Abstract
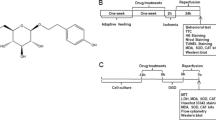
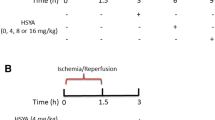
Hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) is the major active chemical component of the flower of the safflower plant, Carthamus tinctorius L. Previously, its neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia–reperfusion (I/R) injury was reported by anti-oxidant action and suppression of thrombin generation. Here, we investigate the role of HSYA in cerebral I/R-mediated apoptosis and possible signaling pathways. Male Wistar rats were subjected to transient middle cerebral artery occlusion for 2 h, followed by 24 h reperfusion. HSYA was administered via tail-vein injection just 15 min after occlusion. The number of apoptotic cells was measured by TUNEL assay, apoptosis-related proteins Bcl-2, Bax and the phosphorylation levels of Akt and GSK3β in ischemic penumbra were assayed by western blot. The results showed that administration of HSYA at the doses of 4 and 8 mg/kg significantly inhibited the apoptosis by decreasing the number of apoptotic cells and increasing the Bcl-2/Bax ratio in rats subjected to I/R injury. Simultaneously, HSYA treatment markedly increased the phosphorylations of Akt and GSK3β. Blockade of PI3K activity by wortmannin dramatically abolished its anti-apoptotic effect and lowered both Akt and GSK3β phosphorylation levels. Taken together, these results suggest that HSYA protects against cerebral I/R injury partly by reducing apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dirnagl U, Iadecola C, Moskowitz MA (1999) Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends Neurosci 22(9):391–397
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40(5):e331–e339. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.531632
Sun B, Chen L, Wei X, Xiang Y, Liu X, Zhang X (2011) The Akt/GSK-3beta pathway mediates flurbiprofen-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 409(4):808–813. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.05.095
Liu H, Liu X, Wei X, Chen L, Xiang Y, Yi F, Zhang X (2012) Losartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, ameliorates cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt-mediated eNOS phosphorylation. Brain Res Bull 89(1–2):65–70. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2012.06.010
Zhang J, Deng Z, Liao J, Song C, Liang C, Xue H, Wang L, Zhang K, Yan G (2013) Leptin attenuates cerebral ischemia injury through the promotion of energy metabolism via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(4):567–574. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2012.202
Noshita N, Lewen A, Sugawara T, Chan PH (2001) Evidence of phosphorylation of Akt and neuronal survival after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21(12):1442–1450. doi:10.1097/00004647-200112000-00009
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296(5573):1655–1657. doi:10.1126/science.296.5573.1655
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS, Michalek SM (2005) Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat Immunol 6(8):777–784. doi:10.1038/ni1221
Jope RS, Johnson GV (2004) The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci 29(2):95–102. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2003.12.004
Beurel E, Jope RS (2006) The paradoxical pro- and anti-apoptotic actions of GSK3 in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis signaling pathways. Prog Neurobiol 79(4):173–189. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.07.006
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2006) Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/akt survival signal pathways are implicated in neuronal survival after stroke. Mol Neurobiol 34(3):249–270. doi:10.1385/MN:34:3:249
Zhu H, Wang Z, Ma C, Tian J, Fu F, Li C, Guo D, Roeder E, Liu K (2003) Neuroprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A: in vivo and in vitro studies. Planta Med 69(5):429–433. doi:10.1055/s-2003-39714
Wei X, Liu H, Sun X, Fu F, Zhang X, Wang J, An J, Ding H (2005) Hydroxysafflor yellow A protects rat brains against ischemia–reperfusion injury by antioxidant action. Neurosci Lett 386(1):58–62. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2005.05.069
Sun X, Wei X, Qu S, Zhao Y, Zhang X (2010) Hydroxysafflor Yellow A suppresses thrombin generation and inflammatory responses following focal cerebral ischemia–reperfusion in rats. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(14):4120–4124. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.05.076
Shan LQ, Ma S, Qiu XC, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Zheng LH, Ren PC, Wang YC, Fan QY, Ma BA (2010) Hydroxysafflor Yellow A protects spinal cords from ischemia/reperfusion injury in rabbits. BMC Neurosci 11:98. doi:10.1186/1471-2202-11-98
Yang Q, Yang ZF, Liu SB, Zhang XN, Hou Y, Li XQ, Wu YM, Wen AD, Zhao MG (2010) Neuroprotective effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A against excitotoxic neuronal death partially through down-regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Neurochem Res 35(9):1353–1360. doi:10.1007/s11064-010-0191-6
