Abstract
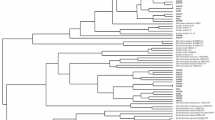
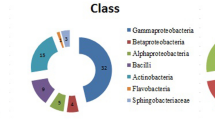
In this study, we isolated bacteria from rhizosphere and endorhizophere of wheat crops of the central region of Argentina. The isolates were phenotypically characterized and the restriction patterns of 16S rDNA (ARDRA) using endonuclease AluI were analysed. Representative isolates were used to evaluate the effect of the inoculation on the growth of wheat under greenhouse conditions. The effects of plant growth-promoting bacteria on wheat plants were studied by evaluating shoot fresh and dry weights and root fresh and dry weights. One native strain increased the shoot and root dry biomass by 23% and 45% respectively. Other strains increased the shoot dry biomass. A 1.5 kb fragment of the 16S rRNA gene of one isolate was sequenced. This isolate showed high identity with different species of Pseudomonas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alquilanti L, Mannazzu I, Papa R, Cavalca L, Clementi F (2004) ARDRA (Amplified Ribosomal DNA Restriction Analysis) Characterization of Azotobacteraceae: a contribution to the study of these free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 57:197–206
Altschul S, Stephen F, Madden T, Schäffer A, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman D (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bagwell CE, Piceno YM, Ashburne AL, Lovell CR (1998) Physiological diversity of the rhizosphere diazotroph assemblages of selected salt marsh grasses. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1609–1616
Bainotti C, Fraschina J, Salines J, Masiero B, Cuniberti M, Alberione E, Riberi L, Gomez D (2005) Evaluación de cultivares de trigo en EEA Marcos Juarez- Campaña 2004/05. http://www.inta.gov.ar/mjuarez/info/documentos/Trigo/evatr05.pdf
Bashan Y (1998) Inoculants of plant growth promoting bacteria for use in Agriculture. Biotechnol Adv 16:729–770
Bashan Y, Holguin G (1997) Azospirillum—plant relationships: environmental and physiological advances (1990–1996). Can J Microbiol 43:103–121
Bellis P, Ercolani GL (2001) Growth interactions during bacterial colonization of seedling rootlets. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1945–1948
Benizri E, Courtade A, Picard C, Guckert A (1998) Role of maize root exudates in the production of auxins by Pseudomonas fluorescens M.3.1. Soil Biol Biochem 30:1481–1484
Bilal R, Rasul G, Quershi JA, Malik KA (1990) Characterization of Azospirillum and related diazotrophs associated with roots of plant growing in saline soils. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 6:46–52
Cáceres E. 1982 Improved medium for isolation of Azospirillum species. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:990–991
Capper AL, Higgins KP (1993) Application of Pseudomonas fluorescens isolates to wheat as potential biological control agents against take-all. Plant Pathol 42:560–567
De Smedth J, Bauwens M, Tytgat R, De Ley J (1980) Intra- and intergeneric similarities of ribosomal ribonucleic acid cistrons of free-living bacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 30:106–122
Dobbelaere S, Vanderleyden J, Okon Y (2003) Palnt growth-promoting effects of diazotrophs in the rhizosphere. Crit Rev Plant Sci 22:107–149
Döbereiner J (1995) Isolation and identification of aerobic nitrogen fixing bacteria from soil and plants. In: Alef K, Nannipier P (eds) Methods in applied soil microbiology and biochemistry. Academic Press, London, pp 134–141, ISBN: 0-12-513840-7
Duffy BK, Ownley BH, Weller DM (1997) Soil chemical and physical properties associated with suppression of take-all of wheat by Trichoderma koningii. Phytopathology 87:1118–1124
Eid MMA, Sherwood JE (1995) Pulsed-field gel-electrophoresis fingerprinting for identification of Azospirillum species. Curr Microbiol 30:127–131
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fischer SE, Rivarola V, Mori GB (2000) Colonization of wheat by Azospirillum brasilense Cd is impaired by saline stress. Plant Soil 225:187–191
Fischer SE, Marioli JM, Mori GB (2003) Effect of root exudates on EPS composition and LPS profile of Azospirillum brasilense Cd under saline stress. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219:53–62
Frioni L (1990) Ciclo biológico del fosforo. In: Procesos microbianos, ed. Fundación Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, pp 273, ISBN: 950–665–110
Glick BR (1995) The enhancement of plant growth by free-living bacteria. Can J Microbiol 41:109–117
