Abstract
Objective
To explore the effect and mechanism of schisandrin B (Sch B) in the treatment of cerebral ischemia in rats.
Methods
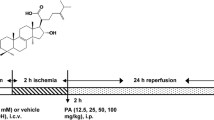
The cerebral ischemia models were induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and reperfusion. Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into 6 groups using a random number table, including sham, MCAO, MCAO+Sch B (50 mg/kg), MCAO+Sch B (100 mg/kg), MCAO+Sch B (100 mg/kg)+LY294002, and MCAO+Sch B (100 mg/kg)+wortmannin groups. The effects of Sch B on pathological indicators, including neurological deficit scores, cerebral infarct volume, and brain edema, were subsequently studied. Tissue apoptosis was identified by terminal transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) staining. The protein expressions involved in apoptosis, inflammation response and oxidative stress were examined by immunofluorescent staining, biochemical analysis and Western blot analysis, respectively. The effect of Sch B on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling was also explored.
Results
Sch B treatment decreased neurological deficit scores, cerebral water content, and infarct volume in MCAO rats (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Neuronal nuclei and TUNEL staining indicated that Sch B also reduced apoptosis in brain tissues, as well as the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 expression (P<0.01). Sch B regulated the production of myeloperoxidase, malondialdehyde, nitric oxide and superoxide dismutase, as well as the release of cytokine interleukin (IL)-1 β and IL-18, in MCAO rats (P<0.05 or P<0.01). Sch B promoted the phosphorylation of PI3K and AKT. Blocking the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway with LY294002 or wortmannin reduced the protective effect of Sch B against cerebral ischemia (P<0.05 or P<0.01).
Conclusions
Sch B reduced apoptosis, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress of MCAO rats by modulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. Sch B had a potential for treating cerebral ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu W, Wei W, Lu M, Zhu X, Liu N, Niu Y, et al. Neuroprotective effect of chitosan oligosaccharide on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. Neurochem Res 2017;42:3186–3198.
Xu LX, Lv Y, Li YH, Ding X, Wang Y, Han X, et al. Melatonin alleviates brain and peripheral tissue edema in a neonatal rat model of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: the involvement of edema related proteins. BMC Pediatr 2017;17:90.
Mao L, Wu DH, Hu GH, Fan JH. TLR4 enhances cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy. Mediators Inflamm 2023;2023:9335166.
Xiao WC, Zhou G, Wan L, Tu J, Yu YJ, She ZG, et al. Carnosol inhibits cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting AMPK activation. Brain Res Bull 2023;195:37–46.
Ke F, Wang H, Geng J, Jing X, Fang F, Fang C, et al. MiR-155 promotes inflammation and apoptosis via targeting SIRT1 in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Exp Neurol 2023;362:114317.
Li M, Tang H, Li Z, Tang W. Emerging treatment strategies for cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neuroscience 2022;507:112–124.
Shen Z, Geng Q, Huang H, Yao H, Du T, Chen L, et al. Antioxidative and cardioprotective effects of Schisandra chinensis bee pollen extract on isoprenaline-induced myocardial infarction in rats. Molecules 2019;24:1090.
Xu M, Yan T, Fan K, Wang M, Qi Y, Xiao F, et al. Polysaccharide of Schisandra chinensis Fructus ameliorates cognitive decline in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol 2019;237:354–365.
Chen S, Ding YH, Shi SS, Tu XK. Schisandrin B inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and attenuates early brain injury in rats of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Chin J Integr Med 2022;28:594–602.
Lin QN, Liu YD, Guo SE, Zhou R, Huang Q, Zhang ZM, et al. Schisandrin B ameliorates high-glucose-induced vascular endothelial cells injury by regulating the Noxa/Hsp27/NF-κ B signaling pathway. Biochem Cell Biol 2019;97:681–692.
Feng S, Qiu B, Zou L, Liu K, Xu X, Zhu H. Schisandrin B elicits the Keap1-Nrf2 defense system via carbene reactive metabolite which is less harmful to mice liver. Drug Des Devel Ther 2018;12:4033–4046.
Li J, Lu Y, Wang D, Quan F, Chen X, Sun R, et al. Schisandrin B prevents ulcerative colitis and colitis-associated-cancer by activating focal adhesion kinase and influence on gut microbiota in an in vivo and in vitro model. Eur J Pharmacol 2019;854:9–21.
Luo W, Lin K, Hua J, Han J, Zhang Q, Chen L, et al. Schisandrin B attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by targeting MyD88 and inhibiting MyD88-dependent inflammation. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2022;9:e2202590.
Zhang H, Chen Q, Dahan A, Xue J, Wei L, Tan W, et al. Transcriptomic analyses reveal the molecular mechanisms of schisandrin B alleviates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats by RNA-sequencing. Chem Biol Interact 2019;309:108675.
Jiang EP, Li H, Yu CR, Yu CY, Jing S, Sun HX, et al. Schisandrin B protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress of neurodegenerative diseases. Neuroreport 2015;26:360–366.
