Abstract
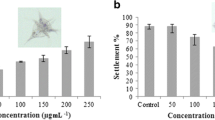
The brown seaweed Sargassum vulgare C. Agardh abounds along the southeast coast of Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil, creating unique habitats, and its polyphenols play an important ecological role as antifouling agents. In order to understand more precisely this defensive strategy of S. vulgare, we collected this macroalga at Ilha de Itacuruçá in May and October 2009. Thalli were separated according to tissue type: pneumatocysts, receptacles, leaflets, and axis. Phenolic extracts from each specific part of the plant were obtained and the associated antifouling activity was tested in order to assess whether a tissue specialisation/antifouling activity pattern exists. Preliminary separation process was carried out on a phenolic extract to separate the polyphenols from the remaining compounds. Such fractionation allowed us to study the involvement of strictly phenolic compounds in antifouling activity. Within-thallus variation in both phenolic content and antifouling activity were highlighted, and seasonal variation in both those characters was also observed. For both experiments, pneumatocyst and leaflet phenolic extracts were the most active against the attachment of Perna perna, but no correlation was observed between phenolic concentration and antifouling activity. On the contrary, the extract containing only phenolic compounds was twice less active than the extract from which 80 % of the polyphenols were removed. These results led us to hypothesise that polar compounds other than polyphenols are involved in the antifouling activity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfaro AC, Jeffs AG, Creese RG (2004) Bottom-drifting algal/mussel spat associations along a sandy coastal region in northern New Zealand. Aquaculture 241:269–290
Amsler CD, Fairhead VA (2006) Defensive and sensory chemical ecology of brown algae. Adv Bot Res 43:1–91
Amsler CD, McClintock JB, Baker BJ (2008) Macroalgal chemical defenses in polar marine communities. In: Amsler CD (ed) Algal chemical ecology. Springer, Berlin, pp 91–103
Arnold TM, Tanner CE, Hatch WI (1995) Phenotypic variation in polyphenolic content of the tropical brown alga Lobophora variegata as a function of nitrogen availability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 123:177–183
Bernstein BB, Jung N (1979) Selective pressure and coevolution in a kelp canopy community in Southern California. Ecol Monogr 493:335–355
Brawley SH (1992) Mesoherbivores. In: John DH, Hawkins SJ, Price JH (eds) Plant-animal interactions in the marine benthos. Systematics Association. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 235–263
Connan S, Goulard F, Stiger V, Deslandes E, Gall EA (2004) Interspecific and temporal variation in phlorotannin levels in an assemblage of brown algae. Bot Mar 47:410–416
Connan S, Delisle F, Deslandes E, Gall EA (2006) Intra-thallus phlorotannin content and antioxidant activity in Phaeophyceae of temperate waters. Bot Mar 49:39–46
Connan S, Deslandes E, Gall EA (2007) Influence of day–night and tidal cycles on phenol content and antioxidant capacity in three temperate intertidal brown seaweeds. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 349:359–369
Cronin G, Hay ME (1996) Effect of light and nutrient availability on the growth, secondary chemistry, and resistance to herbivory of two brown seaweeds. Oikos 77:93–106
Da Gama BAP, Pereira RC, Soares AR, Teixeira VL, Yoneshigue-Valentin Y (2003) Is the mussel test a good indicator of antifouling activity? A comparison between laboratory and field assays. Biofouling 19:161–169
Davis AR, Moreno CA (1995) Selection of substrata by juvenile Choromytilus chorus (Mytilidae): are chemical cues important? J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 191:167–180
Deal MS, Hay ME, Wilson D, Fenical W (2003) Galactolipids rather than phlorotannins as herbivore deterrents in the brown seaweed Fucus vesiculosus. Oecologia 136:107–114
Dixon J, Schroeter SC, Kastendiek J (1981) Effects of the encrusting bryozoan, Membranipora membranacea, on the loss of blades and fronds by the giant kelp, Macrocystis pyrifera (Laminariales). J Phycol 17:341–345
