIH/NCI (T32A009523-24) for a fellowship to E. M., and NIH Grants (CA100851, NS053398) for support of the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Mevers, E., Matainaho, T., Allara’, M. et al. Mooreamide A: A Cannabinomimetic Lipid from the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea bouillonii . Lipids 49, 1127–1132 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-014-3949-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-014-3949-9