Summary
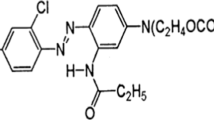
Samples collected from various effluent-contaminated soils in the vicinities of dyestuff manufacturing units of Ahmedabad, India, were studied for screening and isolation of organisms capable of decolorizing textile dyes. A novel bacterial consortium was selected on the basis of rapid decolorization of Direct Red 81 (DR 81), which was used as model dye. The bacterial consortium exhibited 90% decolorization ability within 35 h. Maximum rate of decolorization was observed when starch (0.6 g l−1) and casein (0.9 g l−1) were supplemented in the medium. Decolorization of DR 81 was monitored by high performance thin layer chromatography, which indicated that dye decolorization was due to its degradation into unidentified intermediates. The optimum dye-decolorizing activity of the culture was observed at pH 7.0 and incubation temperature of 37 °C. Maximum dye-decolorizing efficiency was observed at 200 mg l−1 concentration of DR 81. The bacterial consortium had an ability to decolorize nine other structurally different azo dyes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banat I.M., Nigam P., Singh D., Marchant R, 1996 Microbial decolorization of textile dye containing effluents: a review Bioresource Technology 58: 217–227
Bras R., Ferra I.A., Pinheiro H.M., Goncalves I.C., 2001 Batch tests for assessing decolorization of azo dyes by methanogenic and mixed cultures Journal of Biotechnology 89: 155–162
Calabro V., Drioli E., Matera F., 1991 Membrane distillation in the textile wastewater treatment. Desalination 83: 209–224
Chang J.S., Lin Y.C., 2001 Decolorization kinetics of recombinant E. coli strain harboring azo dye decolorization determinants for Rhodococcus sp Biotechnology Letters 23: 631–636
Coughlin M.F., Kinkle B.K., Tepper A., Bishop P.L., 1997 Characterization of aerobic azo dye degrading bacteria and their activity in biofilms Water Science and Technology 36: 215–220
Coughlin M.F., Kinkle B.K., Bishop P.L., 2002 Degradation of acid orange 7 in an aerobic biofilm Chemosphere 46: 11–19
Forgacs E., Cserhati T., Oros G., 2004 Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review Environmental International 30: 953–971
He F., Hu W., Li Y., 2004 Biodegradation mechanisms and kinetics of azo dye 4BS by a microbial consortium Chemosphere 57:293–301
Horitsu H, Takada M., Idaka E., Tomoyeda M., Ogawa T., 1977 Degragation of p-aminoazobenzeneEuropean Journal of Applied Microbiology 4:217–224
Hu T.L., 1994 Decolourization of reactive azo dyes by transformation with Pseudomonas luteolaBioresource Technology 49:47–51
Hu T.L., 1996 Removal of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions by different bacterial genera Water Science and Technology 34:89–95
Hu T.L., 1998 Degradation of Azo Dye RP2B by Pseudomonas luteolaWater Science and Technology 38:299–306
Idaka E., Ogawa Y., 1978 Degradation of azo compounds by Aeromonas hydrophila var. 2413Journal of the Society of Dyers and Colorists 94:91–94
Kapdan I.K, Kargi F, McMullan G, Marchant R., 2000 Decolorization of textile dyestuffs by a mixed bacterial consortium Biotechnology Letters 22:1179–1181
Keharia H., Patel H., Madamwar D., 2004 Decolorization screening of synthetic dyes by anaerobic methanogenic sludge using a batch decolorization assay World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 20:365–370
Kim S.J., Shoda M., 1999 Purification and characterization of novel peroxidase from Geotrichum candidum Dec 1 involved in decolorization of dyes Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65:1029–1035
Knapp J.S., Newby P.S., 1995 The microbiological decolorization of an industrial effluent containing a diazo linked chromophore Water Research 29:1807–1809
Lin S.H., Peng F.C., 1994 Treatment of textile wastewater by electrochemical methods Water Research 2:277–282
Lin S.H., Peng F.C., 1996 Continuous treatment of textile waste-water by combined coagulation, electrochemical oxidation and activated sludge Water Research 3: 587–592
Marmion, D.M. 1991 Handbook of US Colorants. 3rd edn. pp. 573. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. ISBN 0-471-50074-7
Mali P.L., Mahajan M.M., Patil D.P., Kulkarni M.V., 2000 Biodecolorization of members of triphenylmethanes and azo groups of dyes Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research 59:221–224
Nigam P., Banat I.M., Marchant R., 1996 Microbial process for the decolorization of textile effluent containing azo, diazo and reactive dyes Process Biochemistry 3:435–442
Ogawa T., Yatome C., Idaka E., Kamiya H., 1986 Biodegradation of azo acid dyes by continuous cultivation of Pseudomonas cepacia 13NA Journal of the Society of Dyers and Colorists 102:12–14
O’Neill C., Hawkes F.R., Esteves S., Hawkes D.L., Wilcox S.J., 1999 Anaerobic and aerobic treatment of simulated textile effluent Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology 74:993–999
Pagga U., Brown D., 1986 The degradation of dyestuffs: Part II: behavior of dyestuffs in aerobic biodegradation tests Chemosphere 15:479–491
Paszcezynski A., Pasti-Grigsby M., Goszceynski S., Crawford R., Crawford D.L., 1992 Mineralization of sulfonated azo dyes and sulfanilic acid by Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Streptomyces chromofuscusApplied and Environmental Microbiology 58:3598–3604
Pearce C.I., Lloyd J.R., Guthrie J.T., 2003 The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review Dyes and Pigments 58:179–186
Rajaguru P., Kalaiselvi K., Palanival M., Subburam V., 2000 Biodegradation of azo dyes in sequential anaerobic-aerobic system Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 54:268–273
Sani R., Banerjee U., 1999 Decolorization of triphenylmethanes dyes and textile and dye stuff effluent by Kurthia sp Enzyme and Microbial Technology 24:433–437
Spadary J.T., Isebelle L., Renganathan V., 1994 Hydroxyl radical mediated degradation of azo dyes: evidence for benzene generation Environmental Science and Technology 28:1389–1393
Verma P., Madamwar D., 2002 Comparative study on transformation of azo dyes by different white rot fungi Indian Journal of Biotechnology 1:393–396
Verma P, Madamwar D., 2003 Decolourization of synthetic dyes by a newly isolated strain of Serratia marcescensWorld Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology., 19:615–618
Wong P.K., Yuen P.Y., 1996 Decolorization and biodegradation of methyl red by Klebsiella pneumoniae RS-13 Water Research 30:1736–1744
Wuhrmann K., Mechsner K.L., Kappeler T., 1980 Investigation on rate determining factors in the microbial reduction of azo dyes European Journal of Applied Microbiology 9:325–338
Yatome C., Ogawa T., Koga D., Idaka E., 1981 Biodegradability of azo and triphenylmethanes dyes by Pseudomonas pseudomallei 13NA Journal of the Society of Dyers and Colorists 97:166–169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Junnarkar, N., Murty, D.S., Bhatt, N.S. et al. Decolorization of diazo dye Direct Red 81 by a novel bacterial consortium. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 22, 163–168 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9014-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-005-9014-3