Eyster LS, Pechenik JA (1988) Attachment of Mytilus edulis L. larvae on algal and byssal filaments is enhanced by water agitation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 114:99–110
Fairhead VA, Amsler CD, McClintock JB, Baker BJ (2005) Variation in phlorotannin content within two species of brown macroalgae (Desmarestia anceps and D. menziesii) from the Western Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 28:680–686
Gomez I, Huovinen P (2010) Induction of phlorotannins during UV exposure mitigates inhibition of photosynthesis and DNA damage in the Kelp Lessonia nigrescens. Photochem Photobiol 86:1056–1063
Hellio C, Marechal JP, Veron B, Bremer G, Clare AS, Le Gal Y (2004) Seasonal variation of antifouling activities of marine algae from the Brittany Coast (France). Mar Biotechnol 6:67–82
Helmuth B, Veit RR, Holberton R (1994) Long-distance dispersal of a subantarctic brooding bivalve (Gaimardia trapesina) by kelp-rafting. Mar Biol 120:421–426
Hemmi A, Jormalainen V (2004) Geographic covariation of chemical quality of the host alga Fucus vesiculosus with fitness of the herbivorous isopod Idotea baltica. Mar Biol 145:759–768
Holbrook SJ, Denny MW, Koehl MAR (1991) Intertidal trees-consequences of aggregation on the mechanical and photosynthetic properties of seapalms Postelsia palmaeformis Ruprecht. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 146:39–67
Ilvessalo H, Tuomi J (1989) Nutrient availability and accumulation of phenolic compounds in the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. Mar Biol 101:115–119
Jennings JG, Steinberg PD (1997) Phlorotannins versus other factors affecting epiphyte abundance on the kelp Ecklonia radiata. Oecologia 109:461–473
Jormalainen V, Honkanen T (2001) Multiple cues for phenotypic plasticity in phlorotannin production of the bladder wrack Fucus vesiculosus. Phycologia 40:59–60
Jormalainen V, Honkanen T (2008) Macroalgal chemical defenses and their roles in structuring temperate marine communities. In: Amsler CD (ed) Algal chemical ecology. Springer, Berlin, pp 57–89
Keshava Rao C, Untawale AG (1991) Polyphenol contents of Indian seaweeds. Mahasagar 24:99–102
Koivikko R, Loponen J, Honkanen T, Jormalainen V (2005) Contents of soluble, cell-wall-bound and exuded phlorotannins in the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus, with implications on their ecological functions. J Chem Ecol 31:195–212
Koivikko R, Loponen J, Pihlaja K, Jormalainen V (2007) High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of phlorotannins from the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. Phytochem Anal 18:326–332
Langlois G (1976) Effects of algal exudates on substratum selection by the motile marine telotrochs Vorticella marina. J Protozool 22:115–123
Lasiak TA, Barnard TCE (1995) Recruitment of the brown mussel Perna perna onto natural substrata: a refutation of the primary/secondary settlement hypothesis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 120:147–153
Lau SCK, Qian PY (1997) Phlorotannins and related compounds as larval settlement inhibitors of the tube-building polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 159:219–227
Lau SCK, Qian PY (2000) Inhibitory effect of phenolic compounds and marine bacteria on larval settlement of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite amphitrite Darwin. Biofouling 16:47–58
Magalhaes PJ, Vieira JS, Goncalves LM, Pacheco JG, Guido LF, Barros AA (2010) Isolation of phenolic compounds from hop extracts using polyvinylpolypyrrolidone: characterization by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1217:3258–3268
Nagayama K, Iwamura Y, Shibata T, Hirayama I, Nakamura T (2002) Bactericidal activity of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome. J Antimicrob Chemother 50:889–893
Nagayama K, Shibata T, Fujimoto K, Honjo T, Nakamura T (2003) Algicidal effect of phlorotannins from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome on red tide microalgae. Aquaculture 218:601–611
Orth RJ, van Montfrans J (1984) Epiphyte–seagrass relationships with an emphasis on the role of micrograzing: a review. Aquat Bot 18:43–69
Parys S, Kehraus S, Pete R, Kupper FC, Glombitza KW, Konig GM (2009) Seasonal variation of polyphenolics in Ascophyllum nodosum (Phaeophyceae). Eur J Phycol 44:331–338