Glick BR, Karaturovic DM, Newel PC (1995) A novel procedure for rapid isolation of plant growth promoting Pseudomonas. Can J Microbiol 41:533–536
Glick BR, Bashan Y (1997) Genetic manipulation of plant growth-promoting bacteria to enhance biocontrol of phytopathogens. Biotechnol Adv 15:353–378
Hartmann A, Zimmer W (1994) Physiology of Azospirillum. In: Okon Y (eds) Azospirillum/Plant associations. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 15–39, ISBN:0-8493-4925-7
Herman RP, Provencio K, Torrez R, Seager G (1994) Seasonal and spatial population dynamics of the nitrogen-efficient guild in a desert bajada grassland. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1160–1165
Jarsún, B., Gorgas JA, Zamora E, Bosnero E, Lovera E, Ravelo A, Tassile JL (2003) Los suelos. Geografia e inventarios del recurso. In: Gorga JA, Tassile JL (eds) Recursos naturales de la provincia de Cordoba. Los suelos, Agencia Cordoba D.A.C y T.S.E.M dirección de ambiente and Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria Cordoba, Argentina, pp 97–183, ISBN: 987-20198-3-5
Jofré EC, Fischer SE, Rivarola V, Balegno H, Mori GB (1998) Saline stress affects the attachment of Azospirillum brasilense Cd to maize and wheat roots. Can J Microbiol 44:416–422
Jofré EC, Lagares A, Mori GB (2004). Disruption of d-TDP-rhamnose biosynthesis modifies lipopolysaccharide core, exopolysaccharide production, and root colonization in Azospirillum brasilense. FEMS Microbiol Lett 231:267–275
Johnsson L, Hokeberg M, Gerhardson B (1998) Performance of the Pseudomonas chlororaphis biocontrol agent MA 342 against cereal seedborne diseases in field experiments. Eur J Plant Pathol 104:701–711
Kloepper JW (1993) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as biological control agents. In: Metting FB Jr (ed) Soil microbial ecology-applications in agricultural and environmental management. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 255–274, ISBN: 0824787374
Lægreid, M., Bøckman, O.C. & Kaarstad O (1999) World cereal production-challenges and opportunities. In: Agriculture, fertilizers and environment. CABI publishing in association with Norsk Hydro ASA, UK, pp 219–234, ISBN: 0-85199-358-3
Lugtenberg BJJ, Bloemberg GV, Bolwerk A, vanden Broek D, Cazorla-Lopez F, Chin-A-Woeng TFC, Eijkemans K, Kamilova FD, Kuiper I, Mulders IH, van Rij ET, deWeert S (2004) Biocontrol of pathogens. In: Tikhonovich I, Lugtenberg BJJ, Provorov N (eds) Biology of plant-microbe interactions, vol 4 International Society for Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, St Paul, Minnesota, USA, pp 305–309, ISBN: 0-954625-3-6
Perriére G, Gouy M (1996) WWW-query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 78:364–369
Richardson AE (2001) Prospects for using soil microorganisms to improve the acquisition of phosphorus by plants. Aust J Plant Physiol 28:897–906
Ross IL, Alami Y, Harvey PR, Achouak W, Ryder MH (2000) Genetic diversity and biological control activity of novel species of closely related Pseudomonads isolated from wheat field soils in South Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1609–1616
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, ISBN: 0-87969-309-6
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assays for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Tripathi AK, Verma SC, Ron EZ (2002) Molecular characterization of a salt-tolerant bacterial community in the rice rhizosphere. Res Microbiol 153:579–584
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequences alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Vessey JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255:571–586
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Mario Aguilar, from the Universidad de La Plata (Argentina) for his cooperation in the ARDRA performance. Sonia Fischer is member of the Scientific Researcher Career-CONICET (National Council of Technological Researchs). This research was supported by SECYT of the Universidad Nacional de Río Cuarto, PICTO-AGENCIA (n° 01 - 11430) y Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (Argentina).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, S.E., Fischer, S.I., Magris, S. et al. Isolation and characterization of bacteria from the rhizosphere of wheat. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 895–903 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9312-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9312-4