Abstract
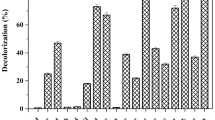
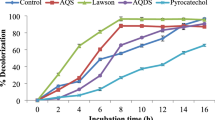
A bacterial consortium (consortium GR) consisting of Proteus vulgaris NCIM-2027 and Micrococcus glutamicus NCIM-2168 could rapidly decolorize and degrade commonly-used sulfonated reactive dye Green HE4BD and many other reactive dyes. Consortium GR shows markedly higher decolorization activity than that of the individual strains. The preferable physicochemical parameters were identified to achieve higher dye degradation and decolorization efficiency. The supplementation of cheap co-substrates (e.g., extracts of agricultural wastes) could enhance the decolorization performance of consortium GR. Extent of mineralization was determined with TOC and COD measurements, showing nearly complete mineralization of Green HE4BD by consortium GR (up to 90% TOC and COD reduction) within 24 h. Oxidoreductive enzymes seemed to be involved in fast decolorization/degradation process with the evidence of enzymes induction in the bacterial consortium. Phytotoxicity and microbial toxicity studies confirm that the biodegraded products of Green HE4BD by consortium GR are non-toxic. Consortium GR also shows significant biodegradation and decolorization activities for mixture of reactive dyes as well as the effluent from actual dye manufacturing industry. This confers the possibility of applying consortium GR for the treatment of industrial wastewaters containing dye pollutants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA–AWWA–WEF (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, method 2120 E, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Asgher H, Bhatti HN, Shah SAH, Asad MJ, Legge RL (2007) Decolorization potential of mixed microbial consortia for reactive and disperse textile dyestuffs. Biodegradation 18:311–316
Bhosale S, Saratale G, Govindwar S (2006) Mixed function oxidase in Cunninghamella blakesleeana (NCIM-687). J Basic Microbiol 46:444–448
Chang JS, Chou C, Lin YC, Lin PJ, Ho JY, Hu TL (2001) Kinetic characteristics of bacterial azo-dye decolorization by Pseudomonas luteola. Water Res 35:2841–2850
Chen BY (2002) Understanding decolorization characteristics of reactive azo dye by Pseudomonas luteola: toxicity and kinetics. Process Biochem 38:437–446
Chen BY, Chang JS (2007) Assessment upon species evolution of mixed consortia for azo dye decolorization. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 38:259–266
Chen KC, Wu JY, Liou DJ, Hwang SCJ (2003) Decolorization of the textile dyes by newly isolated bacterial strains. J Biotechnol 101:57–68
Dafale N, Rao NN, Meshram SU, Wate SR (2008) Decolorization of azo dyes and simulated dye bath wastewater using acclimatized microbial consortium—biostimulation and halo tolerance. Bioresour Technol 99:2552–2558
Dhanve RS, Shedbalkar UU, Jadhav JP (2008) Biodegradation of diazo reactive dye Navy Blue HE2R (Reactive Blue 172) by an isolated Exiguobacterium sp. RD3. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 13:53–60
Fontecave M, Eliasson R, Reichard P (1987) NAD(P)H: flavin oxidoreductase of E. coli: a ferric iron reductase participating in the generation of the free radical of ribonucleotide reductase. J Biol Chem 262:12325–12331
Gottlieb A, Shaw C, Smith A, Wheatley A, Forsythe S (2003) The toxicity of textile reactive azo dyes after hydrolysis and decolourisation. J Biotechnol 101:49–56
Gou M, Qu Y, Zhou J, Ma F, Tan L (2009) Azo dye decolorization by a new fungal isolate, Penicillium sp. QQ and fungal-bacterial cocultures. J Hazard Mater 170:314–319
Hatvani N, Mecs I (2001) Production of laccase and manganese peroxidase by Lentinus edodes on malt containing by product of the brewing process. Process Biochem 37:491–496
Jadhav SU, Jadhav MU, Kagalkar AN, Govindwar SP (2008) Decolorization of Brilliant Blue G dye mediated by degradation of the microbial consortium of Galactomyces geotrichum and Bacillus sp. J Chin Inst Chem Eng 39:563–570
Jadhav JP, Kalyani DC, Telke AA, Phugare SS, Govindwar SP (2010) Evaluation of the efficacy of a bacterial consortium for the removal of color, reduction of heavy metals, and toxicity from textile dye effluent. Bioresour Technol 101:165–173
Jiranuntipon S, Chareonpornwattana S, Damronglerd S, Albasi C, Delia ML (2008) Decolorization of synthetic melanoidins-containing wastewater by a bacterial consortium. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1313–1321
Jirasripongpun K, Nasanit R, Niruntasook J, Chotikasatian B (2007) Decolorization and degradation of C. I. Reactive Red 195 by Enterobacter sp. Thammasat Int J Sci Technol 12:6–11
Junnarkar N, Murty DS, Bhatt NS, Madamwar D (2006) Decolorization of diazo dye direct red 81 by a novel bacterial consortium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22:163–168
Kalyani DC, Telke AA, Dhanve R, Jadhav JP (2009) Ecofriendly biodegradation and detoxification of Reactive Red 2 textile dye by newly isolated Pseudomonas sp. SUK1. J Hazard Mater 163:735–742