Chen L, Zhang Y, Sun X, Li H, LeSage G, Javer A, Zhang X, Wei X, Jiang Y, Yin D (2009) Synthetic resveratrol aliphatic acid inhibits TLR2-mediated apoptosis and an involvement of Akt/GSK3beta pathway. Bioorg Med Chem 17(13):4378–4382. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2009.05.029
Chen L, Shi W, Li H, Sun X, Fan X, Lesage G, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Yin D (2010) Critical role of toll-like receptor 9 in morphine and Mycobacterium tuberculosis-Induced apoptosis in mice. PLoS ONE 5(2):e9205. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009205
Benchoua A, Guegan C, Couriaud C, Hosseini H, Sampaio N, Morin D, Onteniente B (2001) Specific caspase pathways are activated in the two stages of cerebral infarction. J Neurosci 21(18):7127–7134
Ferrer I, Friguls B, Dalfo E, Justicia C, Planas AM (2003) Caspase-dependent and caspase-independent signalling of apoptosis in the penumbra following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the adult rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 29(5):472–481
Sugawara T, Chan PH (2003) Reactive oxygen radicals and pathogenesis of neuronal death after cerebral ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal 5(5):597–607. doi:10.1089/152308603770310266
Ji DB, Zhang LY, Li CL, Ye J, Zhu HB (2009) Effect of hydroxysafflor yellow A on human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hypoxia. Vascul Pharmacol 50(3–4):137–145. doi:10.1016/j.vph.2008.11.009
Ji DB, Zhu MC, Zhu B, Zhu YZ, Li CL, Ye J, Zhu HB (2008) Hydroxysafflor yellow A enhances survival of vascular endothelial cells under hypoxia via upregulation of the HIF-1 alpha-VEGF pathway and regulation of Bcl-2/Bax. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 52(2):191–202. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e318181fb02
Murphy KM, Streips UN, Lock RB (1999) Bax membrane insertion during Fas(CD95)-induced apoptosis precedes cytochrome c release and is inhibited by Bcl-2. Oncogene 18(44):5991–5999. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203001
Li F, Omori N, Jin G, Wang SJ, Sato K, Nagano I, Shoji M, Abe K (2003) Cooperative expression of survival p-ERK and p-Akt signals in rat brain neurons after transient MCAO. Brain Res 962(1–2):21–26
Friguls B, Justicia C, Pallas M, Planas AM (2001) Focal cerebral ischemia causes two temporal waves of Akt activation. NeuroReport 12(15):3381–3384
Liu SX, Zhang Y, Wang YF, Li XC, Xiang MX, Bian C, Chen P (2012) Upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression by hydroxysafflor yellow A conferring protection from anoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Int J Cardiol 160(2):95–101. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.03.033
Yu SM, Kim SJ (2013) Thymoquinone-induced reactive oxygen species causes apoptosis of chondrocytes via PI3K/Akt and p38kinase pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). doi:10.1177/1535370213492685
Kwon SH, Hong SI, Kim JA, Jung YH, Kim SY, Kim HC, Lee SY, Jang CG (2011) The neuroprotective effects of Lonicera japonica THUNB. against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via phosphorylation of MAPKs and PI3K/Akt in SH-SY5Y cells. Food Chem Toxicol 49(4):1011–1019. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2011.01.008
Woodgett JR (2005) Recent advances in the protein kinase B signaling pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(2):150–157. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2005.02.010
Leroy K, Brion JP (1999) Developmental expression and localization of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in rat brain. J Chem Neuroanat 16(4):279–293
Pap M, Cooper GM (1998) Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J Biol Chem 273(32):19929–19932
Linseman DA, Butts BD, Precht TA, Phelps RA, Le SS, Laessig TA, Bouchard RJ, Florez-McClure ML, Heidenreich KA (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta phosphorylates Bax and promotes its mitochondrial localization during neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 24(44):9993–10002. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2057-04.2004
Kaga S, Zhan L, Altaf E, Maulik N (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin promotes angiogenic and anti-apoptotic signaling through the induction of VEGF, Bcl-2 and surviving expression in rat ischemic preconditioned myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 40(1):138–147. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.09.009
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81100874, No. 81200904), Young Excellent Scientists of Shandong Province (No. BS2010YY037, 2011BSE27078) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2012HM032, ZR2010HM082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Xiang, Y., Kong, L. et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Anti-apoptotic Effect Through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β Pathway in Rat. Neurochem Res 38, 2268–2275 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1135-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1135-8