Abstract
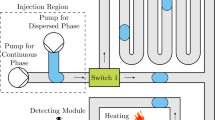
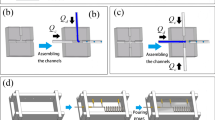
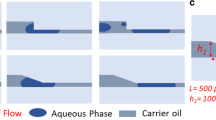
We describe the behavior of droplet formation within 3D cross-junctions and 2D T-junctions with various cross-sectional geometries that were manually fabricated using the hydrogel-molding method. The method utilizes wire-shaped hydrogels as molds to construct 3D and 2D microchannel structures. We investigated the flow patterns and droplet formation within the microchannels of these microfluidic devices. Despite being fabricated manually, the microchannels with 3D cross-junctions and 2D T-junctions were reproducible and formed highly monodispersed droplets. Additionally, the sizes of the droplets formed within the microchannels could be predicted using an experimental formula. This technique of droplet formation involves the use of a device fabricated by hydrogel molding. This method is expected to facilitate studies on droplet microfluidics and promote the use of droplet-based lab-on-a-chip technologies for various applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aketagawa K, Hirama H, Torii T (2013) Hyper-miniaturisation of monodisperse janus hydrogel beads with magnetic anisotropy based on coagulation of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Chem Eng 1(2):1–5. doi:10.4236/msce.2013.12001
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82(3):364. doi:10.1063/1.1537519
Chan EM, Alivisatos AP, Mathies RA (2005) High-temperature microfluidic synthesis of CdSe nanocrystals in nanoliter droplets. J Am Chem Soc 127(40):13854–13861. doi:10.1021/Ja051381p
Choi WK, Lebrasseur E, Al-Haq MI, Tsuchiya H, Torii T, Yamazaki H, Shinohara E, Higuchi T (2007) Nano-liter size droplet dispenser using electrostatic manipulation technique. Sens Actuator A-Phys 136(1):484–490. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2006.12.028
Garstecki P, Fuerstman MJ, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2006) Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction—scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 6(3):437–446. doi:10.1039/B510841a
Hirama H, Odera T, Torii T, Moriguchi H (2012) A lithography-free procedure for fabricating three-dimensional microchannels using hydrogel molds. Biomed Microdevices 14(4):689–697. doi:10.1007/s10544-012-9649-4
Hirama H, Kambe T, Aketagawa K, Ota T, Moriguchi H, Torii T (2013) Hyper alginate gel microbead formation by molecular diffusion at the hydrogel/droplet interface. Langmuir 29(2):519–524. doi:10.1021/la303827u
Kawakatsu T, Kikuchi Y, Nakajima M (1996) Visualization of microfiltration phenomena using microscope video system and silicon microchannels. J Chem Eng Jpn 29(2):399–401
Kobayashi I, Nakajima M, Chun K, Kikuchi Y, Fukita H (2002) Silicon array of elongated through-holes for monodisperse emulsion droplets. AIChE J 48(8):1639–1644. doi:10.1002/aic.690480807
Kobayashi I, Mukataka S, Nakajima M (2004a) CFD simulation and analysis of emulsion droplet formation from straight-through microchannels. Langmuir 20(22):9868–9877. doi:10.1021/La0487489
Kobayashi I, Mukataka S, Nakajima M (2004b) Effect of slot aspect ratio on droplet formation from silicon straight-through microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 279(1):277–280. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.06.028
Lee W, Walker LM, Anna SL (2009) Role of geometry and fluid properties in droplet and thread formation processes in planar flow focusing. Phys Fluids. doi:10.1063/1.3081407
Lee M, Park W, Chung C, Lim J, Kwon S, Ahn KH, Lee SJ, Char K (2010) Multilayer deposition on patterned posts using alternating polyelectrolyte droplets in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 10(9):1160–1166. doi:10.1039/B919753b
Liu HH, Zhang YH (2009) Droplet formation in a T-shaped microfluidic junction. J Appl Phys. doi:10.1063/1.3187831
Muluneh M, Issadore D (2013) Hybrid soft-lithography/laser machined microchips for the parallel generation of droplets. Lab Chip. doi:10.1039/c3lc50979f
Nie ZH, Xu SQ, Seo M, Lewis PC, Kumacheva E (2005) Polymer particles with various shapes and morphologies produced in continuous microfluidic reactors. J Am Chem Soc 127(22):8058–8063. doi:10.1021/ja042494w
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2002) Droplet formation in a microchannel network. Lab Chip 2(1):24–26. doi:10.1039/b108740c
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2004) Novel microreactors for functional polymer beads. Chem Eng J 101(1–3):23–29. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2003.11.019
Nisisako T, Ando T, Hatsuzawa T (2012) High-volume production of single and compound emulsions in a microfluidic parallelization arrangement coupled with coaxial annular world-to-chip interfaces. Lab Chip 12(18):3426–3435. doi:10.1039/c2lc40245a
Okushima S, Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2004) Controlled production of monodisperse double emulsions by two-step droplet breakup in microfluidic devices. Langmuir 20(23):9905–9908. doi:10.1021/la0480336
Samie M, Salari A, Shafii MB (2013) Breakup of microdroplets in asymmetric T junctions. Phys Rev E. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.87.053003
Sollier E, Murray C, Maoddi P, Di Carlo D (2011) Rapid prototyping polymers for microfluidic devices and high pressure injections. Lab Chip 11(22):3752–3765. doi:10.1039/c1lc20514e
Stone HA, Bentley BJ, Leal LG (1986) An experimental-study of transient effects in the breakup of viscous drops. J Fluid Mech 173:131–158. doi:10.1017/S0022112086001118
Sugiura S, Nakajima M, Iwamoto S, Seki M (2001) Interfacial tension driven monodispersed droplet formation from microfabricated channel array. Langmuir 17(18):5562–5566. doi:10.1021/La010342y
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2001) Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 86(18):4163–4166
Utada AS, Lorenceau E, Link DR, Kaplan PD, Stone HA, Weitz DA (2005) Monodisperse double emulsions generated from a microcapillary device. Science 308(5721):537–541. doi:10.1126/science.1109164
Xu JH, Li SW, Tan J, Luo GS (2008) Correlations of droplet formation in T-junction microfluidic devices: from squeezing to dripping. Microfluid Nanofluidics 5(6):711–717. doi:10.1007/s10404-008-0306-4
Yeom S, Lee SY (2011) Dependence of micro-drop generation performance on dispenser geometry. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 35(8):1565–1574. doi:10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2011.07.008
Zhang J, Coulston RJ, Jones ST, Geng J, Scherman OA, Abell C (2012) One-step fabrication of supramolecular microcapsules from microfluidic droplets. Science 335(6069):690–694. doi:10.1126/science.1215416
Zheng B, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF (2004) Formation of droplets of in microfluidic channels alternating composition and applications to indexing of concentrations in droplet-based assays. Anal Chem 76(17):4977–4982. doi:10.1021/ac0495743
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odera, T., Hirama, H., Kuroda, J. et al. Droplet formation behavior in a microfluidic device fabricated by hydrogel molding. Microfluid Nanofluid 17, 469–476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1327-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-013-1327-1