Abstract
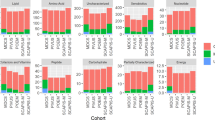
Non-targeted metabolomic profiling is used to simultaneously assess a large part of the metabolome in a biological sample. Here, we describe both the analytical and computational methods used to analyze a large UPLC–Q-TOF MS-based metabolomic profiling effort using plasma and serum samples from participants in three Swedish population-based studies of middle-aged and older human subjects: TwinGene, ULSAM and PIVUS. At present, more than 200 metabolites have been manually annotated in more than 3600 participants using an in-house library of standards and publically available spectral databases. Data available at the metabolights repository include individual raw unprocessed data, processed data, basic demographic variables and spectra of annotated metabolites. Additional phenotypical and genetic data is available upon request to cohort steering committees. These studies represent a unique resource to explore and evaluate how metabolic variability across individuals affects human diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodsky, L., Moussaieff, A., Shahaf, N., Aharoni, A., & Rogachev, I. (2010). Evaluation of peak picking quality in LC-MS metabolomics data. Analytical Chemistry, 82(22), 9177–9187. doi:10.1021/ac101216e.
Broeckling, C. D., Heuberger, A. L., Prince, J. A., Ingelsson, E., & Prenni, J. E. (2013). Assigning precursor–product ion relationships in indiscriminant MS/MS data from non-targeted metabolite profiling studies. Metabolomics, 9(1), 33–43. doi:10.1007/s11306-012-0426-4.
Buscher, J. M., Czernik, D., Ewald, J. C., Sauer, U., & Zamboni, N. (2009). Cross-platform comparison of methods for quantitative metabolomics of primary metabolism. Analytical Chemistry, 81(6), 2135–2143. doi:10.1021/ac8022857.
Dudley, E., Yousef, M., Wang, Y., & Griffiths, W. J. (2010). Targeted metabolomics and mass spectrometry. Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology, 80, 45–83. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-381264-3.00002-3.
Floegel, A., Stefan, N., Yu, Z., Muhlenbruch, K., Drogan, D., Joost, H. G., et al. (2013). Identification of serum metabolites associated with risk of type 2 diabetes using a targeted metabolomic approach. Diabetes, 62(2), 639–648. doi:10.2337/db12-0495.
Ganna, A., Lee, D., Ingelsson, E., & Pawitan, Y. (2014a). Rediscovery rate estimation for assessing the validation of significant findings in high-throughput studies. Briefings in Bioinformatics,. doi:10.1093/bib/bbu033.
Ganna, A., Salihovic, S., Sundstrom, J., Broeckling, C. D., Hedman, A. K., Magnusson, P. K., et al. (2014b). Large-scale metabolomic profiling identifies novel biomarkers for incident coronary heart disease. PLoS Genetics, 10(12), e1004801. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004801.
Ingelsson, E., Sundstrom, J., Arnlov, J., Zethelius, B., & Lind, L. (2005). Insulin resistance and risk of congestive heart failure. JAMA, 294(3), 334–341. doi:10.1001/jama.294.3.334.
Kerr, M. K., & Churchill, G. A. (2001). Statistical design and the analysis of gene expression microarray data. Genetical Research, 77(2), 123–128.
Leek, J. T., Scharpf, R. B., Bravo, H. C., Simcha, D., Langmead, B., Johnson, W. E., et al. (2010). Tackling the widespread and critical impact of batch effects in high-throughput data. Nature Reviews Genetics, 11(10), 733–739. doi:10.1038/nrg2825.
Lind, L., Fors, N., Hall, J., Marttala, K., & Stenborg, A. (2005). A comparison of three different methods to evaluate endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the elderly: the Prospective Investigation of the Vasculature in Uppsala Seniors (PIVUS) study. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 25(11), 2368–2375. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000184769.22061.da.
Magnusson, P. K., Almqvist, C., Rahman, I., Ganna, A., Viktorin, A., Walum, H., et al. (2013). The Swedish twin registry: establishment of a biobank and other recent developments. Twin Reserch and Human Genetics, 16(1), 317–329. doi:10.1017/thg.2012.104.
Menni, C., Fauman, E., Erte, I., Perry, J. R., Kastenmuller, G., Shin, S. Y., et al. (2013a). Biomarkers for type 2 diabetes and impaired fasting glucose using a non-targeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes,. doi:10.2337/db13-0570.
Menni, C., Kastenmuller, G., Petersen, A. K., Bell, J. T., Psatha, M., Tsai, P. C., et al. (2013b). Metabolomic markers reveal novel pathways of ageing and early development in human populations. International Journal of Epidemiology, 42(4), 1111–1119. doi:10.1093/ije/dyt094.
Patti, G. J., Tautenhahn, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). Meta-analysis of untargeted metabolomic data from multiple profiling experiments. Nature Protocols, 7(3), 508–516. doi:10.1038/nprot.2011.454.
