Abstract
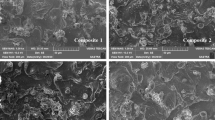
Aluminum metal matrix composites (MMCs) reinforced with nanoceramics are ideal materials for the manufacture of lightweight automotive and other commercial parts. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system combined with particle swarm optimization method is implemented in this research study in order to optimize the parameters in processing of aluminum MMCs. In order to solve the problems associated with poor wettability, agglomeration and gravity segregation of nanoparticles in the melt, a mixture of alumina and aluminum particles was used as the reinforcement instead of raw nanoalumina. Microstructural characterization shows dendritic microstructure for the sand cast and non-dendritic microstructure for the compo cast samples. The fine equiaxed structure of compo cast nanocomposite arises from copious nucleation triggered by a pressure.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rahimipour MR, Tofigh AA, Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2014) Strategic developments to improve the optimization performance with efficient optimum solution and produce high wear resistance aluminum–copper alloy matrix composites. Neural Comput Appl 24:1531–1538
Ares AE, Schvezov CE (2013) Columnar-to-equiaxed transition in metal-matrix composites reinforced with silicon carbide particles. J Metall doi:10.1155/2013/628495
Agaliotis E, Rosenberger M, Ares AE, Schvezov C (2012) Numerical modeling of the interaction between a foreign particle an solidifying crystalline interface. In: Nastac L, Zhang L, Thomas BG, Sabau A, El-Kaddah N, Powell AC, Combeau H (eds) CFD modeling and simulation in materials processing. Wiley, Hoboken
Mazahery A, Abdizadeh H, Baharvandi HR (2009) Development of high-performance A356/nano-Al2O3 composites. Mater Sci Eng A 518:61–64
Agaliotis EM, Rosenberger MR, Ares AE, Schvezov CE (2012) Influence of the shape of the particles in the solidification of composite materials. Proc Mater Sci 1:58–63
Agaliotis EM, Schvezov CE, Rosenberger MR, Ares AE (2012) A numerical model study of the effect of interface shape on particle pushing. J Cryst Growth 354(1):49–56
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2014) Modification mechanism and microstructural characteristics of eutectic Si in casting Al–Si alloys: a review on experimental and numerical studies. JOM 66(5):726–738
Agaliotis EM, Rosenberger MR, Ares AE, Schvezov CE (2012) Modeling the interaction of convex solidifying interfaces with spherical particles. RSC Adv 2:12000–12006
Ares AE, Gassa LM, Mendez CM (2012) Corrosion resistance of directionally solidified casting zinc–aluminum matrix. In: Shih H (ed) Corrosion resistance. Chapter 2, 35–54 p. INTECH Publishers
Bauri R, Surappa MK (2009) Processing and compressive strength of Al–Li–SiCp composites fabricated by compound billet technique. J Mater Process Technol 209:2077–2084
Mazahery A, Shabani MO, Rahimipour MR et al (2012) The numerical modeling of abrasion resistance in casting aluminum–silicon alloy matrix composites. J Compos Mater 46(21):2647–2658
Hashim J, Looney L, Hashmi MSJ (2002) Particle distribution in cast metal matrix composites: part I. J Mater Process Technol 123:251–257
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2012) Prediction performance of various numerical model training algorithms in solidification process of A356 matrix composites. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 19:129–134
Blumenthal WR, Gray GT, Claytor TN (1994) Response of aluminium-infiltrated boron carbide cermets to shock wave loading. J Mater Sci 29:4567
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2011) Investigation on mechanical properties of nano-Al2O3-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. J Compos Mater 45(24):2579–2586
Pyzik AJ, Aksay IA (1989) Processing of ceramic and metal matrix composites. In: Proceedings of the international symposium on advances in processing of ceramic and metal matrix composites, New York, NY p 269
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2012) The GA optimization performance in the microstructure and mechanical properties of MMNCs. Trans Indian Inst Met 65(1):77–83
Karnezis PA, Durrant G, Cantor B (1998) Characterization of reinforcement distribution in cast Al-alloy/SiC composites. Mater Char 40:97–109
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2013) Development of the principle of simulated natural evolution in searching for a more superior solution: proper selection of processing parameters in AMCs. Powder Technol 245:146–155
Quaak CJ, Kool WH (1994) Properties of semisolid aluminium matrix composites. Mater Sci Eng A 188:277–282
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2011) Prediction of mechanical properties of cast A356 alloy as a function of microstructure and cooling rate. Arch Metall Mater 56(3):671–675
Leon CA, Drew RL (2000) Preparation of nickel-coated powders as precursors to reinforced metal matrix composites. J Mater Sci 35:4763–4768
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2012) Mechanical properties of squeeze-cast A356 composites reinforced with B 4C particulates. J Mater Eng Perform 21(2):247–252
Tham LM, Gupta M, Cheng L (2001) Effect of limited matrix–reinforcement interfacial reaction on enhancing the mechanical properties of aluminium–silicon carbide composites. Acta Mater 49:3243–3253
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2013) Application of GA to optimize the process conditions of Al Matrix nano-composites. Compos B 45:185–191
