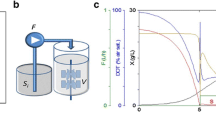
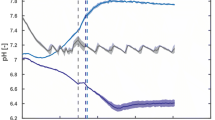
Abstract
Intracellular production of recombinant proteins in prokaryotes necessitates subsequent disruption of cells for protein recovery. Since the cell disruption and subsequent purification steps largely contribute to the total production cost, scalable tools for protein release into the extracellular space is of utmost importance. Although there are several ways for enhancing protein release, changing culture conditions is rather a simple and scalable approach compared to, for example, molecular cell design. This contribution aimed at quantitatively studying process technological means to boost protein release of a periplasmatic recombinant protein (alkaline phosphatase) from E. coli. Quantitative analysis of protein in independent bioreactor runs could demonstrate that a defined oscillatory feeding profile was found to improve protein release, about 60 %, compared to the conventional constant feeding rate. The process technology included an oscillatory post-induction feed profile with the frequency of 4 min. The feed rate was oscillated triangularly between a maximum (1.3-fold of the maximum feed rate achieved at the end of the fed-batch phase) and a minimum (45 % of the maximum). The significant improvement indicates the potential to maximize the production rate, while this oscillatory feed profile can be easily scaled to industrial processes. Moreover, quantitative analysis of the primary metabolism revealed that the carbon dioxide yield can be used to identify the preferred feeding profile. This approach is therefore in line with the initiative of process analytical technology for science-based process understanding in process development and process control strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waites MJ, Morgan Neil L, Rockey John S, Gary H (2001) Industrial microbiology: an introduction. Wiley-Blackwell, London
Balasundaram B, Harrison S, Bracewell DG (2009) Advances in product release strategies and impact on bioprocess design. Trends Biotechnol 27:477–485
Shokri A, Sanden A, Larsson G (2003) Cell and process design for targeting of recombinant protein into the culture medium of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:654–664
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:625–635
Naglak TJ, Wang HY (1990) Recovery of a foreign protein from the periplasm of Escherichia coli by chemical permeabilization. Enzy Microb Tech 12:603–611
Bothmann H, Plückthun A (1998) Selection for a periplasmic factor improving phage display and functional periplasmic expression. Nat Biotechnol 16:376–380
Hayhurst A, Harris WJ (1999) Escherichia coli Skp chaperone coexpression improves solubility and phage display of single-chain antibody fragments. Protein Expr Purif 15:336–343
Nagahari K, Kanaya S, Munakata K, Aoyagi Y, Mizushima S (1985) Secretion into the culture medium of a foreign gene product from Escherichia coli: use of the ompF gene for secretion of human beta-endorphin. EMBO J 4:3589–3592
Pugsley AP (1992) Translocation of a folded protein across the outer membrane in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:12058–12062
Gitter B, Diefenbach R, Keweloh H, Riesenberg D (1995) Influence of stringent and relaxed response on excretion of recombinant proteins and fatty acid composition in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:89–92
Gitter B, Riesenberg D (1996) Influence of phospholipid composition on excretion of beta-lactamase from a stringent/relaxed Escherichia coli K12 strain pair. Microbiol Res 151:337–342
DiRienzo JM, Inouye M (1979) Lipid fluidity-dependent biosynthesis and assembly of the outer membrane proteins of E. coli. Cell 17:155–161
Arneborg N, Salskov-Iversen A, Mathiasen T (1993) The effect of growth rate and other growth conditions on the lipid composition of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:353–357
McGarrity JT, Armstrong JB (1981) The effect of temperature and other growth conditions on the fatty acid composition of Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol 27:835–840
Knivett VA, Cullen J (1965) Some factors affecting cyclopropane acid formation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 96:771–776
Shokri A, Sanden AM, Larsson G (2002) Growth rate-dependent changes in Escherichia coli membrane structure and protein leakage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:386–392
Caspeta L, Flores N, Pérez NO, Bolívar F, Ramírez OT (2009) The effect of heating rate on Escherichia coli metabolism, physiological stress, transcriptional response, and production of temperature-induced recombinant protein: a scale-down study. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:468–482
Neubauer P, Ahman M, Törnkvist M, Larsson G, Enfors SO (1995) Response of guanosine tetraphosphate to glucose fluctuations in fed-batch cultivations of Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 43:195–204
Amanullah A, McFarlane CM, Emery AN, Nienow AW (2001) Scale-down model to simulate spatial pH variations in large-scale bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:390–399
Bylund F, Guillard F, Enfors SO, Trägradh C, Larsson G (1999) Scale down of recombinant protein production: a comparative study of scaling performance. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 20:377–389
Jazini M, Herwig C (2011) Effect of post-induction substrate oscillation on recombinant alkaline phosphatase production expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 112:606–610
Lara A, Galindo E, RamÃrez O, Palomares L (2006) Living with heterogeneities in bioreactors. Mol Biotechnol 34:355–381
Herwig C, Marison I, Von Stockar U (2001) On-line stoichiometry and identification of metabolic state under dynamic process conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:345–354
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Sanden AM, Prytz I, Tubulekas I, Förrberg C, Le H, Hektor A, Neubauer P, Pragai Z, Harwood C, Ward A, Picon A, De Mattos JT, Postma P, Farewell A, Nyström T, Reeh S, Pedersen S, Larsson G (2003) Limiting factors in Escherichia coli fed-batch production of recombinant proteins. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:158–166
Wilms B, Hauck A, Reuss M, Syldatk C, Mattes R, Siemann M, Altenbuchner J (2001) High-cell-density fermentation for production of l-N-carbamoylase using an expression system based on the Escherichia coli rhaBAD promoter. Biotechnol Bioeng 73:95–103
Andersson L, Strandberg L, Enfors SO (1996) Cell segregation and lysis have profound effects on the growth of Escherichia coli in high cell density fed batch cultures. Biotechnol Prog 12:190–195
Seyfzadeh M, Keener J, Nomura M (1993) spoT-dependent accumulation of guanosine tetraphosphate in response to fatty acid starvation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:11004–11008
Stein JP Jr, Bloch KE (1976) Inhibition of E. coli beta-hydroxydecanoyl thioester dehydrase by ppGpp. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 73:881–884
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted within the concept of the PhD thesis of Mr. Mohammadhadi Jazini and authors fully acknowledge joint supervision of professor Roosta Azad, the professor of Sharif University of Technology, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jazini, M., Herwig, C. Substrate oscillations boost recombinant protein release from Escherichia coli . Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37, 881–890 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-013-1059-3