Abstract
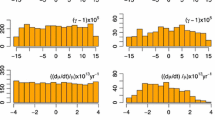
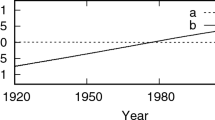
This paper outlines the progress in development of the numerical planet ephemerides EPM—Ephemerides of Planets and the Moon. EPM was first created in the 1970s in support of Russian space flight missions and constantly improved at IAA RAS. Comparison between various available EPM ephemerides (EPM2004, EPM2008, EPM2011) is shown. The first results of the updated EPM2013 version which takes into account the two-dimensional annulus of small asteroids are presented. Currently two main factors drive the progress of planet ephemerides: dynamical models of planet motion and observational data, with the crucial role of spacecraft ranging. EPM ephemerides are the basis for the Russian Astronomical and Nautical Astronomical Yearbooks, are planned to use in the GLONASS and LUNA-RESOURCE programs, and are being used for determination of physical parameters: masses of asteroids, planet rotation parameters and topography, the \(GM_\odot \) and its secular variation, the PPN parameters, and the upper limit on the mass of dark matter in the Solar System. The files containing polynomial approximation for EPM ephemerides (EPM2004, EPM2008, EPM2011) along with TT–TDB and ephemerides of Ceres, Pallas, Vesta, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Sedna are available from ftp://quasar.ipa.nw.ru/incoming/EPM/. Files are provided in IAA’s binary and ASCII formats, as well as in the SPK format.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz, M., Stegun, I.A.: Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs and mathematical tables. Washington (1964)
Aleshkina, E.Y., Krasinsky, G.A., Vasilyev, M.V.: Analysis of LLR data by the program system ERA. In: Wytrzyszczak, I.M., Lieske, J.H., Feldman, R.A. (eds.) Dynamics and Astrometry of Natural and Artificial Celestial Bodies, IAU Colloquium, vol. 165, pp. 227–238. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1997)
Brumberg, V.A.: Essential relativistic celestial mechanics. Adam Huger, Bristol, Philadelphia and New York (1991)
Carry, B.: Density of asteroids. Planet. Space Sci. 73, 98–118 (2012)
Duboshin, G.N.: Theory of gravitation. Phyzmatgiz, Moscow (1961) (in Russian)
Duriez, L., Vienne, A.: Theory of motion and ephemerides of Hyperion. A&A 324, 366–380 (1997)
Fairhead, L., Bretagnon, P.: An analytical formula for the time transformation TB-TT. A&A 229, 240–247 (1990)
Fienga, A.: Private communications 2006–2014
Fienga, A., Manche, H., Laskar, J., Gastineau, M.: INPOP06: a new numerical planetary ephemeris. A&A 477, 315–327 (2008)
Fienga, A., Laskar, J., Morley, T., et al.: INPOP08, a 4-D planetary ephemeris: from asteroid and time-scale computations to ESA Mars Express and Venus Express contributions. A&A 507, 1675–1686 (2009)
Fienga, A., Laskar, J., Kuchynka, P., et al.: The INPOP10a planetary ephemeris and its applications in fundamental physics. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 111, 363–385 (2011)
Folkner, W.M.: Private communications 2006–2014
Folkner, W.M.: Results from VLBI measurement of Venus on April 1, 1994, JPL IOM 335.1-94-014 (1994)
Folkner, W. M.: New Horizons project. JPL Interoffice Memorandum, Pasadena, 392R–14-003, 1–11 (2014)
Folkner, W.M., Williams, J.G., Boggs D.H., et al.: The Planetary and Lunar Ephemeris DE 430 and DE 431, JPL IPN progress report 42–196 (2014)
Hildebrand, C.E., Iijima, B.A., Kroger, P.M., Folkner, W.M.: Radio-planetary frame tie from Phobos-2 VLBI data. JPL TDA Prog. Rep. 42–119, 46–82 (1994)
Hilton, J.L., Hohenkerk, C.Y.: A comparison of the high accuracy planetary ephemerides DE421, EPM2008, and INPOP08. In: Proceedings of the “Journees-2010 / Systems de reference spatio-temporels”, / Ed. Capitaine N. Observatoire de Paris, pp. 77–80 (2011)
Jones, D.L., Fomalont, E., Dhawan V., et al.: Very long baseline array astrometric observations of the Cassini spacecraft at Saturn. Astron. J. 141(2), Article 29 (2011)
Konopliv, A.S., Asmar, S.W., Folkner, W.M., et al.: Mars high resolution gravity field from MRO, Mars seasonal gravity, and other dynamical parameters. Icarus 211, 401–428 (2011)
