Abstract
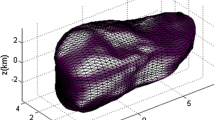
Dust comnplexes make one of the components of the Solar System. The surface shape of a typical dust complex consisting of particles ejected by a celestial body is found analytically, under reasonable assumptions (the main one being the smallness of perturbations). Parametric equations of the surface are obtained. The main properties of the surface are established and studied. Singular points are found, and the topological type of the surface as a whole and in the vicinity of the singular points (one conic points and one constriction) is examined.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Battin, R.H.: An Introduction to the Mathematics and Methods of Astrodynamics, Revised edn. AIAA Education Series, Reston, Virginia, USA (1999)
Bordovitsyna, T.V., Avdiushev, V.A.: Theory of Motion of Artificial Earth Satellites.Tomsk University Publishing House, Tomsk (2007) (in Russian)
Bordovitsyna T.V., Vassilchenko O.I.: Numerical modelling of disintegration and evolution of a satellite fragments on the geostationary orbit. In: Fundamental and Applied Problems of Modern Mechanics. Report Conference Tomsk, Tomsk University Publishing House, pp. 125–126 (2000) (in Russian)
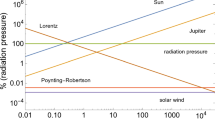
Burns, J.A., Lamy, P.L., Soter, S.: Radiation forces on small particles in the solar system. Icarus 40, 1–48 (1979)
Favard, J.: Cours de Géométrie Différentielle Locale. Gauthier-Villars, Paris (1957) (in French)
Kholshevnikov, K.V., Krivov, A.V., Sokolov, L.L., Titov, V.B.: The dust torus around Phobos orbit. Icarus 105, 351–362 (1993)
Kholshevnikov K.V., Orlov S.A.: Dust torus. Part I: equations of the enveloping surface of trajectories family of isotropic ejected particles. Vestnik St. Petersburg University, series 1, issue 3 (N 17), 118–123 (2000) (in Russian)
Kholshevnikov K.V., Orlov S.A., Jazmati M.S.: Dust torus. Part II: analysis of the enveloping surface of trajectories family of isotropic ejected particles. Vestnik St. Petersburg University, series 1, issue 4 (N 25), 119–130 (2003) (in Russian)
Kholshevnikov, K.V., Titov, V.B.: Two Body Problem. St. Petersburg University Publishers, St. Petersburg (2007) (in Russian)
Kozai, Y.: The motion of a close earth satellite. Astron. J. 64, 367–377 (1959)
Krivov A.V., Sokolov L.L., Kholshevnikov K.V., Shor V.A.: On the existence of particles swarm around Phobos orbit. Astronomichesky Vestnik 25(N 3), 317–326 (1991) (in Russian)
Krivov, A.V., Sokolov, L.L., Dikarev, V.V.: Dynamics of Mars-orbiting dust: effects of light pressure and planetary oblateness. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 63, 313–339 (1996)
Mishkin A.V., Bordovitsyna T.V., Avdiushev V.A.: Modelling of the evolution of a geostationary satellite fragments on a long time-scale. Researches on the Ballistics and Related Problems of Mechanics. Tomsk, Tomsk University Publishing House, pp. 132–133 (2002) (in Russian)
Orlov, S.A., Kholshevnikov, K.V.: The orbital dust torus as an enveloping surface of a family of trajectories of isotropically ejected particles. Sol. Syst. Res. 42(2), 91–110 (2008)
Orlov, S.A., Kholshevnikov, K.V.: Dust torus produced by particles ejected in the apsidal points. Sol. Syst. Res. 46(3), 208–219 (2012)
Pástor, P.: Influence of fast interstellar gas flow on the dynamics of dust grains. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 112, 23–45 (2012)
Ryabova G.O.: Density of particles flow under disintegration of an orbiting body. Astronomy and Geodesy. vol. 16, pp. 75–78. Tomsk University Publishing House (1998), (in Russian)
Ryabova, G.O.: Mathematical modelling of the Geminid meteoroid stream. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 375, 1371–1380 (2007)
Soter S.: The Dust Belts of Mars. Report of Center for Radiophysics and Space Research. N 462, Cornell University, Ithaca (1971)
Subbotin, M.F.: Introduction to the Theoretical Astronomy. Nauka, Moscow (1968) (in Russian)
Valsecchi, G.B., Milani, A., Gronchi, G.F., Chesley, S.R.: Resonant returns to close approaches: analytical theory. A &A 408, 1179–1196 (2003)
Wyatt, M.C., Clarke, C.J., Booth, M.: Debris disk size distributions: steady state collisional evolution with Poynting—Robertson drag and other loss processes. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 111, 1–28 (2011)
Zalgaller, V.A.: Theory of Envelopes. Nauka, Moscow (1975) (in Russian)
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor R. Ya. Kezerashvili, Dr. M. Efroimsky, and the anonymous reviewers for their numerous valuable suggestions. This work is supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Researches (grant 11-02-00232a) and the St. Petersburg State University Program on Research in Priority Areas (grant 6.37.110.2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orlov, S.A., Kholshevnikov, K.V. Dust torus formed by particles ejected from a celestial body at an arbitrary point of its elliptic orbit. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 116, 35–52 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-013-9473-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-013-9473-z