Xin DQ, Hu ZM, Huo HJ, Yang XJ, Han D, Xing WH, et al. Schisandrin B attenuates the inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by traumatic spinal cord injury via inhibition of p53 signaling in adult rats. Mol Med Rep 2017;16:533–538.
Luo Z, Zhang M, Niu X, Wu D, Tang J. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway impedes the restoration of neurological function following hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in a neonatal rabbit model. J Cell Biochem 2019;120:10175–10185.
Lei JR, Tu XK, Wang Y, Tu DW, Shi SS. Resveratrol downregulates the TLR4 signaling pathway to reduce brain damage in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Ther Med 2019;17:3215–3221.
Zhang HB, Tu XK, Chen Q, Shi SS. Propofol reduces inflammatory brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage: involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2019;28:104375.
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 1986;17:472–476.
Lin TN, He YY, Wu G, Khan M, Hsu CY. Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral ischemia model in rats. Stroke 1993;24:117–121.
Li TF, Ma J, Han XW, Jia YX, Yuan HF, Shui SF, et al. Chrysin ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Neurochem Int 2019;129:104496.
An P, Xie J, Qiu S, Liu Y, Wang J, Xiu X, et al. Hispidulin exhibits neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Life Sci 2019;232:116599.
Montes P, Vigueras-Villaseñor RM, Rojas-Castañeda JC, Monfil T, Cervantes M, Moralí G. Progesterone treatment in rats after severe global cerebral ischemia promotes hippocampal dentate gyrus neurogenesis and functional recovery. Neurol Res 2019;41:429–436.
Luo SY, Li R, Le ZY, Li QL, Chen ZW. Anfibatide protects against rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via TLR4/JNK/caspase-3 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 2017;807:127–137.
Xie YL, Zhang B, Jing L. MiR-125b blocks Bax/Cytochrome C/Caspase-3 apoptotic signaling pathway in rat models of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting p53. Neurol Res 2018;40:828–837.
Liu S, Pei H, Chen W, Zhu X, Wang Y, Li J, et al. Evaluating the effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on CPF-induced brain injury in mice via PI3K/AKT pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2023:e23319.
Teertam SK, Phanithi PB. Up-regulation of Sirtuin-1/autophagy signaling in human cerebral ischemia: possible role in caspase-3 mediated apoptosis. Heliyon 2022;8:e12278.
Shin N, Yi MH, Kim S, Baek H, Triantafillu UL, Park J, et al. Astrocytic expression of CTMP following an excitotoxic lesion in the mouse hippocampus. Exp Neurobiol 2017;26:25–32.
Ryu KY, Lee HJ, Woo H, Kang RJ, Han KM, Park H, et al. Dasatinib regulates LPS-induced microglial and astrocytic neuroinflammatory responses by inhibiting AKT/STAT3 signaling. J Neuroinflammation 2019;16:190.
Cheng Z, Zhang M, Ling C, Zhu Y, Ren H, Hong C, et al. Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides against cerebral ischemia. Molecules 2019;24:1102.
Dias C, Lourenço CF, Laranjinha J, Ledo A. Modulation of oxidative neurometabolism in ischemia/reperfusion by nitrite. Free Radic Biol Med 2022;193:779–786.
Zhai L, Jia YL, Ji YQ, Zou JM, Liu XY, Gao J, et al. Protective effects of tetramethylpyrazine analogue Z-11 on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharmacol 2019;844:156–164.
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y, et al. The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol 2018;94:7–17.
Wang L, Wu D, Xu Z. USP10 protects against cerebral ischemia injury by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis through the inhibition of TAK1 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019;516:1272–1278.
Wang XP, Li XJ, Wu JF, Deng F, Peng M. Higenamine alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2019;24:859–869.
Chi OZ, Mellender SJ, Kiss GK, Liu X, Weiss HR. Blood-brain barrier disruption was less under isoflurane than pentobarbital anesthesia via a PI3K/Akt pathway in early cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Bull 2017;131:1–6.
Wei Y, Hong H, Zhang X, Lai W, Wang Y, Chu K, et al. Salidroside inhibits inflammation through PI3K/Akt/HIF signaling after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Inflammation 2017;40:1297–1309.
Zhang W, Song JK, Yan R, Li L, Xiao ZY, Zhou WX, et al. Diterpene ginkgolides protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion damage in rats by activating Nrf2 and CREB through PI3K/Akt signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2018;39:1259–1272.
Ou B, Tao W, Yang S, Feng J, Wang J, Yang T, et al. The antiapoptosis effect of Geum japonicum Thunb. var. chinense extracts on cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018;2018:7290170.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hong QL, Ding YH, Chen JY and Tu XK were responsible for the study conception, design, experimental operation, data analysis, and manuscript drafting. Shi SS, Liang RS and Tu XK contributed to the study conception and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (No. 2022J01245), the Quanzhou City Science & Technology Program of China (No. 2020N020s), and the Excellent Young Scholars Cultivation Project of Fujian Medical University Union Hospital (No. 2022XH040)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Ql., Ding, Yh., Chen, Jy. et al. Schisandrin B Protects against Ischemic Brain Damage by Regulating PI3K/AKT Signaling in Rats. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 29, 885–894 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-023-3596-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-023-3596-1