Plumb, R. S., Johnson, K. A., Rainville, P., Smith, B. W., Wilson, I. D., Castro-Perez, J. M., et al. (2006). UPLC/MS(E); a new approach for generating molecular fragment information for biomarker structure elucidation. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 20(13), 1989–1994. doi:10.1002/rcm.2550.
Prince, J. T., & Marcotte, E. M. (2006). Chromatographic alignment of ESI-LC-MS proteomics data sets by ordered bijective interpolated warping. Analytical Chemistry, 78(17), 6140–6152. doi:10.1021/ac0605344.
Sheehan, N. A., Didelez, V., Burton, P. R., & Tobin, M. D. (2008). Mendelian randomisation and causal inference in observational epidemiology. PLoS Medicine, 5(8), e177. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050177.
Smith, C. A., Want, E. J., O’Maille, G., Abagyan, R., & Siuzdak, G. (2006). XCMS: processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Analytical Chemistry, 78(3), 779–787. doi:10.1021/ac051437y.
Stegemann, C., Pechlaner, R., Willeit, P., Langley, S. R., Mangino, M., Mayr, U., et al. (2014). Lipidomics profiling and risk of cardiovascular disease in the prospective population-based Bruneck study. Circulation, 129(18), 1821–1831. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.113.002500.
Sumner, L. W., Amberg, A., Barrett, D., Beale, M. H., Beger, R., Daykin, C. A., et al. (2007). Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. chemical analysis working group (CAWG) metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics, 3(3), 211–221. doi:10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2.
Tautenhahn, R., Bottcher, C., & Neumann, S. (2008). Highly sensitive feature detection for high resolution LC/MS. BMC Bioinformatics, 9, 504. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-504.
Tautenhahn, R., Patti, G. J., Rinehart, D., & Siuzdak, G. (2012). XCMS online: a web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Analytical Chemistry, 84(11), 5035–5039. doi:10.1021/ac300698c.
Thiele, I., Swainston, N., Fleming, R. M., Hoppe, A., Sahoo, S., Aurich, M. K., et al. (2013). A community-driven global reconstruction of human metabolism. Nature Biotechnology, 31(5), 419–425. doi:10.1038/nbt.2488.
Tzoulaki, I., Ebbels, T. M., Valdes, A., Elliott, P., & Ioannidis, J. P. (2014). Design and analysis of metabolomics studies in epidemiologic research: a primer on -omic technologies. American Journal of Epidemiology, 180(2), 129–139. doi:10.1093/aje/kwu143.
Wang, T. J., Larson, M. G., Vasan, R. S., Cheng, S., Rhee, E. P., McCabe, E., et al. (2011). Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nature Medicine, 17(4), 448–453. doi:10.1038/nm.2307.
Wang-Sattler, R., Yu, Z., Herder, C., Messias, A. C., Floegel, A., He, Y., et al. (2012). Novel biomarkers for pre-diabetes identified by metabolomics. Molecular Systems of Biology, 8, 615. doi:10.1038/msb.2012.43.
Wurtz, P., Havulinna, A. S., Soininen, P., Tynkkynen, T., Prieto-Merino, D., Tillin, T., et al. (2015). Metabolite profiling and cardiovascular event risk: a prospective study of 3 population-based cohorts. Circulation, 131(9), 774–785. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013116.
Zhu, Z. J., Schultz, A. W., Wang, J., Johnson, C. H., Yannone, S. M., Patti, G. J., et al. (2013). Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by the METLIN database. Nature Protocols, 8(3), 451–460. doi:10.1038/nprot.2013.004.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Alexandra Jauhiainen for helpful insights and comments. Further, we want to extend our thanks to all participants of the TwinGene, ULSAM and PIVUS studies for the kind contribution to science. The computations were performed on resources provided by SNIC through Uppsala Multidisciplinary Center for Advanced Computational Science (UPPMAX) under project b2011036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
All participants gave informed written consent and the Ethics Committees of Karolinska Institutet or Uppsala University approved the respective study protocol.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from Knut och Alice Wallenberg Foundation (Wallenberg Academy Fellow), European Research Council (ERC-2013-StG; Grant No. 335395), Swedish Diabetes Foundation (Grant No. 2013-024), Swedish Heart–Lung Foundation (Grant No. 20120197), the Family Ernfors Fund, the Swedish Government’s strategic research area EXODIAB (Excellence of Diabetes Research in Sweden), and Swedish Research Council (Grant No. 2012-1397). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
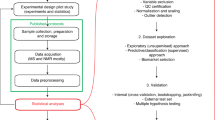
Samples, subjects, and data outputs
We uploaded this information as ISA-Tab metadata format to the Metabolights repository.
Additional information
Andrea Ganna and Tove Fall have equal contribution to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganna, A., Fall, T., Salihovic, S. et al. Large-scale non-targeted metabolomic profiling in three human population-based studies. Metabolomics 12, 4 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0893-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0893-5