Abstract
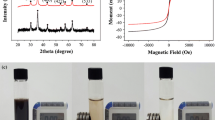
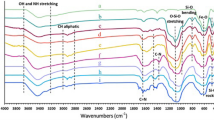
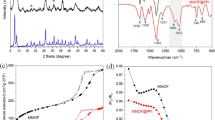
Dendrimers are novel nanostructure materials that possess a unique three-dimensional molecular configuration. They have high adsorption capacities of heavy metals. Dendrimer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles (Gn-MNPs) combining the superior adsorbent of dendrimers with magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) have been developed for effective removal and recovery of Zn(II). In this study, the Gn-MNPs were synthesized, characterized, and examined as reusable adsorbents of Zn(II). Characterization conducted by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and elemental analysis revealed that dendrimers were successfully coated onto the surface of MNPs made of magnetite (Fe3O4). The pH effect studies indicate the Zn(II) adsorption with Gn-MNPs is a function of pH. The adsorption efficiency increases with increasing pH. At pH less than 3, Zn(II) is readily desorbed. Hence, the Gn-MNPs can be regenerated using the diluted HCl aqueous solution (0.1 M) where Zn(II) can be recovered in a concentrated form. It was found that the Gn-MNPs underwent 10 consecutive adsorption–desorption processes still retained the original removal capacity of Zn(II). The adsorption data were fitted well with both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms. The maximum adsorption capacity determined by the Langmuir model is 24.3 mg/g at pH 7 and 25°C. A synergistic effect between the complexation reaction and the electrostatic interaction may account for the overall performance of Gn-MNPs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrzejewska A, Krysztafkiewicz A, Jesionowski T (2004) Adsorption of organic dyes on the aminosilane modified TiO2 surface. Dyes Pigments 62:121–130
Clifford DA, Ghurye GL (2002) Metal-oxide adsorption, ion exchange, and coagulation-microfiltration for arsenic removal from water. In: Frankenberger WT Jr (ed) Environmental chemistry of arsenic. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 217–245
Crooks RM, Zhao M, Sun L, Chechik V, Yeung LK (2001) Dendrimer-encapsulated metal nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and applications to catalysis. Acc Chem Res 31:181–190
Cullity BD, Stock SR (2001) Elements of X-ray diffraction, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall
Deliyanni EA, Peleka EN, Matis KA (2007) Removal of zinc ion from water by sorption onto iron-based nanoadsorbent. J Hazard Mater 141:176–184
Diallo MS, Balogh L, Shafagati A, Johnson JH Jr, Goddard WA, Tomalia DA (1999) Poly (amidoamine) dendrimer: a new class of high capacity chelating agents for Cu(II) ions. Environ Sci Technol 33:820–824
Diallo MS, Christie S, Swaminathan P, Johnson JH Jr, Goddard WA (2005) Dendrimer enhanced ultrafiltration. 1. Recovery of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using PAMAM dendrimers with ethylene diamine core and terminal NH2 groups. Environ Sci Technol 39:1366–1377
Ebner AD, Ritter JA, Ploehn HJ, Kochen RL, Navratil JD (1999) New magnetic field-enhanced process for the treatment of aqueous wastes. Sep Sci Technol 34:1277–1285
Gan F, Pan BF, Zheng WM, Ao LM, Gu HC (2005) Study of streptavidin coated onto PAMAM dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 293:45–54
Hattori S, Watanabe M, Sasaki K, Yasuharu H (2002) Magnetization of activated sludge by an external magnetic field. Biotechnol Lett 24:65–69
Hu J, Lo MC, Chen GH (2004) Adsorption of Cr(VI) by magnetite nanoparticles. Water Sci Technol 50:139–146
Hu J, Chen G, Lo IMC (2005) Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from wastewater by maghemite nanoparticles. Water Res 39:4528–4536
Kaczorowska MA, Cooper HJ (2009) Electron capture dissociation and collision-induced dissociation of metal ion (Ag+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, and Fe3+) complexes of polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 20:674–681