Krasinsky, G.A., Pitjeva, E.V., Sveshnikov, M.L., Chunajeva, L.I.: The motion of major planets from observations 1769–1988 and some astronomical constants. Celest. Mech. Dynam. Astron. 55, 1–23 (1993)
Krasinsky, G.A., Vasilyev, M.V.: ERA: knowledge base for ephemeris and dynamic astronomy. In: Wytrzyszczak, I.M., Lieske, J.H., Feldman, R.A. (eds.) Dynamics and Astrometry of Natural and Artificial Celestial Bodies, IAU Colloquium, vol. 165, pp. 239–244. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1997)
Krasinsky, G.A.: Dynamical history of the Earth–Moon system. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 84(1), 27–55 (2002)
Krasinsky, G.A., Pitjeva, E.V., Vasilyev, M.V., Yagudina, E.I.: Hidden mass in the asteroid belt. Icarus 158(1), 98–105 (2002)
Kuchynka, P., Folkner, W.M.: A new approach to determining asteroid masses from planetary range measurements. Icarus 222(1), 243–253 (2013)
Laskar, J., Jacobson, R.A.: GUST86—an analytical ephemeris of the Uranian satellites. A&A 188, 212–224 (1987)
Lieske, J.H.: Theory of motion of Jupiter’s Galilean satellites. Astron. Astrophys. 56, 333–352 (1977)
Love, S.G., Brownlee, D.E.: The IRAS dust band contribution to the interplanetary dust complex—evidence seen at 60 and 100 microns. Astron. J. 104(6), 2236–2242 (1992)
Luzum, B., Capitaine, N., Fienga, A., et al.: The IAU 2009 system of astronomical constants: tlhe report of the IAU working group on numerical standards for fundamental astronomy. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 110, 293–304 (2011)
McBride, N., Hughes, D.W.: The spatial density of asteroids and its variation with asteroidal mass. MNRAS 244, 513–520 (1990)
Newhall, X.X., Standish, E.M., Williams, J.G.: DE102: a numerical integrated ephemeris of the Moon and planets spanning forty-four centuries. A&A 125, 150–167 (1983)
Pavlov, D.A., Skripnichenko, V.I.: Preliminary results in implementation of a cross-platform version of the ERA software system (in Russian). IAA RAS Trans. 28, 1–8 (2014) Science, St. Petersburg
Petit, J.-M., Chambers, J., Franklin, F., Nagasawan, M.: Primordial excitation and depletion of the main belt. In: Bottke, W.F. Jr., Cellino, A., Paolicchi, P., Binzel, R.P. (eds.) Asteroids III. University of Arizona Press, Tucson, pp. 711–723 (2002)
Pitjev, N.P., Pitjeva, E.V.: Constraints on dark matter in the solar system. Ast. Lett. 39, 141–149 (2013)
Pitjeva, E.V.: EPM98: the new numerical motion theory for planets and its comparison with DE403 ephemerides of Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Trudy Inst. Appl. Astron. Russ. Acad. Sci. 3, 5–23 (1998)
Pitjeva, E.V.: Study of Mars dynamics from analysis of Viking and Pathfinder lander radar data. IAA RAS Trans. 4, 22–35 (1999). St. Petersburg (in Russian)
Pitjeva, E.V.: Modern numerical ephemerides of planets and the importance of ranging observations for their creation. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 80, 249–271 (2001)
Pitjeva, E.V.: High-precision ephemerides of planets—EPM and determination of some astronomical constants. Solar Syst. Res. 39(3), 176–186 (2005)
Pitjeva, E.V.: Influence of trans-neptunian objects on motion of major planets and limitation on the total TNO mass from planet and spacecraft. In: Lazzaro, D., Prialnik, D., Schulz, R., Fernandez, J.A. (eds.) Proceedings of 263th IAU Symposium on Icy Bodies of the Solar System, pp 93–97. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010a)
Pitjeva, E. V.: EPM ephemerides and relativity. In: Klioner, S.A., Seidelmann, P.K., Soffel, M.H., (eds.) Proceedings of 261th IAU Symposium. Relativity in Fundamental Astronomy: Dynamics, Reference, Frames, and Data Analysis, pp. 170–178. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2010b)
Pitjeva E.V.: Values of some astronomical parameters (\( au, GM_{\odot }, M_{\odot }\)), their possible variations from modern observations and interrelations between them. In: Schuh, H., Bohm, S., Nilsson, T., Capitaine, N. (eds.) In: Proceedings of the “Journees-2011 / Systems de Reference Spatio-temporels, pp. 17–20. Vienna (2012)