Khehra MS, Saini HS, Sharma DK, Chadha BS, Chimni SS (2005) Decolorization of various azo dyes by bacterial consortium. Dyes Pigm 67:55–61
Kumar K, Devi SS, Krishnamurthi K, Dutta D, Chakrabarti T (2007) Decolorisation and detoxification of Direct Blue-15 by a bacterial consortium. Bioresour Technol 98:3168–3171
Kurosumi A, Erika K, Nakamura Y (2008) Degradation of reactive dyes by ozonation and oxalic acid-assimilating bacteria isolated from soil. Biodegradation 19:489–494
Lourenco ND, Novais JM, Pinheiro HM (2000) Reactive textile dye colour removal in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci Technol 42:321–328
Moosvi S, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2005) Decolorization of textile dye Reactive Violet by a newly isolated bacterial consortium RVM 11.1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:667–672
Moosvi S, Kher X, Madamwar D (2007) Isolation characterization and decolorization of textile dyes by a mixed bacterial consortium JW-2. Dyes Pigm 74:723–729
Ong SA, Katsuhiro U, Daisuke I, Kazuaki Y (2009) Simultaneous removal of color, organic compounds and nutrients in azo dye-containing wastewater using up-flow constructed wetland. J Hazard Mater 165:696–703
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR, Guthriea JT (2003) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dyes Pigm 58:179–196
Pourbabaee AA, Malekzadeh F, Sarbolouki MN, Najafi F (2006) Aerobic decolorization and detoxification of a disperse dye in textile effluent by a new isolate of Bacillus sp. J Biotechnol Bioeng 93:631–635
Rai H, Bhattacharya M, Singh J, Bansal TK, Vats P, Banerjee UC (2005) Removal of dyes from the effluent of textile and dyestuff manufacturing industry: a review of emerging techniques with reference to biological treatment. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 35:219–238
Rys P, Zollinger H (1989) Reactive dye-fiber systems. In: Johnson A (ed) The theory of coloration of textiles. J Soc Dyers Color, West Yorkshire, 552 pp
Sandhya S, Padmavathy S, Swaminathan K, Subrahmanyam YV, Kaul SN (2005) Microaerophilic-aerobic sequential batch reactor for treatment of azo dyes containing simulated wastewater. Process Biochem 40:885–890
Saratale GD, Kalme SD, Govindwar SP (2006) Decolorization of textile dyes by Aspergillus ochraceus. Ind J Biotechnol 5:407–410
Saratale GD, Bhosale SK, Kalme SD, Govindwar SP (2007) Biodegradation of kerosene in Aspergillus ochraceus (NCIM-1146). J Basic Microbiol 47:400–405
Saratale RG, Saratale GD, Chang JS, Govindwar SP (2009) Decolorization and biodegradation of textile dye Navy Blue HER by Trichosporon beigelii (NCIM-3326). J Hazard Mater 166:1421–1428
Saratale GD, Saratale RG, Lo YC, Chang JS (2010) Multicomponenet cellulase production by Cellulomonas biazotea NCIM-2550 and their applications for cellulosic biohydrogen production. Biotechnol Prog 26:406–416
Senan RC, Abraham TE (2004) Bioremediation of textile azo dyes by aerobic bacterial consortium. Biodegradation 15:275–280
Sheth NT, Dave SR (2009) Optimisation for enhanced decolourization and degradation of Reactive Red BS C.I. 111 by Pseudomonas aeruginosa NGKCTS. Biodegradation 20:827–836
Telke A, Kalyani D, Jadhav J, Govindwar S (2008) Kinetics and mechanism of Reactive Red 141 degradation by a bacterial isolate Rhizobium radiobacter MTCC 8161. Acta Chim Slov 55:320–329
Tony BD, Goyal D, Khanna S (2009) Decolorization of textile azo dyes by aerobic bacterial consortium. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 63:462–469
Watanapokasin RY, Boonyakamol A, Sukseree S, Krajarng A, Sophonnithiprasert T, Kanso S, Imai T (2008) Hydrogen production and anaerobic decolorization of wastewater containing Reactive Blue 4 by a bacterial consortium of Salmonella subterranea and Paenibacillus polymyxa. Biodegradation 20:411–418
Yoo ES, Libra J, Adrian L (2000) Mechanism of decolorization of azo dyes in anaerobic mixed culture. J Environ Eng 127:844–849
Zimmermann T, Kulla H, Leisinger T (1982) Properties of purified Orange II azoreductase, the enzyme initiating azo dye degradation by Pseudomonas KF46. Eur J Biochem 129:197–203
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Prof. Sang Eun Oh, Kangwon National University, South Korea for his support during wastewater study. The authors would like to acknowledge the technical help from Dr. G. S. Ghodake, Kyungpook National University, South Korea, as well as Dr. Chun-Yen Chen, Miss Kuey-Ling Yeh and Dr. Shing-Der Chen from National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saratale, R.G., Saratale, G.D., Chang, J.S. et al. Decolorization and biodegradation of reactive dyes and dye wastewater by a developed bacterial consortium. Biodegradation 21, 999–1015 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9360-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-010-9360-1