Li R, Bu JA (2004) Study on the reaction kinetics of dendrimerization by FT-IR spectroscopy: propagation of PAMAM dendrimer on silica gel. Korean J Chem Eng 21:98–103
Lien HL, Wilkin R (2005) High-level arsenite removal from groundwater by zero-valent iron. Chemosphere 59:377–386
Lo IMC, Hu J, Chen G (2009) Iron-based magnetic nanoparticles for removal of heavy metals from electroplating and metal-finishing waste water. In: Zhang TC, Surampalli RY, Lai KCK, Hu Z, Tyagi RD, Lo IMC (eds) Nanotechnologies for water environment applications, 1st edn. American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), USA, pp 213–268
Lu C, Chiu H (2006) Adsorption of zinc(II) from water with purified carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng Sci 61:1138–1145
Mehta RV, Upadhyay RV, Charles SW, Ramchand CN (1997) Direct binding of protein to magnetic particles. Biotechnol Technol 77:493–496
Mikhailik OM, Fedorenko OM, Mikhailova SS, Povstugar VI, Lyakhovich AM, Kurbatova GT, Shklovskaya NI, Chuiko AA (1991) Surface structure of finely dispersed iron powders III. Structure of a γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-modified coating. Colloids Surf 52:331–338
Newkome GR, Moorefield CN, Vögtle F (2001) Dendrimers and dendrons: concepts syntheses, applications. Wiley-VCH, New York
Ngomsik A, Bee A, Draye M, Cote G, Cabuil V (2005) Magnetic nano- and microparticles for metal removal and environmental applications: a review. C R Chimie 8:963–970
Norton L, Baskaran K, McKenzie ST (2004) Biosorption of zinc from aqueous solutions using biosolids. Adv Environ Res 8:629–635
Pan BF, Gao F, Gu HC (2005) Dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles for protein immobilization. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:1–5
Sun YP (2006) Dispersion of nanoscale iron particles. Ph.D. Dissertation, Lehigh University, United States
United States Environmental Protection Agency Title 40, Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), 2001 revision, Part 143, National Secondary Drinking Water Regulations
Van der Bruggena B, Mänttäri M, Nyström M (2008) Drawbacks of applying nanofiltration and how to avoid them: a review. Sep Purif Technol 63:251–263
Vassilev K, Ford WT (1999) Poly (propylene imine) dendrimer complexes of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Co(III) as catalysts of hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl diphenyl phosphate. J Polym Sci Part A 37:2727–2736
Wapner K, Grundmeier G (2005) Spectroscopic analysis of the interface chemistry of ultra-thin plasma polymer films on iron. Surf Coat Technol 200:100–103
World Health Organization (WHO) (2003) Zinc in drinking-water
Xu Y, Zhao D (2005) Removal of copper from contaminated soil by use of poly (amidoamine) dendrimers. Environ Sci Technol 39:2369–2375
Xu Z, Liu Q, Finch JA (1997) Silanation and stability of 3-aminopropyl triethoxy silane on nanosized superparamagnetic particles. I. Direct silanation. Appl Surf Sci 120:269–278
Yavuz CT, Mayo JT, Yu WW, Prakash A, Falkner JC, Yean S, Cong L, Shipley HJ, Kan A, Tomson M, Natelson D, Colvin VL (2006) Low-field magnetic separation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocrystals. Science 314:964–967
Ye L, Pelton R, Brook MA (2007) Biotinylation of TiO2 nanoparticles and their conjugation with streptavidin. Langmuir 23:5630–5637
Yuan C, Lien H-L (2006) Removal of arsenate from aqueous solution using nanoscale iron particles. Water Qual Res J Can 41:210–215
Zeng F, Zimmerman SC (1997) Dendrimers in supramolecular chemistry: from molecular recognition to self-assembly. Chem Rev 97:1681–1712
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Science Council (NSC), Taiwan, R.O.C. for the financial support under Grant no. NSC 98-2221-E-390-008-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, CM., Lien, HL. Dendrimer-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles for removal of zinc (II) from aqueous solutions. J Nanopart Res 13, 2099–2107 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9967-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-010-9967-5