Pitjeva, E.V.: Updated IAA RAS planetary ephemerides—EPM2011 and their use in scientific research. Sol. Syst. Res. 47, 386–402 (2013)
Pitjeva, E., Bratseva, O., Panfilov, V.: EPM—Ephemerides of Planets and the Moon of IAA RAS: their model, accuracy, availability. In: Capitaine N. (ed.) Proceeedings of the “Journees-2010 / Systems de Reference Spatio-temporels, pp. 49–54. Observatoire de Paris (2011)
Pitjeva, E.V., Pitjev, N.P.: Changes in the Sun’s mass and gravitational constant estimated using modern observations of planets and spacecraft. Sol. Syst. Res. 46, 78–87 (2012)
Pitjeva, E.V., Pitjev, N.P.: Relativistic effects and dark matter in the Solar system from observations of planets and spacecraft. MNRAS 432, 3431–3437 (2013)
Pitjeva, E.V., Standish, E.M.: Proposals for the masses of the three largest asteroids, the Moon–Earth mass ratio and the Astronomical Unit. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 103(4), 365–372 (2009)
Poroshina, A., Kosmodamianskiy, G., Zamarashkina, M.: Construction of the numerical motion theories for the main satellites of Mars, Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus. IAA RAS Trans. 26, 75–87 (2012) Science, St. Petersburg
Rossi, G.B., Vieira-Martins, R., Camargo, J.I., Assafin, M.: Detailed astrometric analysis of Pluto. Am. Astron. Soc. DDA Meet. 44, 204.43 (2013)
Russell, C.T., Raymond, C.A., Coradini, A., et al.: Dawn at Vesta: testing the protoplanetary paradigm. Science 336, 684–686 (2012)
Standish Jr, E.M.: Orientation of the JPL ephemerides, DE200/LE200, to the dynamical equinox of J2000. A&A 114, 297–302 (1982)
Standish Jr, E.M.: The observational basis for JPL’s DE200, planetary ephemerides of the Astronomical Almanac. A&A 233, 252–271 (1990)
Standish, E. M.: JPL Planetary and Lunar Ephemerides, DE405/LE405. JPL Interoffice Memorandum 312.F-98-048, 1–18 (1998)
Standish, E.M.: Planetary and lunar ephemerides: testing alternate gravitational theories. In: Proceedingd AIP Conference of 3rd Mexican Meeting on Mathematicaland Experimental Physics, vol. 977, pp. 254–263 (2008)
Standish, E.M., Newhall, XX, Williams, J.G., Folkner, W.M.: JPL Planetary and Lunar Ephemerides, DE403/LE403. JPL Interoffice Memorandum, Pasadena, 314.10-127, pp. 1–22 (1995)
Standish, E.M., Williams, J.G.: Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical, 3rd edn, (chapter 8), University Science Books (2012)
Tedesco, E.F., Noah, P.V., Noah, M., Price, S.D.: The supplemental IRAS minor planet survey. Astron. J. 123, 1056–1085 (2002a)
Tedesco, E.F., Egan, M.P., Price, S.D.: The midcourse space experiment infrared minor planet survey. Astron J. 124, 583–591 (2002b)
Vasilyev, M.V., Yagudina, E.I.: Russian Lunar ephemerides EPM-ERA 2012. Sol. Syst. Res. 49, 56–76 (2014)
Verma, A.K., Fienga, A., Laskar, J. et al.: Use of MESSENGER radioscience data to improve planetary ephemeris and to test general relativity. A&A 561, id. A115, 13 p. (2014)
Vienne, A., Duriez, L.: TASS 1.6: ephemerides of the major Saturnian satellites. A&A 297, 588–605 (1995)
Vinogradova, T.: The mass of the asteroid belt. Trudy Inst. Appl. Astron. Russ. Acad. Sci. 26, 110–115 (2012)
Yeomans, D.K., Antreasian, P.G., Barriot, J.-P., et al.: Radio science results during the NEAR-Shoemaker spacecraft rendezvous with Eros. Science 289, 2085–2088 (2000)
Yoder, C.F., Standish, E.M.: Martian precession and rotation from Viking lander range data. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 4065–4080 (1997)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from the RAS Presidium Program 22 “Fundamental Problems of Research and Exploration of the Solar System”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pitjeva, E.V., Pitjev, N.P. Development of planetary ephemerides EPM and their applications. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 119, 237–256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-014-9569-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-014-9569-0