Pavia H, Cervin G, Lindgren A, Aberg P (1997) Effects of UV-B radiation and simulated herbivory on phlorotannins in the brown alga Ascophyllum nodosum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 157:139–146
Pereira RC, Yoneshigue-Valentin Y (1999) The role of polyphenols from the tropical brown alga Sargassum furcatum on the feeding by amphipod herbivores. Bot Mar 42:441–448
Pereira RC, Da Gama BAP, Teixeira VL, Yoneshigue-Valentin Y (2003) Ecological roles of natural products of the Brazilian red seaweed Laurencia obtusa. Braz J Biol 63:665–672
Petersen JH (1984) Larval settlement behavior in competing species Mytilus californianus Conrad and Mytilus edulis L. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 82:147–159
Plouguerné E, Le Lann K, Connan S, Jechoux G, Deslandes E, Stiger-Pouvreau V (2006) Spatial and seasonal variation in density, reproductive status, length and phenolic content of the invasive brown macroalga Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt along the coast of Western Brittany (France). Aquat Bot 85:337–344
Plouguerné E, Hellio C, Cesconetto C, Thabard M, Mason K, Veron B, Pereira RC, da Gama BAP (2010a) Antifouling activity as a function of population variation in Sargassum vulgare from the littoral of Rio de Janeiro (Brazil). J Appl Phycol 22:717–724
Plouguerné E, Ioannou E, Georgantea P, Vagias C, Roussis V, Hellio C, Kraffe E, Stiger-Pouvreau V (2010b) Anti-microfouling activity of lipidic metabolites from the invasive brown alga Sargassum muticum (Yendo) Fensholt. Mar Biotechnol 12:52–61
Ragan MA, Glombitza KW (1986) Phlorotannins, brown algal polyphenols. Prog Phycol Res 4:129–241
Reed DC (1990) An experimental evaluation of density dependence in a subtidal algal population. Ecology 71:2286–2296
Sanoner P, Guyot S, Marnet N, Molle D, Drilleau JF (1999) Polyphenol profiles of French cider apple varieties (Malus domestica sp.). J Agric Food Chem 47:4847–4853
Sieburth JM, Conover JT (1965) Sargassum tannin, an antibiotic which retards fouling. Nature 208:52–53
Stewart HL (2006) Morphological variation and phenotypic plasticity of buoyancy in the macroalga Turbinaria ornata across a barrier reef. Mar Biol 149:721–730
Svensson CJ, Pavia H, Toth GB (2007) Do plant density, nutrient availability, and herbivore grazing interact to affect phlorotannin plasticity in the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum. Mar Biol 151:2177–2181
Targett NM, Arnold TM (2001) Effects of secondary metabolites on digestion in marine herbivores. In: McClintock JB, Baker BJ (eds) Marine chemical ecology. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 391–411
Targett NM, Coen LD, Boettcher AA, Tanner CE (1992) Biogeographic comparisons of marine algal polyphenolics: evidence against a latitudinal trend. Oecologia 89:464–470
Toth GB, Pavia H (2001) Removal of dissolved brown algal phlorotannins using insoluble polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP). J Chem Ecol 27:1899–1910
Tuomi J, Ilvessalo H, Niemelä P, Sirén S, Jormalainen V (1989) Within-plant variation in phenolic content and toughness of the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus L. Bot Mar 32:505–509
Van Alstyne KL, McCarthy JJ III, Hustead CL, Kearns LJ (1999) Phlorotannin allocation among tissues of northeastern Pacific kelps and rockweeds. J Phycol 35:482–492
Wikström SA, Pavia H (2004) Chemical settlement inhibition versus post-settlement mortality as an explanation for differential fouling of two congeneric seaweeds. Oecologia 138:223–230
Williams GA, Seed R (1992) Interactions between macrofaunal epiphytes and their host algae. In: John DH, Hawkins SJ, Price JH (eds) Plant–animal interactions in the marine benthos. Systematics Association. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 189–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plouguerné, E., Cesconetto, C., Cruz, C.P. et al. Within-thallus variation in polyphenolic content and antifouling activity in Sargassum vulgare . J Appl Phycol 24, 1629–1635 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9826-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9826-0