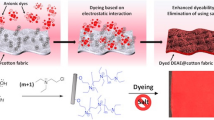
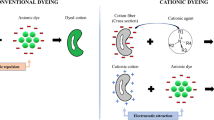
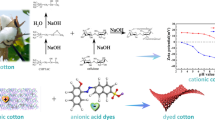
Abstract
Cationisation during the mercerisation process with an epihalohydrin results in novel cotton cellulose that gives a new dimension to cotton pre-treatment and finishing. The modified cotton retains all the beneficial properties of mercerised cotton with a change of the surface charge that ensures further quality improvement. The present paper deals with systematic investigations of the interface phenomena of cationised cotton fabric with an epihalohydrin; 2,3-epoxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride during and after mercerisation process. The water, ionic surfactant and dyestuff adsorption, as well as surface free energy, electrokinetic potential, isoelectric point and point of zero charge determined according to the streaming current/streaming potential method; and specific amount of surface charge of modified cotton fabrics are researched.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bišćan J (2007) Electrokinetic data: approaches, interpretations and applications. Croat Chem Acta 80:357–365
Chibowski E, Gonzalez-Caballero F (1993) Theory and practice of thin-layer wicking. Langmuir 9:330–340
Grancaric AM, Tarbuk A, Dekanic T (2004) Electropositive cotton. Tekstil 53:47–51
Grancaric AM, Tarbuk A, Pusic T (2005) Electrokinetic properties of textile fabrics. Color Technol 121:221–227
Grancaric AM, Ristić N, Tarbuk A, Ristić I (2013) Electrokinetic phenomena of cationized cotton and its dyeability with reactive dyes. Fibres Text East Eur 6(102):106–110
Grancarić AM, Chibowski E, Pušić T, Soljačić I, Plantić Lj (2002) Surface free energy of conventional and enzymatically scoured cotton fabrics. In: Book of proceedings of the 1st ITC&DC, Faculty of Textile Technology, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, pp 267–273
Grancarić AM, Chibowski E, Tarbuk A (2008) Surface free energy of textiles. Tekstil 57:29–39
Grancarić AM, Tarbuk A, Ujević D, Petrak S (2010) Electrokinetic properties of cationized cotton with EPTAC. In: Proceedings of 87th Textile Institute world conference, Manchester, Textile Institute, vol 1, pp 2532–2547
Hashem M (2006) Development of a one-stage process for pre-treatment and cationization of cotton fabric. Color Technol 122:135–144
Hashem M, Hauser P, Smith B (2003) Reaction efficiency for cellulose cationization using 3-chloro-2-2hydroxypropyl trimethyl ammonium chloride. Text Res J 73:1017–1023
Hauser PJ, Tabba AH (2001) Improving the environmental and economic aspects of dyeing cotton. Color Technol 117:282–288
Hauser PJ, Smith CB, Hashem MM (2004) Ionic crosslinking of cotton. AUTEX Res J 4:95–100
Jacobasch HJ, Schurz J (1988) Characterization of polymer surfaces by means of electrokinetic measurements. Prog Colloid Polym Sci 77:40–48
Kanik M, Hauser PJ (2002) Printing of cationized cotton with reactive dye. Color Technol 118:300–306
McKelvey JB, Webre BG, Klein E (1959) Reaction of epoxides with cotton cellulose in the presence of sodium hydroxide. Text Res J 29:918–925
Nevell TP (1995) Cellulose: structure, properties and behavior in the dyeing process, chapter 1. In: Shore J (ed) Cellulosics dyeing. Society of Dyers and Colourists, Bradford, pp 1–80
Patino A, Canal C, Rodriguez C, Caballero G, Navarro A, Canal JM (2011) Surface and bulk cotton fibre modifications: plasma and cationization. Influence on dyeing with reactive dye. Cellulose 18:1073–1083
Preston JM, Nimkar MV (1949) Measuring the swelling of fibers in water. J Text Inst 40:674–688
Pusic T, Cunko R, Tomljenovic A, Soljacic I (1999) Study of cotton fiber swelling affecting the degree of mercerization. Am Dyest Report 88(6):15–18
Pušić T, Grancarić AM, Tarbuk A, Šauperl O, Soljačić I (2010) Adsorption and desorption of ionic surfactants. Tenside, Surfactants, Deterg 47:173–178
Rupin M, Veatue J, Balland B (1970) Utilization of reactive epoxy-ammonium quaternaries on cellulose treatment for dyeing with direct and reactive dyes. Textilveredlung 5:829–838
Stana-Kleinschek K, Strand S, Ribitsch V (1999) Surface characterization and adsorption abilities of cellulose fibers. Polym Eng Sci 39:1412–1424
Tabba AH, Hauser PJ (2000) Effect of a cationic pretreatment on pigment printing of cotton fabric. TCC ADR 32(2):30–33
Tarbuk A, Grancarić AM, Bišćan J (2010) Adsorption properties of cationized cotton with EPTAC. In: Book of proceedings 5th ITC&DC, Zagreb, Faculty of Textile Technology, University of Zagreb, pp 401–406
Tarbuk A, Grancaric AM, Pusic T, Soljacic I (2005) Adsorption properties of cationized cotton. In: Book of papers of 5th world textile conference AUTEX 2005, Portorose, Slovenia, pp 255–260
Tarbuk A, Grancarić AM, Majcen le Mareshal A (2012) Cationization of cellulose materials—possible usage in waste water treatment systems. Tekstil 61:346–348
Tarbuk A, Grancarić AM, Leskovac M (2014) Novel cotton cellulose by cationization during the mercerization—Part 1: Chemical and morphological changes. Cellulose (R1) (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarbuk, A., Grancaric, A.M. & Leskovac, M. Novel cotton cellulose by cationization during mercerization—part 2: the interface phenomena. Cellulose 21, 2089–2099 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0194-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0194-6