Moustafa SF, Badry SAL, Sanad AM et al (2002) Friction and wear behavior of graphite–copper composites. Wear 253:699–710
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2011) The accuracy of various training algorithms in tribological behavior modeling of A356-B 4C composites. Russ Metall (Metally) 7:699–707
Cocen U, Onel K (2002) Ductility and strength extruded aluminum alloy composites. Compos Sci Technol 62:275–282
McKimpson M, Scott T (1989) Processing and properties of metal matrix composites containing discontinuous reinforcement. Mater Sci Eng 107:93–106
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2012) A comparative study on abrasive wear behavior of semisolid–liquid processed Al–Si matrix reinforced with coated B4C reinforcement. Trans Indian Inst Met 65(2):145–154
Varma VK, Kamath SV, Kutumabarao VV (2000) Tensile behaviour of powder metallurgy processed (Al–Cu–Mg)/SiCp composites. Mater Sci Technol 17:921–936
Zhong L (2000) Deformation behavior and microstructure effect in 2124Al/SiCp. Compos J Compos Mater 34:101–115
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2011) Microstructural prediction of cast A356 alloy as a function of cooling rate. JOM 63(8):132–136
Wei Liang-Ying (2013) A GA-weighted ANFIS model based on multiple stock market volatility causality for TAIEX forecasting. Appl Soft Comput 13:911–920
Petalas YG, Antonopoulos CG, Bountis TC et al (2009) Detecting resonances in conservative maps using evolutionary algorithms. Phys Lett A 373:334–341
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2012) Assistance of novel artificial intelligence in optimization of aluminum matrix nanocomposite by genetic algorithm. Metall Mater Trans A 43:5279–5285
Wu CH, Dong N, Ip WH et al (2010) Chaotic hybrid algorithm and its application in circle detection. Lecture Notes Comput Sci 6024:302–311
Shabani MO, Alizadeh M, Mazahery A (2011) Modelling of mechanical properties of cast A356 alloy. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 34:1035–1040
Zhao SZ, Suganthan PN (2011) Two-lbests based multiobjective particle swarm optimizer. Eng Optim 43(1):1–17
Sathiya P, Aravindan S, Haq AN et al (2009) Optimization of friction welding parameters using evolutionary computational techniques. J Mater Process Technol 209:2576–2584
Tripathi PK, Bandyopadhyay S, Pal SK (2007) Multiobjective particle swarm optimization with time variant inertia and acceleration coefficients. Inf Sci 177(22):5033–5049
Mazahery A, Shabani MO, Alizadeh M et al (2012) Concurrent fitness evaluations in searching for the optimal process conditions of Al matrix nanocomposites by linearly decreasing weight. J Compos Mater 47(14):1765–1772
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on neural networks, vol IV, Perth, Australia, p 1942–1948
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2013) Optimization of Al Matrix reinforced with B4C particles. JOM 65:272–277
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2012) Process conditions optimization in Al–Cu alloys matrix composites. Powder Technol 225:101–106
Liang JJ, Qin AK, Suganthan PN et al (2006) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 10:281–295
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2012) Artificial intelligence in numerical modeling of nano sized ceramic particulates reinforced metal matrix composites. Appl Math Model 36:5455–5465
Beasley D, Bull DR, Martin RR (1993) A sequential niching technique for multimodal function optimization. Evol Comput 1(2):101–125
Brits R (2002) Niching strategies for particle swarm optimization. Master’s thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2012) Application of FEM and ANN in characterization of Al matrix nano composites using various training algorithms. Metall Mater Trans A 43:2158–2165
Fieldsend JE (2009) Optimizing decision trees using multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Stud Comput Intell 242:93–114
Mazahery A, Shabani MO (2012) A356 reinforced with nano particles: numerical analysis of mechanical properties. JOM 64(2):323–329
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2012) Application of a linearly decreasing weight particle swarm to optimize the process conditions of AL matrix nanocomposites. Metallurgist 56(5–6):414–422
Kennedy J, Mendes R (2002) Population structure and particle swarm performance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE world congress on evolutionary computation, Honolulu, Hawaii. 1671–1676
van den Bergh F, Engelbrecht AP (2006) A study of particle swarm optimization particle trajectories. Inform Sci 176(8):937–971
Shabani MO, Mazahery A (2012) The performance of various artificial neurons interconnections in the modeling and experimental manufacturing of the composites. Mater Tehnol 46(2):109–113
Arora N, Vij SK (2013) Reckoner for health risk and insurance premium using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Neural Comput Appl 23(7–8):2121–2128
Dilmaç H, Demir F (2013) Stress-strain modeling of high-strength concrete by the adaptive network-based fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) approach. Neural Comput Appl 23(7–8):385–390
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shabani, M.O., Rahimipour, M.R., Tofigh, A.A. et al. Refined microstructure of compo cast nanocomposites: the performance of combined neuro-computing, fuzzy logic and particle swarm techniques. Neural Comput & Applic 26, 899–909 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1724-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-014-1724-8